Understanding Numerical Methods for Approximating Analytic Equations
Introduction to approximating solutions to analytic equations, focusing on differential equations, integral equations, and integro-differential equations. Exploring ordinary and partial derivatives, differential and integral equations, and the involvement of unknown functions and their derivatives a
2 views • 15 slides
Understanding Projectile Motion: Characteristics, Examples, and Formulas
Projectile motion involves the motion of objects under the influence of gravity, with both vertical and horizontal components. This type of motion is seen in activities such as throwing a ball, kicking a football, or dropping objects. The motion is described by specific formulas, including calculati
1 views • 19 slides
Understanding Newton's First Law of Inertia
Newton's first law of inertia states that objects remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. This law, also known as the law of inertia, explains how objects tend to maintain their current state of motion unless influenced by an external force. Objects at rest stay a
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Maxwell Equations in Thermodynamics
In thermodynamics, Maxwell equations are derived using Euler's reciprocity relation. They involve characteristic functions such as internal energy, free energy, enthalpy, and Gibbs free energy, along with parameters like temperature, entropy, pressure, and volume. These equations form the foundation
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Motion: Frames of Reference and Relative Motion
Motion is defined as a change in position over time. To describe motion accurately, one needs to understand frames of reference and relative motion. Frames of reference are systems of objects used to determine if something is in motion, while relative motion involves movement in relation to a refere
3 views • 14 slides
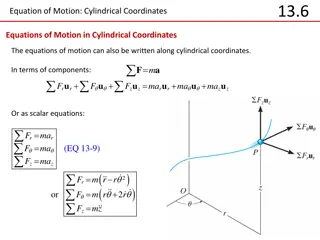
Equations of Motion in Cylindrical Coordinates
Equations of motion in cylindrical coordinates can be expressed in terms of components or scalar equations. Practical applications include analyzing motion in various engineering systems. In-class practice problems involve dealing with spring forces and applying the chain rule to determine forces in
1 views • 9 slides
Differential Equations of First Order & Higher Degree: Lecture 18
This lecture covers differential equations of first order but not of the first degree, general forms of such equations, methods for solving them, and examples of differential equations to be solved. The content includes detailed explanations, equations, solutions, and problem-solving techniques.
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Linear Equations in Algebra: A Comprehensive Overview
An exploration of algebraic expressions, equations, and linear equations in one variable with detailed explanations and examples. Discover the fundamental concepts, solving methods, and applications of linear equations in various word problems. Master the art of transforming mathematical expressions
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Motion: Concepts and Definitions in Physics
Motion in physics is defined as the change in position of an object over time. It involves concepts like rest, motion, distance, displacement, rate of motion, and types of motion. Rest and motion are relative to a reference point, while distance and displacement differ in their scalar and vector nat
2 views • 25 slides
Understanding Differential Equations: Types, Classification, and Solutions
Differential equations are mathematical equations that relate independent and dependent variables through differential coefficients. They can be classified as ordinary or partial, based on the types of derivatives involved. The order and degree of a differential equation, as well as its linearity an
3 views • 26 slides
Understanding Differential Equations in Economics Honours
Differential equations, introduced by Newton and Leibniz in the 17th century, play a key role in economics. These equations involve derivatives and represent implicit functional relationships between variables and their differentials, often related to time functions. The order and degree of a differ
1 views • 16 slides
Introduction to Differential Equations and Laplace Equations
Understanding differential equations of various orders, solving methods, linear and non-linear equations, ordinary and partial differential equations, definitions of solutions, and general vs. particular solutions in the context of Differential Equations and Laplace Equations.
