400 BHN Plates, Steel 400 BHN Plates, 400 BHN, Wear Resistent 400BHN Steel Plate
Rexton Steel & Alloys is the largest manufacturer and suppliers of 400 BHN Abrasion Resistant Steel Plate, 400 BHN Plate, BHN 400 Steel Plate, Hardox 400 Plates in Mumbai, India.
4 views • 7 slides
Armor Steel Plates
Rexton Steel & Alloys is one of the top leading Supplier, Manufacturer and Exporter of Armor Steel Plates, Armor 500 Plate, Armor Plate, Ballistic Steel Plate, Ballistic Plates, Military Plate, Armor Steel Plate at low prices to our clients from Mumbai, India.
2 views • 6 slides
Armor Steel Plates, Armor 500 Plate, Armor Plate, Ballistic Steel Plate, Ballist
Rexton Steel & Alloys is one of the top leading Supplier, Manufacturer and Exporter of Armor Steel Plates, Armor 500 Plate, Armor Plate, Ballistic Steel Plate, Ballistic Plates, Military Plate, Armor Steel Plate at low prices to our clients from Mumbai, India.
0 views • 6 slides
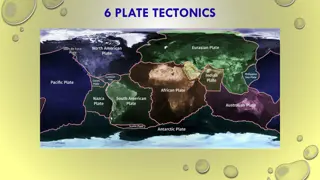
Understanding Plate Tectonics: Meaning, Concepts, and Plate Margins
Plate tectonics is a scientific theory explaining the movement of Earth's lithospheric plates. Developed by various scientists, it involves the drifting of plates over the Earth's surface, leading to phenomena like earthquakes and mountain formation. The theory is based on continental drift and sea-
5 views • 7 slides
ECMC: Open Source Motion Control with EtherCAT Overview
ECMC is an open-source motion control module designed for EPICS environments, integrating EtherLab's EtherCAT master. It offers advanced features like synchronized motion, distributed clocks, and PLC functionalities, making it ideal for various automation applications. The system architecture and ha
0 views • 42 slides
How To Use Wired Motion Sensor Closet Light
Motion sensor lights provide the convenience of constant, powerful illumination without the need to manually turn them on or off. Additionally, it saves time while looking for switches in places with low lighting that you could miss at first. Compared to traditional lighting solutions, motion sensor
1 views • 1 slides
Exploring Plate Motion and Fossils in Science Class
Dive into the fascinating world of plate motion and fossils in this science lesson. Students will learn about the role of scientists, investigate fossils as time capsules, meet a paleontologist, and explore how Dr. Wilson's research sheds light on Earth's geologic history. Engaging activities such a
0 views • 25 slides
Understanding Projectile Motion: Characteristics, Examples, and Formulas
Projectile motion involves the motion of objects under the influence of gravity, with both vertical and horizontal components. This type of motion is seen in activities such as throwing a ball, kicking a football, or dropping objects. The motion is described by specific formulas, including calculati
1 views • 19 slides
Understanding Projectile Motion: Components and Trajectories
Projectile motion involves the horizontal and vertical components of motion, where objects follow parabolic trajectories under the influence of gravity. The horizontal and vertical motions are independent of each other, leading to a variety of curved paths. This phenomenon is illustrated through exa
1 views • 13 slides
Understanding Newton's First Law of Inertia
Newton's first law of inertia states that objects remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. This law, also known as the law of inertia, explains how objects tend to maintain their current state of motion unless influenced by an external force. Objects at rest stay a
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Motion: Frames of Reference and Relative Motion
Motion is defined as a change in position over time. To describe motion accurately, one needs to understand frames of reference and relative motion. Frames of reference are systems of objects used to determine if something is in motion, while relative motion involves movement in relation to a refere
3 views • 14 slides
Understanding Motion: Concepts and Definitions in Physics
Motion in physics is defined as the change in position of an object over time. It involves concepts like rest, motion, distance, displacement, rate of motion, and types of motion. Rest and motion are relative to a reference point, while distance and displacement differ in their scalar and vector nat
0 views • 25 slides
Methods for Determination of Microbial Growth
