Understanding Oxidation and Reduction Reactions in Chemistry
Dive into the world of oxidation and reduction reactions through displacement reactions and ionic equations. Explore how atoms turn into ions, learn about spectator ions, balance electrons in half equations, and grasp the definitions of oxidation and reduction (OILRIG). Discover which elements are oxidized and reduced in displacement reactions involving solutions of salts.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
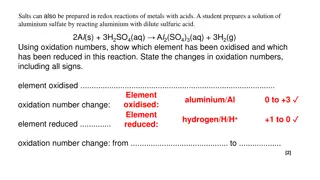
OXIDATION AND REDUCTION
ONE WE HAVE MET BEFORE! Magnesium Aluminium Zinc Iron Copper Magnesium can displace copper from copper oxide WHY? Mg (s) + CuO (s) MgO+ Cu
LETS SEE WHAT HAPPENS TO THE ELECTRONS IN THAT EQUATION Mg + Cu2+O2- Mg2+02- + Cu As you can see the oxide ions have NOT been changed they have just got a different partner. Therefore they are called the SPECTATOR IONS. The Magnesium ATOMS have changed into Magnesium IONS by losing 2 electrons. The Copper ions have become atoms again by gaining 2 electrons.
IONIC EQUATIONS Make sure you can see how the 2 equations you just saw are linked. Now turn it into an IONIC equation - leave out the spectator ions:- Mg +Cu2+ Mg2+ + Cu Can you see what has happened to the Magnesium atoms? They have turned into Magnesium ions Can you see what has happened to the Copper ions? They have turned into Copper atoms. HOW DO ATOMS TURN INTO IONS?
HALF EQUATIONS. THESE SHOW YOU WHAT IS HAPPENING FROM THE POINT OF VIEW OF MG AND CU Mg Mg2+ + 2 e- Magnesium has LOST 2 electrons to make the Magnesium ION. Make sure you BALANCE the number of electrons + Cu2+ + 2e- Cu Copper ion has GAINED 2 electrons (from Magnesium) to make the Copper ATOM. Magnesium Copper
Now we need a different definition for OXIDATION and REDUCTION OXIDATION is the LOSS of Electrons REDUCTION is the GAIN of Electrons OILRIG
WHICH ONES HAS BEEN Magnesium Copper Oxidised? Reduced?
DISPLACEMENT REACTIONS INVOLVING THE SOLUTIONS OF SALTS Remember salts are things like Copper Sulphate. Zn(s) + Cu S04 ZnS04 (aq) + Cu (s) Lets look at the ionic equations for this reaction Zn + Cu 2+ S04 2- Zn 2+ S04 2- + Cu The sulphate ion is the spectator ion so we remove it Zn + Cu 2+ Zn 2+ + Cu
WHICH ONE HAS BEEN Zinc Why? It has LOST electrons Copper Why? It has GAINED electrons Oxidised? Reduced?
HALF EQUATIONS Zn Zn 2+ + 2e- Cu 2+ + 2e- Cu Zinc Copper