Understanding Peptic Ulcer Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
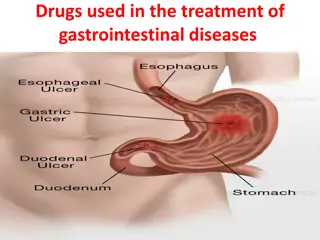
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) involves ulcerations in the duodenal or gastric mucosa caused by factors like Helicobacter pylori infection and NSAID use. Symptoms include abdominal pain and nausea, and treatment often involves H. pylori eradication and proton pump inhibitors to prevent complications lik
0 views • 77 slides
Peptic Ulcer Disease: Treatment Approaches and Helicobacter pylori Eradication
Common gastrointestinal conditions such as peptic ulcers can be effectively treated through approaches like eradicating H. pylori infection, reducing gastric acid secretion, and using mucosal protecting agents. Helicobacter pylori eradication is crucial for healing ulcers and preventing recurrence,
0 views • 27 slides
NHS Pharmacy First: Guidance for Care Navigators and Receptionists
NHS Pharmacy First is a new service launched by NHS England providing urgent repeat medicines supply, referrals for minor illnesses, and clinical pathways through community pharmacies. Patients over 1 year old can be referred for conditions such as colds, coughs, congestion, earache, gastric issues,
1 views • 22 slides
Enteral Tube Use and Maintenance in Brampton and Surrounding Areas
Discover the comprehensive services provided by the William Osler Nurse Practitioner Led Outreach Team in Brampton, North Etobicoke, West Woodbridge, Malton, and Bramalea. Learn about indications for enteral tube use, different types of enteral tubes, maintenance strategies, and more. Explore essent
5 views • 17 slides
Physiologie Digestive PHASE BUCCALE
Digestive physiology involves the breakdown of food into simple nutrients for absorption by the body. It includes mechanical and chemical means of food degradation using enzymes from salivary, gastric, pancreatic, and colonic bacteria. The digestive system comprises the mouth, esophagus, stomach, li
4 views • 25 slides
Key Benefits of Gastric Sleeve Surgery for Weight Loss
Choose Healthy Life Bariatrics for gastric sleeve surgery. It is renowned for its effectiveness in promoting significant and sustained weight loss. This procedure limits food intake, reduces hunger, and alters hormonal signals related to hunger and fullness.
6 views • 11 slides
Protein Digestion and Metabolism in Ruminants and Non-Ruminants
Digestion and metabolism of protein in both ruminants and non-ruminants involve enzymatic breakdown of proteins into polypeptides and amino acids in the stomach and intestines. Key enzymes such as pepsin, trypsin, and chymotrypsin play important roles in protein digestion. Gastric digestion in the s
1 views • 14 slides
Understanding Bloat in Cattle: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Bloat in cattle, characterized by overdistension of the rumenoreticulum with gases of fermentation, can be caused by various factors including diet, obstruction, or diseases. Frothy bloat and free gas bloat are common types, each with its own triggers and symptoms. Diagnosis involves a thorough hist
1 views • 8 slides
Appetite Stimulants, Digestants, and Carminatives in Pharmacology III
Appetite is influenced by various factors including hypothalamic peptides, catecholaminergic pathways, and serotoninergic signaling. Loss of appetite, like anorexia, can stem from both physical and psychological causes. Alcohol can stimulate gastric secretion but chronic consumption may reduce appet
0 views • 8 slides
The Digestive Journey: From Skittles in the Mouth to Nutrient Absorption in the Intestine
The process begins with chewing skittles in the mouth, where salivary amylase breaks down sugar. The bolus then travels down the esophagus via peristalsis into the stomach, further broken down by gastric juice. The pancreas releases enzymes like amylase and lipase to digest sugars and fats. Bile pro
1 views • 15 slides
Immunology Testing in Pernicious Anaemia: A Quick Guide
The article by Dr. Charu, a Consultant Immunologist, provides insights into immunology testing for Pernicious Anaemia (PA). It covers considerations for PA diagnosis, prevalence data, and details intrinsic factor antibody and gastric parietal cell antibody tests. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatme
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Gastric Motility and Secretion in the Stomach
This content delves into the intricate workings of the stomach, focusing on its motor functions, anatomical and physiological divisions, gastric reservoir, storage and mixing functions, and relaxation reflexes. It emphasizes the key roles of the stomach in storing and preparing food for digestion, a
0 views • 47 slides
Understanding Gastric Motility and Secretion in the Stomach
The stomach plays a crucial role in food processing, acting as a reservoir, preparing chyme for digestion, and facilitating absorption. Divided anatomically and physiologically, it functions as a storage unit and mixing chamber for food. Key motor functions include storage, preparation for digestion
0 views • 49 slides
Understanding Gastric Dilatation in Canines: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Gastric Dilatation and Volvulus (GDV) syndrome, commonly known as bloat, is a serious condition in dogs where the stomach dilates and twists, leading to life-threatening consequences. Large breeds, especially deep-chested dogs, are more prone to GDV. The exact cause of GDV is unknown, but factors li
