Force Tractors_ Empowering Indian Farmers
Force tractors, including the strong Force Balwan and adaptable Force Orchard models, are true workhorses intended to meet the diverse requirements of Indian farmers. With a legacy of more than two decades, Force tractors have become inseparable from reliability, sturdiness, and performance.\n
2 views • 2 slides
Understanding Mass and Inertia in Physics
Mass and inertia are fundamental concepts in physics. Mass is the amount of material in an object, determining its inertia - the resistance to change in motion. Objects with greater mass require more force to change their state of motion. Mass should not be confused with volume or weight, as they ar
0 views • 21 slides
Physical Science Unit 1 Test Review Game
This test review game covers various topics in physical science including concepts like floating and sinking, forces, work, inertia, acceleration, and more. It presents multiple-choice questions with explanations related to lifeguard tests, object forces, average force calculations, work calculation
1 views • 71 slides
Understanding Newton's Third Law of Motion
Chapter 7 delves into Newton's Third Law, stating that every force has an equal and opposite force. The law describes the relationship between forces in an interaction - one force being the action force and the other the reaction force. These forces are equal in strength, opposite in direction, and
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Newton's First Law of Inertia
Newton's first law of inertia states that objects remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. This law, also known as the law of inertia, explains how objects tend to maintain their current state of motion unless influenced by an external force. Objects at rest stay a
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Inertia and Motion in the Moving Earth
Inertia and motion in a moving Earth debunk the argument against Earth's movement using examples of birds catching worms on trees and flipping coins in moving vehicles. Objects on Earth move with Earth's motion, showcasing the principle of inertia in action.
2 views • 7 slides
Understanding Net Force in Physics
Explore the concept of net force in physics, including balanced and unbalanced forces, the relationship between force and motion, and how net force affects an object's movement. Learn about scenarios where net force is zero, one force acts on an object, multiple forces cancel out, or combine to prod
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion and Law of Universal Gravitation
Isaac Newton, a giant in scientific history, revolutionized physics with his three laws of motion and law of universal gravitation. His laws of inertia, force, and action and reaction explain the behavior of objects in motion, while the law of gravitation describes the force that governs celestial b
3 views • 10 slides
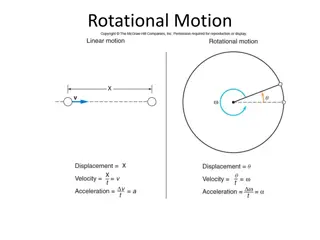
Understanding Rotational Motion in Physics
Exploring rotational motion in physics involves understanding angular velocity, torque, moment of inertia, and rotational kinetic energy. This comprehensive guide covers concepts such as the conversion between degrees and radians, angular variables, Newton's second law for rotating bodies, and momen
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Explore Newton's Laws of Motion including the concepts of force, inertia, acceleration, action and reaction forces, and the role of mass in determining motion. Newton's First Law states that objects at rest remain at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton's Second Law relates accelera
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Explore Sir Isaac Newton's foundational principles of motion through engaging visuals and real-world examples. Discover how inertia, force, and acceleration shape the dynamics of objects in motion, as explained by Newton's First and Second Laws. Delve into the concept of inertia and the relationship
2 views • 13 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's laws of motion, including the principles of inertia and dynamics, explain how objects move and interact with forces. The first law states that objects in motion remain in motion unless acted upon by a force, while the second law explains how a net force is required to change an object's vel
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Forces and Mass
Forces, such as contact and non-contact forces, interact with objects to cause motion or deformation. Mass is the amount of matter in an object, measured in kilograms. Learn about applied force, normal force, frictional force, air resistance, spring force, tensile forces, compressive forces, and she
1 views • 29 slides
Understanding Small Gasoline Engine Performance
This chapter explores the intricacies of measuring and optimizing internal combustion engine performance, focusing on calculating functional horsepower through various formulas and measurements. It delves into the combustion process in a small gasoline engine, detailing how the air/fuel mixture igni
0 views • 66 slides
Understanding Gravity and Inertia: Key Concepts in Motion
Exploring the principles of inertia and gravity, this content delves into how objects resist changes in motion and the force that attracts objects towards each other. From Newton's Law of Gravity to the dynamics of free fall and weight, learn how these fundamental concepts shape our understanding of
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Weight and Mass in Physics
Weight and mass are two fundamental concepts in physics that are often misunderstood. Weight is the gravitational force acting on an object, while mass is the measure of its inertia. This article clarifies the relationship between weight and mass, explains the force of gravity, and discusses how the
2 views • 9 slides
Understanding Use of Force and Control Tactics Training
Explore the legal aspects, civil liability, decision-making practices, de-escalation techniques, and control tactics related to use of force. Emphasizes the sanctity of human life, proportionality in force application, and justifications under the U.S. Constitution and statutes. Examines the criteri
0 views • 42 slides
Newton's First Law of Motion: Inertia and Forces
Understanding the concept of inertia in motion, the role of forces in maintaining or changing motion, and analyzing net forces applied to objects. Also explores scenarios where forces are balanced or unbalanced, affecting the motion of objects.
