Different Types of Chemical Bonds
Metallic bonds involve atoms giving up valence electrons to form an electron sea, covalent bonds entail electron sharing to fill outer orbitals, ionic bonds form when atoms with different electronegativities attract, Van der Waals bonds include London forces between atoms, and hydrogen bonds occur in molecules like water where charges permit weak bonding. Interatomic spacing represents the equilibrium distance between atom centers and requires binding energy to separate atoms to an infinite distance.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
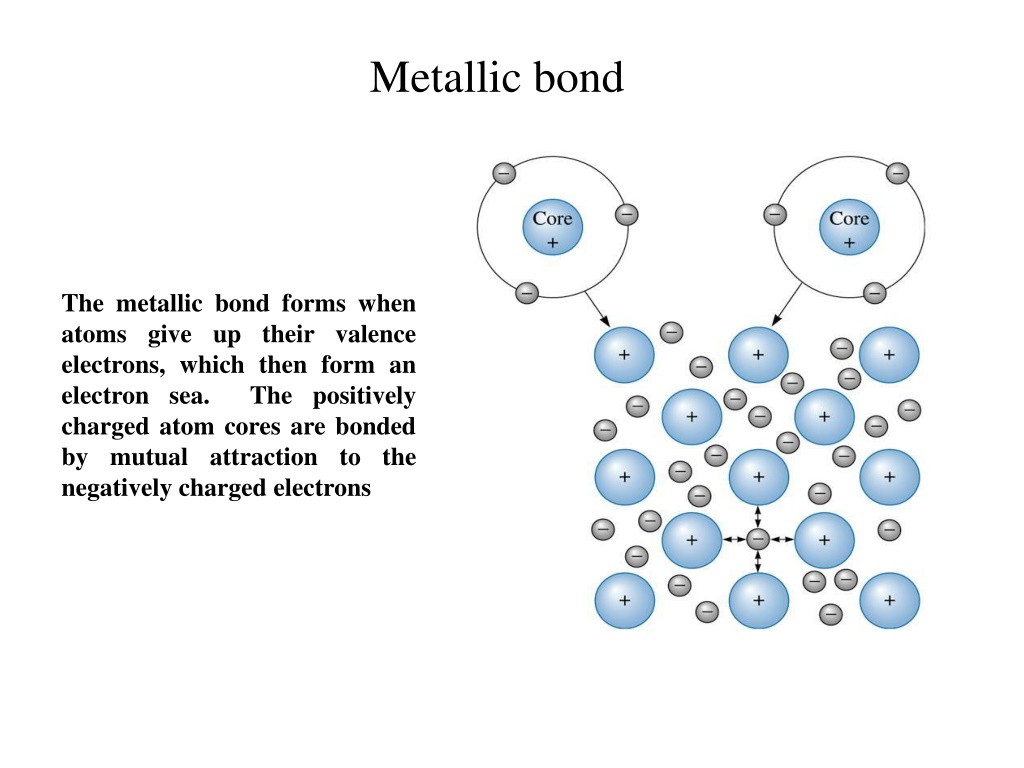
Metallic bond The metallic bond forms when atoms give up their valence electrons, which then form an electron sea. The positively charged atom cores are bonded by mutual attraction to the negatively charged electrons
Covalent bond Covalent bonding requires that electrons be shared between atoms in such a way that each atom has its outer sp orbital filled. In silicon, with a valence of four, four covalent bonds must be formed Covalent bonds are directional. In silicon, a tetrahedral structure is formed, with angles of 109.5 required between each covalent bond
Ionic bond An ionic bond is created between two unlike atoms with different electronegativities. When sodium donates its valence electron to chlorine, each becomes an ion; attraction occurs, and the ionic bond is formed When voltage is applied to an ionic material, entire ions must move to cause a current to flow. Ion movement is slow and the electrical conductivity is poor.
Van der Waals bond Illustration of London forces, a type of a Van der Waals force, between atoms Hydrogen bond In water, electrons in the oxygen tend to concentrate away from the hydrogen. The resulting charge difference permits the molecule to be weakly bonded to other water molecules
Interatomic Spacing Interatomic spacing is the equilibrium spacing between the centers of two atoms. Binding energy is the energy required to separate two atoms from their equilibrium spacing to an infinite distance apart. Atoms separated equilibrium spacing that corresponds minimum energy for a pair of atoms or ions (or when zero force is acting to repel or attract the atoms or ions) or ions by are and to the inter-atomic