0 views • 27 slides
Synthesis of Salicylic Acid: Theory, Derivatives, and Applications
Salicylic acid is synthesized from methyl salicylate through ester hydrolysis with aqueous alkali. It is a versatile compound used in organic synthesis, as a plant hormone, and derived from salicin metabolism. The derivatives of salicylic acid can minimize gastric disturbances and enhance therapeuti
4 views • 12 slides
Anemia in Swine: Causes, Clinical Signs, and Treatment
Anemia in swine can be caused by factors such as gastric ulcers, internal bleeding, and poor nutrition. Clinical signs include pale skin, rapid breathing, and jaundice. Piglet anemia, a highly fatal disease, is marked by decreased hemoglobin levels and liver degeneration. Diagnosis involves examinin
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Peptic Ulcer Disease and Dyspepsia: Causes and Pathogenesis
Peptic ulcer disease and dyspepsia are common gastrointestinal conditions. Dyspepsia presents with upper abdominal pain and may or may not be associated with peptic ulcers. The most prevalent causes of dyspepsia include non-ulcer dyspepsia, GERD, and peptic ulcers. Peptic ulcers account for a signif
0 views • 24 slides
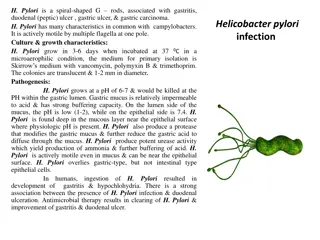
Helicobacter Pylori: Characteristics, Pathogenesis, and Diagnosis
Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped Gram-negative bacterium associated with various gastrointestinal conditions like gastritis, duodenal ulcers, gastric ulcers, and gastric carcinoma. It exhibits unique characteristics in common with Campylobacters and has specific culture and growth requirements
0 views • 5 slides
Managing Second Stage of Labour and AMTSL
Second stage of labour involves the full dilatation of the cervix until the baby is expelled. Proper management during this stage is crucial, including recognizing imminent signs of delivery, supporting controlled delivery of the head, shoulders, and body, and following the steps of Active Managemen
1 views • 10 slides
Understanding Choledochal Cysts: A Congenital Anomaly of the Biliary Tract
Choledochal cysts are congenital anomalies of the biliary tract characterized by cystic dilatation at various segments. They can lead to complications like biliary cirrhosis and recurrent pancreatitis. Clinical features include jaundice, abdominal pain, and right epigastric mass. Early detection is
0 views • 22 slides
Clinical and Laboratory Features of Radical Total Gastrectomy: Early Outcomes
Assessing the clinical and laboratory features, as well as the early outcomes following radical total gastrectomy is crucial in the management of gastric cancer. This study conducted at Hanoi Oncology Hospital retrospectively analyzed 43 patients who underwent this procedure. The overview includes d
0 views • 27 slides
Understanding Normal Parturition: The Stages and Processes
Normal parturition, also known as childbirth, involves several stages including uterine contractions, cervix dilatation, fetal positioning, and the weakening of the placental connection. The process gradually prepares the birth canal for delivery, with the fetus assuming a specific position for birt
1 views • 19 slides
Understanding the Anatomy and Function of the Stomach
The stomach is a vital organ in the digestive system with functions like food storage, mixing with gastric secretions, and controlling chyme delivery to the small intestine. It has a J-shaped structure with various parts like the fundus, body, antrum, and pylorus. The lesser and greater curvatures,
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding the Human Digestive System
The human digestive system is a complex pathway that starts from the mouth and ends at the anus, involving various organs like the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, and stomach. Each part plays a crucial role in breaking down food particles, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste products. From chewing
0 views • 132 slides
Approach to Dysphagia: Esophageal Cancer & Achalasia Cases
This presentation covers the diagnostic approach and management strategies for dysphagia in a 65-year-old patient presenting with symptoms such as odynophagia, cough, hoarseness, and lymphadenopathy. It discusses the use of CBC, CXR, ECG, upper GI endoscopy, CT, and biopsy in assessing the location,
0 views • 38 slides
Overview of Stomach Surgery and Treatment Options
The stomach plays a crucial role in digestion and is divided into four regions - cardia, fundus, body, and pyloric part. Understanding the anatomy of the stomach is essential for surgical interventions, including treatment for benign and malignant gastric diseases like peptic ulcer disease. Surgical
0 views • 30 slides
Gastric Motility and Secretion in the Stomach: Functions and Division Overview
The stomach plays crucial roles in food storage, chyme preparation, water absorption, and slow emptying into the small intestine. Its motor functions include maintaining a reservoir, mixing food, and facilitating relaxation reflexes for optimal digestion. Anatomically and physiologically, the stomac
0 views • 46 slides
Digestive System Clicker Questions
Explore interactive clicker questions related to the human digestive system, covering topics such as bariatric surgery, accessory organs, food passage, macromolecule breakdown, stomach functions, enzyme action, nutrient absorption, and gastric bypass surgery.
