Protein Digestion and Metabolism in Ruminants and Non-Ruminants
Digestion and metabolism of protein in both ruminants and non-ruminants involve enzymatic breakdown of proteins into polypeptides and amino acids in the stomach and intestines. Key enzymes such as pepsin, trypsin, and chymotrypsin play important roles in protein digestion. Gastric digestion in the stomach involves pepsin and HCl, while most digestion and absorption occur in the small intestine, particularly in the duodenum and jejunum. Various digestive processes take place intraluminally, on the mucosal membrane, and intracellularly, contributing to the overall protein metabolism.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DIGESTION & METABOLISM OF PROTEIN IN DIGESTION & METABOLISM OF PROTEIN IN RUMINANTS AND NON RUMINANTS AND NON- -RUMINANTS RUMINANTS Dr. Kaushalendra Kumar Assistant Professor (Animal Nutrition), Bihar Veterinary College, BASU, Patna, India E-mail: drkaushalbvc@gmail.com
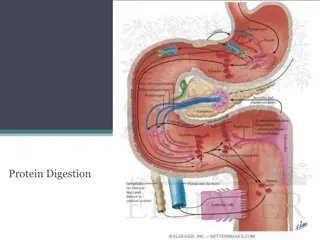
Digestion and absorption of protein in monogastric Digestion and absorption of protein in monogastric species species Digestion Digestion of of protein protein happens happens in in the the stomach stomach and and duodenum duodenum by by the the action action of of enzymes enzymes; ; Pepsin Pepsin (stomach), (stomach), trypsin trypsin and and chymotrypsin chymotrypsin (pancreas) (pancreas). . Breakdown Breakdown of of food food proteins proteins into into polypeptides polypeptides & & further further into into many many exopeptidases exopeptidases & & dipeptidases dipeptidases into into amino amino acids acids. .
Cont.... Gastric digestion Gastric digestion Pepsin Pepsin and and HCl HCl are are principally principally responsible responsible for for gastric gastric digestion digestion. . Pepsinogen Pepsinogen is is the the inactive inactive forms forms of of pepsin pepsin & & HCl HCl activates activates pepsinogen, pepsinogen, convert convert into into pepsin, pepsin, further further hydrolyses hydrolyses peptide peptide bonds bonds. . Pepsin Pepsin also also have have strong strong clotting clotting action action on on milk, milk, & & rennin rennin or or chymosin chymosin, , enzyme enzyme occurs occurs in in the the gastric gastric juice juice of of calf calf & & young young piglet piglet. . Products Products of of protein protein digestion digestion in in the the stomach stomach are are principally principally polypeptides polypeptides of of variable variable chain chain length length & & a a few few amino amino acids acids. .
Cont.... Digestion in the small intestine Digestion in the small intestine Majority Majority of of digestion digestion & & absorption absorption happens happens in in the the small small intestine intestine & & primary primary site site is is the the duodenum duodenum & & jejunum jejunum. . However, However, intestinal intestinal digestion digestion comprises comprises of of intraluminal intraluminal & & membrane membrane and and intracellular intracellular digestion digestion. . Intraluminal Intraluminal digestion digestion Mostly Mostly performed performed by by pancreatic pancreatic enzymes, enzymes, but but some some microbial microbial proteases proteases may may be be involved involved. . Membrane Membrane and and intracellular intracellular digestion digestion Digestion Digestion at at the the external external membrane membrane of of intestinal intestinal mucosa mucosa (brush (brush border) border) and and within within the the small small intestine intestine columnar columnar cell cell. .
Cont.... Some important digestive enzymes of protein Some important digestive enzymes of protein Name of enzymes Name of enzymes Systematic name Systematic name Source Source Substrate Substrate Enzymes hydrolysing peptide links Enzymes hydrolysing peptide links Pepsin Pepsin Gastric mucosa Gastric mucosa Proteins and peptides Proteins and peptides Chymosin (Rennin) Chymosin (Rennin) Gastric mucosa (young Gastric mucosa (young Proteins and peptides Proteins and peptides calves) calves) Trypsin Trypsin Pancreas Pancreas Proteins and peptides Proteins and peptides Chymotrypsin Chymotrypsin Pancreas Pancreas Proteins and peptides Proteins and peptides Carboxypeptidase A Carboxypeptidase A Peptidyl Peptidyl- -L L- -amino amino- -acid acid Small intestine Small intestine Peptides Peptides (Carboxypeptidase) (Carboxypeptidase) hydrolase hydrolase Carboxypeptidase B Carboxypeptidase B Peptidyl Peptidyl- -L L- -lysine ( lysine (- -L L- - Small intestine Small intestine Peptides Peptides (Protaminase) (Protaminase) arginine) hydrolase arginine) hydrolase Aminopeptidases Aminopeptidases - -Aminoacyl Aminoacyl- -peptide peptide Small intestine Small intestine Peptides Peptides hydrolases hydrolases Dipeptidases Dipeptidases Dipeptide hydrolases Dipeptide hydrolases Small intestine Small intestine Dipeptides Dipeptides Credit: McDonald et al. (2011). Credit: McDonald et al. (2011).
