Microplastic Occurrence in South Korean Groundwater by Well Depth and Hydrogeology
The study conducted by Kangwon National University in South Korea analyzed microplastic occurrence in groundwater from wells of varying depths and hydrogeological settings. Samples were collected from the National Groundwater Monitoring Network pipes in Gapyeong and Chuncheon. Water type analysis re
7 views • 6 slides
Understanding Chemical Bonds and Ionic Compounds
Ionic bonds are formed when atoms transfer electrons to achieve stable electron configurations, resulting in the creation of ions with positive or negative charges. Metals are good conductors due to their ability to easily lose electrons. The charges of ions depend on the number of valence electrons
0 views • 49 slides
Understanding Ionic and Metallic Bonding in Chemistry
Explore the concepts of ions, electron dot structures, the octet rule, cations, and anions in Chapter 7. Learn how elements achieve stability through electron configurations, and practice writing electron dot structures and naming ions. Understand the differences between cations and anions and how t
1 views • 52 slides
Exploring Bioinorganic Chemistry: Essential Elements and Structural Functions in Biological Systems
Bioinorganic chemistry focuses on the reactivity of metal ions in biological settings, with essential elements like C, H, N, O, and various mineral macro and micronutrients playing key roles in regulatory, structural, electron transfer, enzyme function, and oxygen transport processes. Understanding
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Electrolysis and Copper Processing
Electrolysis is a process that uses an electrical current to move ions in an electrolyte solution. In the processing of copper ores, electrolysis plays a vital role. Copper ions leave the anode and move towards the cathode in a copper electrolysis setup. This experiment involves using a penny as the
1 views • 27 slides
Understanding Metallic Bonding and Giant Metallic Lattices
Metallic bonding involves the attraction of positive metal ions to delocalized electrons, forming giant metallic lattices. In this structure, positive metal ions occupy fixed positions while electrons move freely throughout. This bonding is different from covalent bonding as it is delocalized, leadi
1 views • 19 slides
Understanding Temperature Independent Paramagnetism (TIP) and Anomalous Magnetic Moments in Metal Ions
Temperature Independent Paramagnetism (TIP) explains the second-order Zeeman effect's magnetic susceptibility unaffected by temperature changes. Anomalous magnetic moments are observed in metal ions, deviating from predicted values based on electron angular momenta. The interaction of spin states in
1 views • 15 slides
Understanding Chemical Equations and Formulae
Learn to construct balanced chemical equations for known reactions, deduce signs and charges of simple ions, and create chemical formulae for ionic compounds. Understand the concepts of reactants, products, molecules, giant structures, state symbols, and chemical formulas for various substances. Gai
3 views • 7 slides
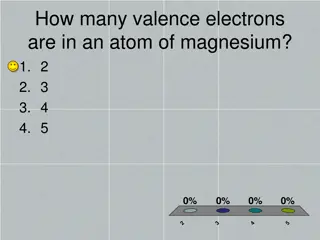
Chemistry Concepts: Valence Electrons, Ion Charges, and Ionic Compounds
Explore various key concepts in chemistry such as valence electrons in magnesium, Lewis Dot structure for silicon, charges on ions like strontium, formation of ions to achieve noble-gas electron configuration, elements forming ions with specific charges, and the octet rule. Learn about the character
1 views • 48 slides
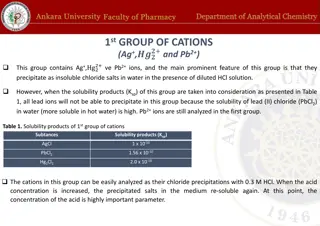
Analysis of 1st Group of Cations: Ag+ and Pb2+ Ions
The analysis of cations in the 1st group involving Ag+ and Pb2+ ions is carried out by precipitating insoluble chloride salts in the presence of diluted HCl solution. The solubility products of AgCl, PbCl2, and Hg2Cl2 play a crucial role in the precipitation reactions. Various reagents such as HCl,
0 views • 7 slides
Magnetic Field Problems: Protons, Wires, and Charged Ions
Solve various problems related to magnetic fields, including determining forces on protons, calculating magnetic forces on wires with currents, finding the radius of paths for charged ions in magnetic fields, and more. Understand concepts such as magnetic forces, circular orbits, and interactions be
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding the Gibbs-Donnan Effect in Biological Systems
The Gibbs-Donnan Effect, named after physicists Gibbs and Donnan, explains the selective permeability of membranes to ions, leading to the establishment of Donnan potential. This phenomenon affects the distribution of ions and proteins across cell membranes, influencing processes like osmosis and io
0 views • 27 slides
Plant Mineral Nutrition: Absorption and Circulation of Ions in Roots
Plant mineral nutrition involves the absorption and translocation of ions across roots. Salts are absorbed passively and actively, with ions moving into the root's apoplasm via free diffusion. The Casparian strip in endodermal cells acts as a barrier, allowing ions to pass only through the protoplas
0 views • 27 slides
Understanding Ionic Bonding and Lattice Energy