Quantitative determination of microbial growth is crucial for various purposes, with two commonly used methods being the standard plate count and spectrophotometric measurement. The standard plate count method estimates living microbial cell density, while spectrophotometric measurement relies on tu
2 views • 6 slides
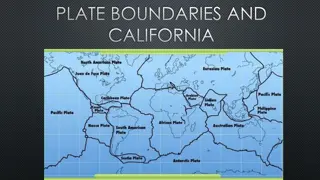
Plate Boundaries and Geological Events in California
California is located on a plate boundary experiencing major geologic events. The state's landforms are shaped by plate tectonic activity. Understanding stress types at plate boundaries can help prevent damage and save lives. The interaction at plate boundaries plays a crucial role in shaping Earth'
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Processes Shaping Earth: Lithosphere, Plate Tectonics, and Effects
Explore the components of our planet, such as the lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere. Learn how the lithosphere, consisting of the Earth's crust and top solid mantle, interacts through plate tectonics, causing movements that shape the Earth's surface. Discover the concept of Pangaea
0 views • 31 slides
Heat Transfer and Drag Force Calculation for Air Flowing over a Heated Flat Plate
Calculating the heat transferred and drag force exerted on the first 40 cm of a flat plate when air at 27°C and 1 atm flows over it at 2 m/s. The plate is heated to 60°C along its entire length. Using fluid friction analogy to analyze the heat transfer and drag force.
3 views • 8 slides
Understanding Linear and Rotational Motion in Physics
Explore the concepts of linear momentum, center of mass, rotational motion, and angular displacement in physics. Learn how to determine the center of mass of objects, analyze motion of particle groups, and understand the conservation of momentum in systems under external forces. Delve into the funda
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Circular Motion in Physics
Circular motion involves objects moving in a circular path at a constant speed, experiencing acceleration and centripetal force. This motion is characterized by angular speed, centripetal acceleration, and the necessary centripetal force. The concept of uniform circular motion and angular displaceme
3 views • 38 slides
Understanding Newton's First Law of Motion
Exploring the foundational concepts of motion and forces, this content delves into Isaac Newton's First Law of Motion. Describing how objects behave when the net force acting on them is zero, the law highlights the significance of inertia and balanced forces in determining an object's state of rest
0 views • 9 slides
Visualizing Relationships with Data: Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Plate Tectonics
Explore the locations of earthquakes and volcanoes to understand plate boundary zones, compare plate motion in different regions, and determine plate boundary zones using various data sources. Follow step-by-step instructions to study maps, analyze earthquake and volcano distributions, and engage in
0 views • 37 slides
Understanding Vertical Motion and Gravity in Kinematics
Explore the principles of vertical motion and gravity in kinematics through scenarios involving throwing objects, free-fall motion, and calculating heights. Learn how to model vertical motion with acceleration due to gravity, find maximum heights of thrown objects, solve extended problems, and under
2 views • 12 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Explore the fundamental concepts of Newton's Laws of Motion, including net forces, combining forces, balanced versus unbalanced forces, and the concept of inertia. Learn how these principles explain the behavior of objects in motion and at rest, and discover the impact of mass on an object's resista
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Joint Motion: Osteokinematic and Arthrokinematic Movements
Joint motion involves osteokinematic movements, which are under voluntary control and include flexion, extension, and more. End-feel sensations like bony, capsular, and springy block indicate different joint conditions. Arthrokinematic motion refers to how joint surfaces move during osteokinematic m
0 views • 17 slides
Umpire Clinic Essentials: What to Wear, Game Time Tips, and Plate Mechanics
Learn key takeaways from a baseball umpire clinic, including guidelines on attire, preparation, game time procedures, plate mechanics, and dealing with coaches and fans. Discover the importance of appearance, proper equipment, and essential plate umpire movements for different game scenarios.