1 views • 20 slides
Understanding Differential Equations: Basics to Applications
Differential equations are fundamental in mathematics, with various types such as first-order, partial, and Clairaut's equations explored in this content. The content covers general equations, solutions, and examples, providing insights into linear and higher-order equations with constant coefficien
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Partial Differential Equations of Second Order
Exploring the concepts of second-order partial differential equations in mathematics, including the general form, linear equations with variable coefficients, and equations with constant coefficients. Learn about integral solutions, examples, and techniques for solving these equations with detailed
0 views • 21 slides
Solving Exponential Equations Algebraically
Learn how to solve exponential equations algebraically with the same base and unlike bases. Understand the properties of equality for exponential equations and practice solving various equations step by step. Improve your skills in rewriting equations with the same base and applying the rules of exp
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Differential Equations in Physical Phenomena
Differential equations play a crucial role in modeling physical phenomena involving rates of change like fluid motion, mechanical systems, and heat dissipation. This content explores examples of differential equations in motion and provides insights on sketching direction fields using tools like Map
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Linear and Rotational Motion in Physics
Explore the concepts of linear momentum, center of mass, rotational motion, and angular displacement in physics. Learn how to determine the center of mass of objects, analyze motion of particle groups, and understand the conservation of momentum in systems under external forces. Delve into the funda
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Circular Motion in Physics
Circular motion involves objects moving in a circular path at a constant speed, experiencing acceleration and centripetal force. This motion is characterized by angular speed, centripetal acceleration, and the necessary centripetal force. The concept of uniform circular motion and angular displaceme
3 views • 38 slides
Understanding Newton's First Law of Motion
Exploring the foundational concepts of motion and forces, this content delves into Isaac Newton's First Law of Motion. Describing how objects behave when the net force acting on them is zero, the law highlights the significance of inertia and balanced forces in determining an object's state of rest
0 views • 9 slides
Physics Chapter 6: Circular Motion Overview
Learn about circular motion in physics, covering concepts like centripetal acceleration, uniform circular motion, and Newton's laws applied to rotational motion. Get ready for the upcoming midterm with key equations provided and practice exams available on the class web page.
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Vertical Motion and Gravity in Kinematics
Explore the principles of vertical motion and gravity in kinematics through scenarios involving throwing objects, free-fall motion, and calculating heights. Learn how to model vertical motion with acceleration due to gravity, find maximum heights of thrown objects, solve extended problems, and under
2 views • 12 slides
Understanding Circular Motion Concepts in Physics
Explore the fundamentals of uniform circular motion, centripetal acceleration, and tangential velocity with real-world examples. Learn how to calculate velocities and accelerations in circular motion scenarios, and understand the difference between tangential speed and velocity in rotating systems.
0 views • 18 slides
Overview of Damping Rings in Linear Colliders
This content provides insights into the basics of damping rings in linear colliders, covering topics such as ring equations of motion, betatron motion, emittance, transverse coupling, dispersion, and momentum compaction factor. It delves into the equations of motion governing particle behavior in el
3 views • 34 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Explore the fundamental concepts of Newton's Laws of Motion, including net forces, combining forces, balanced versus unbalanced forces, and the concept of inertia. Learn how these principles explain the behavior of objects in motion and at rest, and discover the impact of mass on an object's resista
0 views • 17 slides
GCSE Algebra Revision Materials and Equations Practice
Explore a collection of GCSE algebra revision materials, including solving linear equations and common mishaps in algebraic simplification. Practice setting up equations and solving linear equations with provided examples and questions. Enhance your algebra skills through comprehensive content desig
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Joint Motion: Osteokinematic and Arthrokinematic Movements
Joint motion involves osteokinematic movements, which are under voluntary control and include flexion, extension, and more. End-feel sensations like bony, capsular, and springy block indicate different joint conditions. Arthrokinematic motion refers to how joint surfaces move during osteokinematic m
