Computer Components and Microprocessor: Understanding Computer Architecture
Explore the main computer components and learn about the operation of these components, including inputting, storing, processing, outputting, and controlling. Understand the role of the microprocessor in computer processing and its characteristics such as instruction set, bandwidth, and clock speed.
11 views • 20 slides
Understanding Microprocessor Architecture and Software Design
Microprocessor architecture and software design play crucial roles in the development of microprocessors. This article explores the internal features, software design types, and characteristics of Complex Instruction Set Computer (CISC) and Reduce Instruction Set Computer (RISC) architectures. It de
8 views • 73 slides
Understanding BCD and ASCII Arithmetic in 8086 Assembly Language
BCD (Binary-Coded Decimal) and ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) are key concepts in 8086 assembly language for numerical and character manipulations. BCD Arithmetic involves addition and subtraction techniques using instructions like DAA and DAS. The adjustment instructions
1 views • 21 slides
Comprehensive Guide to 8085 Microprocessor Interrupts and Pin Diagram
Explore the PIN diagram of the 8085 microprocessor, understand interrupts, including hardware interrupts like TRAP, RST, INTR, and the classification of interrupts such as maskable, non-maskable, vectored, and more. Learn about the sequence of steps during interrupts and their significance in microp
12 views • 31 slides
Understanding Microcontrollers in Electronics and Communication Engineering
Microcontrollers play a crucial role in embedded systems by combining a microprocessor, memory, I/O ports, and timers on a single chip. They differ from microprocessors in terms of architecture, power consumption, and applications. This content covers the basics of microcontrollers, including the di
0 views • 62 slides
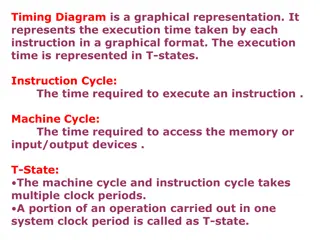
Understanding Timing Diagrams and Machine Cycles in Microprocessors
Timing diagrams provide a visual representation of execution times for instructions in a microprocessor, measured in T-states. This content delves into the concept of machine cycles, such as Opcode fetch cycle and Memory read cycle, in 8085 microprocessors. Exploring the T-states within each cycle,
0 views • 27 slides
Introduction to Intel Assembly Language for x86 Processors
Intel Assembly Language is a low-level programming language designed for Intel 8086 processors and their successors. It features a CISC instruction set, special purpose registers, memory-register operations, and various addressing modes. The language employs mnemonics to represent instructions, with
2 views • 12 slides
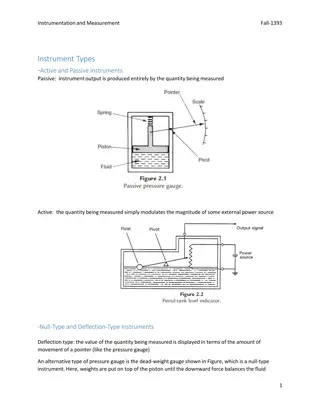
Understanding Instruments in Instrumentation and Measurement
Passive and active instruments play key roles in measurement, with null-type and deflection-type instruments providing different ways to display values. Analogue and digital instruments offer varying outputs, while indicating instruments and those with signal outputs serve different purposes. Smart
3 views • 12 slides
Interfacing the LED with 8086 Microprocessor - JEPPIAAR INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Explore the process of interfacing an LED with the 8086 Microprocessor at JEPPIAAR INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY. Learn about the 8086 Microprocessor, its features, Trainer Board, and the steps involved in the LED interfacing. Discover the internal architecture and operation of the 8086 Microprocessor thr
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Flag Registers in Microprocessor 8086
This content discusses the flag registers in the Microprocessor 8086, covering conditional flags such as Carry Flag (CF), Auxiliary Flag (AF), Parity Flag (PF), Zero Flag (ZF), Sign Flag (SF), and Overflow Flag (OF), as well as control flags including Trap Flag (TP), Interrupt Flag (IF), and Directi
1 views • 23 slides
Understanding Assembly Language and 8086 Microprocessors
Dive into the world of Assembly Language, data representation, and 8086 microprocessors. Explore topics like memory organization, integer representation, and computer registers. Learn about the structure and functionality of machine language instructions, as well as the convenience of using assembly
3 views • 36 slides
Introduction to 8086 Assembly Language Programming
Assembler directives play a crucial role in guiding the assembly process for 8086 assembly language programming. They dictate how operands are handled, memory organization, and more. This content covers essential directives such as ASSUME, DB, DW, DD, DQ, and DT, providing syntax examples and explan
4 views • 29 slides
Overview of Garments Dyeing Machines: Types and Features
Garments dyeing machines are classified as pedal and rotary types. Pedal machines are manual with higher labor costs, while rotary machines are more advanced, with atmospheric pressure and high-temperature variations. The Atmospheric Pressure Rotary Garments Dyeing Machine is widely used in Banglade
3 views • 9 slides
Evolution of Microprocessors: A Historical Overview
The history of microprocessors traces back to Fairchild Semiconductors in 1959, leading to the founding of Intel in 1968. The evolution from 4-bit to 64-bit microprocessors by Intel revolutionized computing. Key milestones include the Intel 4004 and 4040 (4-bit), 8008, 8080, and 8085 (8-bit), and th
2 views • 44 slides
Understanding the Functional Blocks of the 8086 Microprocessor
The 8086 Microprocessor is a pivotal component in computer systems, with various functional blocks storing results as status bits called flags in the flag register. It performs arithmetic and logic operations, utilizes registers for data storage, features an ALU for generating addresses and instruct
3 views • 41 slides
Overview of 8086 Assembly Language Arithmetic Operations
The 8086 assembly language provides instructions for arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, and comparison. These operations are essential for manipulating data in memory and registers. The instructions support various operand types, including registers, memory locations, and immediate
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Addressing Modes in 8086
Delve into the world of addressing modes in the 8086 processor to comprehend how different types of operands are accessed and utilized during instruction execution. Explore immediate, direct, register, register-indirect, and other addressing modes with detailed examples.