0 views • 12 slides
Mechanics Practice Problems with Force and Acceleration
Solve practice problems involving force, mass, and acceleration in physics. Calculate net force accelerating a bicycle, mass of the Space Shuttle based on thrust and acceleration, acceleration of a runner given force and mass, and acceleration of a car with a known force and mass.
0 views • 5 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Dynamics is governed by Newton's three fundamental laws of motion. These laws, formulated by Newton, describe the behavior of objects in motion and at rest. Key terms such as mass, weight, momentum, force, and inertia are crucial in understanding these laws. Rigid bodies, which consist of fixed part
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Rotational Inertia and Conservation of Momentum
Rotational inertia symbolized as I is crucial in quantifying the torque needed for rotation, depending on mass distribution. Torque, rotational inertia, and mass influence an object's spinning motion, affecting stability and speed. Exploring why wheels keep spinning, ice skaters rotate faster when a
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion: Inertia, Forces, and Acceleration
Delve into the fundamentals of Newton's first and second laws of motion, exploring concepts such as inertia, the relationship between forces and acceleration, and the procedure for solving force problems. Discover how objects behave when left to themselves, and grasp the significance of forces in ch
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Rotational Inertia and Torque in Physics
Rotational inertia symbolizes how difficult it is to change the rotation of an object. It depends on mass distribution from the axis, shape, and mass. Torque needed to start rotation is proportional to rotational inertia. Smaller rotational inertia leads to faster rotational acceleration. Examples a
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Robbery: Elements, Definition, and Distinctions
Robbery, defined under Section 8 of the Theft Act 1968, involves the act of stealing with the use of force or threat of force. This offense carries serious consequences, including a potential life imprisonment sentence. The key elements of robbery include the actus reus of theft and force, along wit
0 views • 11 slides
Enhancing Robot Control in Neurosurgery through Force Sensing Integration
The project aims to improve the cooperative control of the Galen robot in neurosurgery by measuring and integrating tool-to-tissue forces. By sensing these forces, the system can enhance visual feedback, establish safety limits, evaluate surgical skills, and allow unbiased comparisons of techniques.
