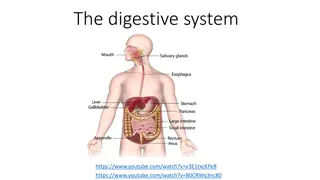
Digestive System Clicker Questions
Explore interactive clicker questions related to the human digestive system, covering topics such as bariatric surgery, accessory organs, food passage, macromolecule breakdown, stomach functions, enzyme action, nutrient absorption, and gastric bypass surgery.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Biology for a Changing World, 2e Clicker Questions Chapter 26
Bariatric surgery refers to A. adjustable gastric banding. B. gastric bypass. C. surgery used to treat obesity. D. More than one of the above are correct. E. None of the above.
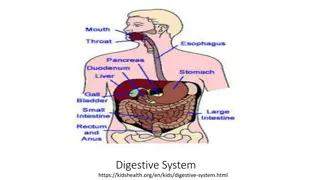
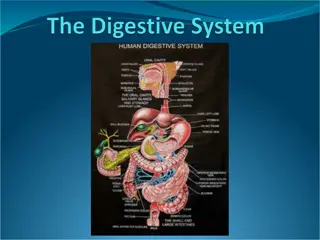
Which of the following is NOT an accessory organ of the human digestive system? A. gall bladder B. liver C. salivary glands D. spleen E. pancreas
Place the following in the order in which food would pass through them: 1. Anus 2. Colon 3. Duodenum 4. Rectum A. 3, 2, 4, 1 B. 3, 2, 1, 4 C. 2, 3, 1, 4 D. 4, 2, 3, 1 E. 1, 2, 3, 4
The first place where biological macromolecules like carbohydrates are actually broken down is in the _______ by _______, which is released from the ______. A. stomach; pepsin; stomach B. duodenum; bile salts; liver C. mouth; amylase; salivary glands D. stomach; stomach acid; pancreas E. duodenum; chyme; pancreas
Stomach acid serves which of the following purposes: 1. denatures proteins 2. kills bacteria 3. neutralizes the pH of food A. 1 only. B. 3 only. C. 1 and 2 only. D. 1 and 3 only. E. 1, 2, and 3.
Pepsin is A. stomach acid. B. an enzyme. C. a protein that breaks down other proteins. D. A and B. E. B and C.
Most nutrient absorption occurs in A. the mouth. B. the stomach. C. the small intestine. D. the large intestine. E. the rectum.
Gastric bypass surgery involves A. placing an inflatable band around the stomach to shrink it. B. rerouting the digestive tract to completely bypass the stomach. C. rerouting the digestive tract to completely bypass the small intestine. D. rerouting the digestive tract to bypass all or most of the duodenum.
The small intestine is not damaged by the low pH of stomach acid because A. it has a thick protective mucus just like the stomach. B. the acid is neutralized primarily by bile salts. C. the acid is neutralized primarily by pancreatic juice. D. stomach acid never enters the small intestine. E. None of the above.
Bile salts are produced in the ______, stored in the _______, and released into the _______. A. gall bladder; liver; small intestine B. pancreas; spleen; large intestine C. liver; gall bladder; stomach D. pancreas; liver; stomach E. liver; gall bladder; small intestine
How many people die when undergoing bariatric surgery? A. There is no risk of death. B. 1 in 100,000 C. 1 in 20,000 D. 1 in 1,000 E. 1 in 200
An organism with an incomplete digestive tract ___________. A. has an esophagus, stomach, and small intestine, but no colon B. has an esophagus, stomach, and colon, but no small intestine C. has a distinct mouth and anus D. has a single opening through which both food and waste pass E. secretes enzymes to digest food externally