Cont.... Absorption of Protein Absorption of Protein Digested product of proteins available in the lumen of the intestine are Digested product of proteins available in the lumen of the intestine are free amino acids & small oligo free amino acids & small oligo- -peptides peptides, , Further enter the epithelial cells of the small intestine & are Further enter the epithelial cells of the small intestine & are hydrolysed hydrolysed by specific di by specific di- - & & tripeptidases tripeptidases. . Some small peptides are Some small peptides are absorbed intact absorbed intact and subsequently appear in and subsequently appear in the portal circulation. the portal circulation. Amino acids, subsequently Amino acids, subsequently pass into the portal blood pass into the portal blood, then to the liver, , then to the liver, are are absorbed from the SI absorbed from the SI by an by an active transport mechanism (sodium active transport mechanism (sodium- - dependent dependent), ), except in glycine, proline and lysine except in glycine, proline and lysine. .
Digestion and absorption of protein in ruminants Digestion and absorption of protein in ruminants Dietary Dietary proteins proteins are are hydrolysed hydrolysed to to peptides peptides & & AA AA by by rumen rumen microbes microbes. . Key Key proteolytic proteolytic organisms organisms present present in in rumen rumen are are Prevotella Prevotella ruminicola ruminicola, , Peptostreptococci Peptostreptococci spp spp. . and and protozoa protozoa. .
Cont.... Factors affecting protein digestibility Factors affecting protein digestibility Presence Presence of of enzyme enzyme inhibitors inhibitors. . Heat Heat damage damage of of protein protein occurs occurs due due to to Maillard Maillard or or browning browning reaction reaction Source Source of of protein protein affect affect the the digestibility digestibility. . Amount Amount of of fibres fibres present present in in the the diet diet. . Digestive Digestive systems systems development development of of animals animals. .
Metabolism of proteins Transamination and deamination process Transamination and deamination process
Cont.... Fate of absorbed amino acids
Cont.... Protein synthesis
Cont.... Significance of protein turnover/metabolism Significance of protein turnover/metabolism Significance Significance of of protein protein turnover/metabolism turnover/metabolism Play Play important important role role in in metabolic metabolic adaptation adaptation such such as as enzymes, enzymes, hormones, hormones, etc etc. . Accelerate Accelerate restructuring restructuring for for growth growth and and others others activity activity (e (e. .g g. ., , muscle, muscle, collagen) collagen). . Helps Helps in in repairing repairing of of cells cells and and tissues tissues. . Play Play crucial crucial role role in in mobilization/transport mobilization/transport of of protein protein during during protein protein- - deficiency deficiency conditions conditions. . It It can can be be used used as as a a source source of of energy energy. . For For removal removal of of faulty faulty molecules molecules or or protein protein from from the the system system. .
Cont.... Factors influencing the body protein turnover/metabolism Factors influencing the body protein turnover/metabolism Genetic variation Genetic variation - - species, breeds, strains, etc. species, breeds, strains, etc. Nutrition Nutrition - - quantity and quality of protein and energy sources of diet. quantity and quality of protein and energy sources of diet. Physiological state Physiological state - - productive vs unproductive, pathological state, etc. productive vs unproductive, pathological state, etc. Age and sex Age and sex - - stage of development and male/female. stage of development and male/female. Different hormones Different hormones such as; such as; o growth hormone (anabolic), growth hormone (anabolic), o insulin (anabolic), insulin (anabolic), o thyroid hormones (anabolic and catabolic), thyroid hormones (anabolic and catabolic), o testosterone (anabolic), testosterone (anabolic), o oestrogen oestrogen (anabolic in ruminants and catabolic in nonruminants), & (anabolic in ruminants and catabolic in nonruminants), & o corticosteroids (catabolic). corticosteroids (catabolic).
Discussion.......... Questions, if any? THANKS