1 views • 17 slides
Assembly Language Programming in Intel 8086: Multiplication, Division, and Array Handling
Assembly language programming in Intel 8086 involves operations like unsigned and signed multiplication using MUL and IMUL instructions, respectively, along with division using DIV and IDIV instructions. This programming also encompasses handling arrays through the use of DUP to define arrays with c
0 views • 10 slides
Evolution of Intel Microprocessors: From 4004 to Pentium 4
Explore the history of Intel microprocessors, from the groundbreaking 4004 and 8008 to the evolution of 16-bit and 32-bit processors like the 8086 and the Pentium 4. Discover how Moore's Law has driven advancements in transistor count and processing capabilities in the world of microprocessors.
0 views • 39 slides
Overview of Intel 8086 Microprocessor and Internal Architecture
Intel 8086 microprocessor is a vital component in electronics, with an internal architecture comprising BIU and EU. The BIU handles bus operations, instruction fetching, and address calculation, while the EU executes instructions from the instruction queue. The pin diagram and internal architecture
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Processor Cycles and Machine Cycles in 8085 Microprocessor
Processor cycles in microprocessors like 8085 involve executing instructions through machine cycles that are essential operations performed by the processor. In the 8085 microprocessor, there are seven basic machine cycles, each serving a specific purpose such as fetching opcodes, reading from memor
0 views • 17 slides
Overview of Assembly Language Programming in 8086 Architecture
Assembly language programming in the 8086 architecture involves writing case-sensitive instructions represented by statements. Each statement corresponds to an 8086 instruction or an assembler directive. Instructions follow a specific format with optional components like labels and comments. Assembl
0 views • 31 slides
Understanding Microprocessor and Assembly Language at University of Basrah
Discover the world of Microprocessor and Assembly Language through lectures and practical examples at the University of Basrah. Topics include memory segmentation, data registers, arithmetic operations, control structures, and implementing programs to find the maximum of two elements. Dive into the
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Memory-Mapped I/O in Microprocessor System Design
Explore the concept of memory-mapped I/O in microprocessor-based systems, where I/O devices are accessed through memory addresses. Learn about bus architectures, bus protocols, and examples of read and write transactions, providing insights into how hardware interacts with a simple bus system.
0 views • 43 slides
Trends in Implicit Parallelism and Microprocessor Architectures
Explore the implications of implicit parallelism in microprocessor architectures, addressing performance bottlenecks in processor, memory system, and datapath components. Prof. Vijay More delves into optimizing resource utilization, diverse architectural executions, and the impact on current compute
0 views • 47 slides
Understanding Microprocessor Architecture and Instruction Processing
Explore the basic architecture of a microprocessor, including CPU registers, memory locations, and instruction processing steps. Learn about Intel microprocessor components, addressing modes, and the operation of pipeline microprocessors. Understand the role of control units, ALU, and bus interfaces
0 views • 38 slides
Memory Address Decoding in 8085 Microprocessor
The 8085 microprocessor with 16 address lines can access 216 locations in physical memory. Utilizing a 74LS138 address decoder, chip select signals are generated for memory block selection. The interfacing involves decoding address lines to enable memory access, with distinctions between RAM and ROM
0 views • 18 slides
Overview of 8085 Microprocessor Architecture
Intel 8085 microprocessor, introduced in 1977 as an 8-bit MP with 40-pin dual-in-line chip, operates on a single +5V supply at a clock speed of about 3MHz. It features 16-bit address bus capable of addressing up to 64KB memory, N-MOS technology, multiplexed data and address buses, interrupt support,
0 views • 52 slides
Understanding the 8085 Microprocessor Programming Model
The 8085 microprocessor, made by Intel, features general purpose registers, an accumulator, flag register, stack pointer, and program counter. The programming model includes ALU operation, flag flip-flops, and different instruction formats and operand types for executing tasks efficiently.
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding 8085 Microprocessor Architecture
The 8085 microprocessor architecture involves key components like register array, ALU, program counter, stack pointer, address latch, and more. Learn about the functionality and importance of each unit in data manipulation and communication. Dive into the details of general-purpose registers, data s
1 views • 17 slides