Explore the world of ionic bonding through images and explanations. Learn how electrons are transferred to form ions, the arrangement of ions in a crystal lattice, and the concept of lattice energy in ionic compounds. Discover the formation of formula units, examples of bond pairs, and the significa
1 views • 18 slides
Spectrophotometric Determination of Cr and Mn in Steel Samples
This experiment aims to determine the concentrations of manganese and chromium in steel samples by converting Cr3+ and Mn2+ ions to light-absorbing forms, followed by spectrophotometric measurements at specific wavelengths. Steel samples are oxidized, dissolved, and further oxidized to form dichroma
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Ionization of Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids, as proton donors, can undergo ionization to form ions in chemical reactions based on the Brønsted-Lowry theory. Ionization involves the complete loss or gain of electrons, leading to the formation of cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions). Through e
1 views • 13 slides
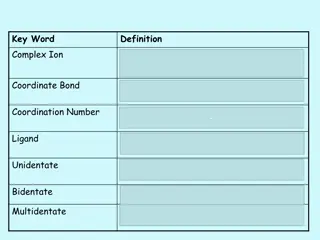
Understanding Complex Ions and Coordinate Bonds in Chemistry
Complex ions in chemistry are formed when transition metals or their ions bond with ligands through coordinate bonds. Ligands utilize their lone pairs of electrons to form dative covalent bonds with transition metals, determining the coordination number of the cation. Complex ions play a crucial rol
1 views • 29 slides
Understanding Valence Electrons and Ionic Charges in Elemental Bonding
Valence electrons play a crucial role in the formation of ions as elements combine. Nonmetals gain electrons to become negatively charged ions, while metals lose electrons to become positively charged ions. This process leads to the creation of electrically attractive elements open for bonding. The
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes in Chemistry
Atoms are neutral with equal protons and electrons. Ions are charged atoms resulting from gaining or losing electrons, while isotopes are atoms with varying numbers of neutrons. The atomic number always signifies the number of protons in an atom, unaffected by electron or neutron changes. Explore th
2 views • 5 slides
Understanding Acids, Bases, and Neutrals in Natural Sciences Grade 7
Acids, bases, and neutrals are vital substances found in various settings like factories and laboratories. They exhibit distinct properties, with acids feeling rough, being corrosive, and containing hydrogen ions, while bases feel slippery, taste bitter, and contain hydroxide ions. While acids like
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Electrolytes in Chemical Solutions and Their Importance in Body Fluid Balance
Chemical compounds in solution can remain intact or dissociate into ions, affecting their electrical charge. Electrolytes like sodium chloride play a crucial role in body fluid balance and acid-base regulation. Electrolyte preparations are used to treat imbalances, with milliequivalents and molar co
0 views • 32 slides
Understanding Oxidation Numbers in Chemistry
Oxidation is a process where atoms or ions gain a more positive oxidation state, while reduction involves attaining a more negative oxidation state. This informative content explains oxidation numbers, uncombined elements, monoatomic ions, and oxidation rules in compounds. Practice determining oxida
5 views • 5 slides
Understanding Ion Exchange Filters for Water Treatment
Ion exchange filters are effective for removing specific contaminants by swapping ions. They are not cheap but can be the only option for hard-to-remove ions. These filters can be regenerated using sodium chloride and are beneficial for small water supplies. However, careful monitoring and maintenan
0 views • 11 slides
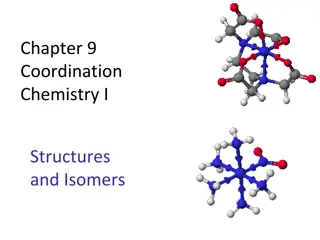
Understanding Coordination Chemistry: Structures, Isomers, and Naming
Exploring coordination chemistry involves understanding structures, isomers, naming conventions, and common coordination numbers, all essential in studying coordination compounds. Coordination compounds consist of central metals, ligands, and charge balancing ions. Naming involves listing cations, l
0 views • 46 slides
Understanding Ions, Ionic Bonds, and Ionic Compounds
Ions are charged particles formed by gaining or losing electrons, leading to the formation of ionic bonds between positively charged cations and negatively charged anions. The octet rule guides electron configurations, and the periodic table helps predict ion formation. Ionic bonding involves electr
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Electrochemical Double Layer Theory
Electrochemical double layer theory explains the distribution of charges and ions at the interface between an electrode and an electrolyte solution. It involves concepts like space charge density, Nernst-Planck equations, and Gouy-Chapman theory to describe the behavior of ions and electric fields i
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Ions and Their Importance in Your Body