0 views • 61 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion explain the relationship between forces and motion. The first law states that an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by a net force, while the second law describes how force is related to an object's mass and acceleration. The third law states that for every ac
0 views • 21 slides
The Theory of Plate Tectonics: Continents in Motion
Earth's crust and lithosphere have changed over geologic time, forming tectonic plates that move due to convection currents. The concept of plate tectonics explains how continents fit together, the existence of a supercontinent called Pangaea, and natural phenomena like earthquakes and mountains. Ea
0 views • 28 slides
Exploring Plate Boundaries: Convergent, Divergent, and Transform Faulting
Delve into the world of plate boundaries by understanding convergent, divergent, and transform faulting. Discover various examples worldwide, describing their physical locations, major tectonic plates involved, resulting landforms, lithosphere types, and associated catastrophic events. Learn about t
0 views • 5 slides
Plate Tectonics and Boundaries Overview
The content discusses various aspects of plate tectonics and boundaries, including the best procedures for assessments, features at convergent and divergent boundaries, the movements of ocean plates relative to islands, identifying plate boundaries on a map, and reasons for the delay in accepting pl
0 views • 7 slides
Advanced Cooling Solutions: ACS Cold Plate Focus Areas
Introduction to ACS Cold Plate focus areas led by Jessica Gullbrand from Intel. The objective is to standardize liquid-cooled solutions without hindering innovation. The ongoing focus includes approval of cold plate requirements, initiation of Open Rack V3 Blind Mate Liquid Cooling, and various work
0 views • 20 slides
DIY Willow Pattern Plate Activity
Dive into the world of Willow Pattern design by creating your own plate art inspired by the classic poem. Gather materials, choose a verse, and let your creativity flow onto a paper plate or circle. Explore examples and get inspired!
0 views • 4 slides
Exploring the Connection Between Plate Tectonics and Oreo Cookies
Discover the unique ties between plate tectonics and Oreo cookies through a creative exploration of tectonic plate boundaries using Oreo cookies as a tangible model. Learn about the structure of the Earth, types of plate boundaries, and the movement of tectonic plates in a hands-on and engaging mann
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Plate Tectonics and Earth's Surface Features
The study of plate tectonics reveals how the Earth's crust is divided into tectonic plates, leading to various types of plate boundaries like divergent, convergent, and transform. These movements result in earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and landform changes such as folding and faulting. Different
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics
Rapid Earth Movement, specifically earthquakes, is a natural disaster causing destruction and fear. Plate tectonics play a crucial role in the occurrence of earthquakes and volcanoes. The movement of Earth's plates at plate boundaries results in different geological features like fold mountains. Thi
0 views • 36 slides
Exploring Plate Tectonics and the Scientific Method
Dive into the world of plate tectonics and the scientific method in this lesson. The session covers vocabulary and grammar review, giving and receiving feedback, learning new concepts related to plate tectonics, and understanding participles and participial adjectives. Explore the theory of plate te
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion describe how objects behave in response to external forces. The first law states that objects in motion remain in motion unless acted upon by a force, while objects at rest stay at rest. The second law relates force, mass, and acceleration, showing how they are interconnected
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Motion and Newton's Laws
Explore the concepts of motion, distance, speed, and velocity as they relate to Newton's Laws of Motion. Learn about measuring motion, calculating speed, graphing motion on distance-time graphs, and understanding velocity. Discover how motion is constant and how relative motion is used. Practice cal
0 views • 36 slides
Development of Head and Neck Mesenchyme in Embryonic Formation
The formation of the head and neck region in embryonic development involves mesenchyme derived from paraxial mesoderm, lateral plate mesoderm, neural crest, and ectodermal placodes. Paraxial mesoderm contributes to brain case and muscle formation, while lateral plate mesoderm forms laryngeal cartila
0 views • 34 slides
Understanding Motion and Newton's Laws
Motion is the constant change in position of objects, measured by distance and displacement. Speed is the rate of motion, while velocity includes direction. Graphing motion helps visualize speed changes over time. Newton's Laws explain the behavior of objects in motion.
0 views • 38 slides
Understanding Dependent and Relative Motion in Dynamics
Dependent Motion and Relative Motion are fundamental concepts in Dynamics, providing the foundation for future analysis. Dependent Motion involves constraints like ropes or cables, while Relative Motion considers observers in motion. Dynamics involves applying a limited set of equations in diverse w
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Motion: Types and Physics
Motion refers to a body changing position with respect to its surroundings. Different types of motion include linear, rotatory, and oscillatory motion. The physics relating to motion is called Mechanics, which comprises Dynamics and Kinematics. Scalars and vectors play a crucial role in describing t
0 views • 8 slides