0 views • 12 slides
Course Weighting Task Force Meeting May 11, 2017
The Course Weighting Task Force meeting held on May 11, 2017, aimed to study and potentially recommend changes to current course weighting practices within SBISD. The task force discussed members' familiarity with the system, concerns, interests, and potential impacts. The executive limitations of t
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Mass and Inertia in Physics
Understanding the concepts of mass and inertia in physics is essential for comprehending the behavior of objects in motion. Mass is the measure of the quantity of inertia of an object, affecting its resistance to changes in motion. In translational cases, inertia is termed as mass, measured in kilog
0 views • 8 slides
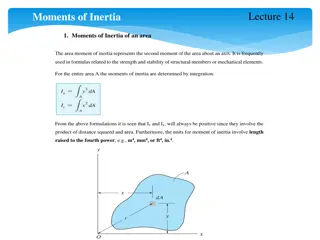
Understanding Moments of Inertia in Structural Mechanics
Moments of inertia of an area play a crucial role in determining the strength and stability of structural members and mechanical elements. This includes concepts such as area moment of inertia, parallel-axis theorem, and radius of gyration. The integration process, positive nature, and units of mome
0 views • 5 slides
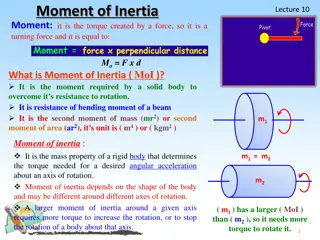
Understanding Moment of Inertia and its Importance in Mechanics
Moment of Inertia (MoI) is a crucial concept in mechanics, representing a body's resistance to rotation. It depends on the shape of the object and influences the torque required for rotation. This property plays a significant role in structural mechanics and stress analysis, contributing to understa
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Power System Inertia in Inverter-Dominated Networks
This study explores the impact of high levels of instantaneous inverter-based renewable energy penetration on power system inertia. It delves into fundamental concepts of energy balance, frequency control, load/frequency characteristics, and the importance of system inertia in maintaining grid stabi
0 views • 20 slides
Moment of Inertia Calculations in Engineering Mechanics - Problems and Solutions
The content covers problems related to calculating moments of inertia in engineering mechanics, specifically focusing on triangular areas, shaded areas, and circles. Detailed step-by-step solutions are provided for each problem, including determining moments of inertia about different axes and findi
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Area Moment of Inertia and Centroidal Axis in Mechanics
Explore the concept of area moment of inertia and centroidal axis in mechanics through detailed explanations and visual representations. Learn how to determine moment of inertia, locate the centroid, and understand the principles behind mass moment of inertia. Dive into the calculation methods and p
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Rotational Kinetic Energy and Moment of Inertia
Rotational kinetic energy arises from the motion of mass in a rotating object, while moment of inertia quantifies an object's resistance to rotational motion. This concept is crucial for analyzing the energy and stability of rotating systems. The content explains the calculation of kinetic energy fo
0 views • 7 slides
Optimus Prime's Transformation Challenge: Angular Momentum and Moment of Inertia Exploration
Dr. Mark Huntress, a Chemistry and Physics professor, devises a transformative assignment on rotation. As Optimus Prime aims to rotate as fast as possible with minimal external forces, students explore whether he should transform into a disk, ring, or solid sphere. Through a four-part exploration in
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Rotational Dynamics in Physics
General announcements for a physics class covering topics on rigid bodies, torque, moment of inertia, and rotational Newton's second law. Learn about the importance of moment of inertia, calculating rotational inertia, and the application of Rotational N2L in problem-solving exercises. Explore the r
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Force and Motion: Key Concepts and Examples
Explore the fundamental concepts of force and motion, including balanced and unbalanced forces, gravity, inertia, friction, Newton's laws, and the unit of force (Newton). Discover how these concepts influence the behavior of objects and their motion through engaging examples and explanations.
0 views • 15 slides
Experimental Determination of Moment of Inertia in Rotational Dynamics Lab
In this university lab experiment, students apply known torques to various objects to measure angular accelerations and determine their moments of inertia. The setup involves rotating discs and rods with masses, using a rotational sensor for data collection. Important steps include measuring diamete
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Momentum in Physics
Momentum, first introduced by Isaac Newton, is symbolized by the letter p and signifies inertia in motion. It is calculated as mass multiplied by velocity (p = m * v) and has the unit of kg * m/s. The amount of momentum depends on the object's mass and speed. A moving object has more momentum if eit
0 views • 18 slides
Exploring Momentum and Impact Force in Egg Drop Lesson Plan
In this physics lesson plan, students will explore the concepts of momentum and impact force by conducting an egg drop experiment. The agenda includes a do-now quiz, content introduction on impact force, practical exploration of impact force, and discussions on methods to reduce impact force on movi
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Robbery: Elements and Distinctions
Robbery, as defined in Section 8 of the Theft Act 1968, involves the act of stealing accompanied by the use of force or the threat of force to instill fear in order to commit the theft. This offense is considered more serious than theft and can lead to a life imprisonment sentence. The key elements
0 views • 11 slides