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion explain the relationship between forces and motion. The first law states that an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by a net force, while the second law describes how force is related to an object's mass and acceleration. The third law states that for every ac
0 views • 21 slides
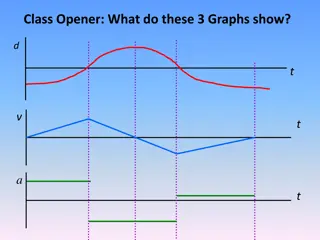
Understanding Kinematics in Physics: Equations, Graphs, and Definitions
Exploring kinematics in physics involves studying the motion of objects through equations, graphs, and definitions. Key concepts include position, distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration, along with scalar and vector quantities. Equations like s = (u + v)t and v = u + at are crucia
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Dynamics is governed by Newton's three fundamental laws of motion. These laws, formulated by Newton, describe the behavior of objects in motion and at rest. Key terms such as mass, weight, momentum, force, and inertia are crucial in understanding these laws. Rigid bodies, which consist of fixed part
0 views • 22 slides
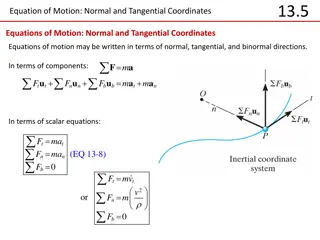
Equations of Motion in Normal and Tangential Coordinates
Equations of motion can be expressed in terms of normal, tangential, and binormal directions. The normal and tangential components play crucial roles in describing the motion of an object. Through scalar equations and component representations, these equations help analyze forces and acceleration in
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion describe how objects behave in response to external forces. The first law states that objects in motion remain in motion unless acted upon by a force, while objects at rest stay at rest. The second law relates force, mass, and acceleration, showing how they are interconnected
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Motion and Newton's Laws
Explore the concepts of motion, distance, speed, and velocity as they relate to Newton's Laws of Motion. Learn about measuring motion, calculating speed, graphing motion on distance-time graphs, and understanding velocity. Discover how motion is constant and how relative motion is used. Practice cal
0 views • 36 slides
Understanding Motion and Newton's Laws
Motion is the constant change in position of objects, measured by distance and displacement. Speed is the rate of motion, while velocity includes direction. Graphing motion helps visualize speed changes over time. Newton's Laws explain the behavior of objects in motion.
0 views • 38 slides
Understanding Dependent and Relative Motion in Dynamics
Dependent Motion and Relative Motion are fundamental concepts in Dynamics, providing the foundation for future analysis. Dependent Motion involves constraints like ropes or cables, while Relative Motion considers observers in motion. Dynamics involves applying a limited set of equations in diverse w
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Motion: Types and Physics
Motion refers to a body changing position with respect to its surroundings. Different types of motion include linear, rotatory, and oscillatory motion. The physics relating to motion is called Mechanics, which comprises Dynamics and Kinematics. Scalars and vectors play a crucial role in describing t
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Projectile Motion in Physics
Projectile motion is the motion of an object near the Earth's surface influenced by gravity. This concept has a historical background from Aristotle to Galileo and Newton, with forces like gravity and air resistance playing crucial roles. Models with and without air resistance are discussed, leading
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Mass Continuity Equations and Convergence-Divergence in Atmospheric Dynamics
Explore the concepts of mass continuity equations in geometric and pressure coordinates, linking them to conservation of mass. Delve into the implications for vertical motion and weather systems' coherence. Understand the role of divergence and convergence in determining vertical motion patterns. Al
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Fixpoint Equations in Programming Languages
Fixpoint equations play a crucial role in programming languages for solving mutually recursive problems like parsing and dataflow analysis. This content explores the concepts of fixpoint equations, assumptions for ensuring solutions, computing solutions, and generalizations for cases with greatest e
0 views • 31 slides
Understanding Motion Perception in Computational Vision
In computational vision, the concept of motion opponency plays a crucial role in how the brain processes left and right motion inputs. By examining psychophysical results and the construction of motion opponent energy filters, we explore how the brain handles motion information. Additionally, the Ve
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Motion in Physics: Definitions and Examples
An object is said to be in motion if it changes position with time, while rest implies no change. Learn about types of motion such as linear and circular, as well as vibratory motion and reference points. Explore how objects can be in motion relative to one reference point while at rest relative to
0 views • 4 slides