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Gastric Motility and Function in the Gastrointestinal Tract
The stomach plays a crucial role in digestion, from storage and mixing of food to slow emptying of chyme into the duodenum. Gastric motility involves peristalsis and retropulsion, essential for propelling food towards the pylorus. Dr. Muntadher Abdulkareem Abdullah provides valuable insights into th
0 views • 13 slides
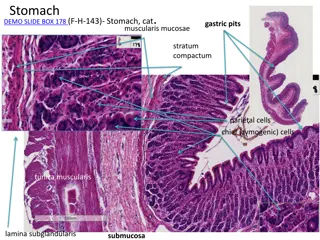
Various Stomach Anatomy Slides of Different Animal Species
Explore a series of detailed histological slides showcasing the stomach anatomy of different animal species including cats, rabbits, dogs, pigs, sheep, and goats. The images highlight key features such as gastric pits, mucosal layers, chief and parietal cells, proper gastric glands, cardiac and pylo
0 views • 29 slides
Overview of Gastrointestinal Secretions and Structural Considerations
In this informative presentation by Assistant Professor Dr. Emre Hamurtekin, the focus is on gastrointestinal secretions including salivary, gastric, pancreatic, biliary, and intestinal fluids. Structural considerations such as the surface area for absorption, sphincters, villi, and crypts are discu
0 views • 33 slides
Understanding Gastrointestinal Agents: Acidifying Agents, Antacids, Saline Cathartics
Gastrointestinal agents such as acidifying agents, antacids, and saline cathartics are used to manage gastrointestinal disturbances. Acidifying agents like Hydrochloric Acid aid in gastric digestion, while antacids help reduce gastric acidity. Saline cathartics are used as laxatives. Achlorhydria, a
0 views • 36 slides
Understanding Peptic Ulcers: Causes, Prevalence, and Treatment
Peptic ulcers are circumscribed ulcerations in the gastrointestinal mucosa, commonly caused by Helicobacter pylori infection. They have a higher prevalence in developing countries and are associated with factors like socioeconomic status, poor hygiene, and genetic links. While peptic ulcers naturall
0 views • 54 slides
Structure of Gastric Mucosa in Glandular Stomach
The glandular stomach features laminae epithelialis lined with simple columnar epithelium, leading to differentiation into gastric pits and glands. The laminae propria houses tubular gastric glands, while the laminae muscularis mucosa is composed of smooth muscles. Different regions exhibit distinct
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Gastrointestinal Agents and Disorders
Learn about gastrointestinal agents used in the treatment of GIT disorders such as achlorhydria, hyperacidity, diarrhea, and constipation. Explore the classification of gastrointestinal agents including gastric acidifiers, antacids, protectives, adsorbents, and cathartics. Discover the causes and sy
0 views • 45 slides
Understanding Helicobacter pylori: Morphology, Pathogenesis, and Identification
In this detailed lecture, Assistant Professor Dr. Dalya Basil discusses the characteristics, identification methods, growth characteristics, and pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori. This spiral-shaped, gram-negative rod bacterium is associated with various gastric conditions, including gastritis, ul
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Abnormal Labor and Prolonged Labor in Childbirth
Labor is considered abnormal when there is poor progress or signs of compromise in the fetus. Prolonged labor, lasting more than 18 hours, may result from various factors affecting cervical dilatation and descent of the presenting part. Causes include issues with power, passage, and passenger. Diagn
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Central and Peripheral Controls of Food Intake and Appetite
This article delves into the intricate mechanisms that regulate food intake and appetite, focusing on central and peripheral factors. Neural signals, gastric distention, glucose influence, circulating lipids' role, and gut hormones all play crucial roles in shaping our eating behavior. These signals
0 views • 15 slides
Comprehensive Overview of Oesophageal and Gastric Cancer: Roles and Statistics
This content delves into Oesophageal and Gastric Cancer, exploring statistics, risk factors, common signs and symptoms, and the role of Oesophago-Gastric Clinical Nurse Specialists. It highlights the prevalence, age factors, survival rates, and key risk factors such as smoking, alcohol, and diet. Th
0 views • 6 slides
SWAG Network Oesophago-gastric Cancer Research Update
SWAG Network Oesophago-gastric (OG) Cancer Clinical Advisory Group provided a research update on Upper GI Cancer Studies, National Recruitment data, and Regional Recruitment trends in the UK. The update included information on open cancer studies, sample sizes, recruitment statistics, and participat
0 views • 16 slides