Neutral atoms have the same number of protons and electrons, with the charge of the nucleus always positive. The mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons. The number of neutrons can be calculated by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number. Ions are atoms with a positive or negative
0 views • 15 slides
Essential Information on Naming Compounds, Cations, and Anions
Learn about the essential elements, symbols, and polyatomic ions you need to know for naming compounds correctly. Understand rules for naming compounds when elements combine, including diatomic molecules, halogens, oxygen, and sulfur. Explore polyatomic ions with different charges and their names to
0 views • 12 slides
African American Studies Program at San Jose State University
The Department of African American Studies at San Jose State University offers a major, minors, and a dedicated faculty team. Graduation requirements include earning 120 units, completing core classes, GE core classes, American institution classes, and major and minor requirements. The major require
0 views • 10 slides
Trends and Analysis of Major Ions at Russian EMEP Stations (2002-2012)
This research study by Alisa Trifonova-Iakovleva focuses on the trends of major ions at Russian EMEP stations from 2002 to 2012. The analysis includes time series for different locations such as Danki, Janiskoski, and Pinega, examining air and wet concentrations as well as depositions. The structure
0 views • 23 slides
Chapter 2. Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
Explore the historical timeline of atomic theory advancements, from Demokritos' initial concept of "atomos" to Dalton's Atomic Theory, Thomson's discovery of the electron, and modern breakthroughs by scientists like Rutherford and Lawrence. Avogadro's contributions to the mole concept and gas laws a
0 views • 46 slides
Understanding Coordination Complexes and Transition Metals
Today's lecture covers transition elements, coordination complexes, ligand types, geometries, naming, isomers, and bonding in coordination complexes. Transition metals form coordination complexes with metal ions, ligands, and counter ions. The types of ligands include monodentate and bidentate ligan
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Oxidation and Reduction Reactions in Chemistry
Dive into the world of oxidation and reduction reactions through displacement reactions and ionic equations. Explore how atoms turn into ions, learn about spectator ions, balance electrons in half equations, and grasp the definitions of oxidation and reduction (OILRIG). Discover which elements are o
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Naming of Polyatomic Ions, Acids, and Covalent Compounds
Exploring the nomenclature of polyatomic ions, oxyanions, acids, and covalent compounds. Learn how to name compounds based on their composition, whether they contain oxygen, and the type of bond they form.
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Electrolyte Activity Coefficients and Equilibrium Constants
This article delves into the practical aspects of dealing with individual ions in aqueous solutions, particularly focusing on partitioning thermodynamic parameters between ions in salts. It explores the Debye-Hückel theory, which explains the electrostatic interactions between ions in solution and
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Ionic and Molecular Compounds in Chemistry
Discover the fundamental concepts of ionic and molecular compounds in chemistry with insights into the nature of elements, formation of compounds, and properties of ions. Explore the differences between ionic and covalent bonds, positive and negative ions, as well as examples of common everyday comp
0 views • 54 slides
Understanding Acids and Bases in Chemistry
Acids and bases play essential roles in chemistry, where they release hydrogen ions or hydroxide ions when mixed with water. Acids, like vinegar and lemon juice, are corrosive and can cause chemical burns. On the other hand, bases, such as bleach and dish soap, contain the hydroxide group in their f
0 views • 19 slides
Detecting Cobalt(II) Ion Reactions in Solutions
This experiment outlines various methods for detecting Cobalt(II) ions (Co2+) in solution using reagents like sodium hydroxide, ammonia, sodium or potassium carbonate, and more. Observations and changes in color are noted throughout the process to identify the presence of the Cobalt ions. The reacti
0 views • 19 slides
Optical Sideband Cooling of Ions in a Penning Trap - Research Summary
Researchers at Imperial College London, led by Richard Thompson, have made significant contributions in the field of optical sideband cooling of ions in a Penning trap. This technique involves laser cooling in the trap, large Lamb-Dicke parameters, sideband cooling of ions, coherent manipulation of
0 views • 34 slides
Understanding Acids and Bases in Chemistry
Acids, derived from the Latin word "acidus" meaning sour, produce hydrogen ions when dissolved in water. Bases, defined as compounds dissociating into metal ions and hydroxide ions in water, have common characteristics like a bitter taste. The Brønsted-Lowry theory expanded the definitions of acids
1 views • 50 slides