Understanding Key Dashboard Metrics for Business Management
In today's data-driven world, companies rely on various metrics and tools to make informed decisions and track performance. From HR metrics to manufacturing and finance indicators, this article explores the importance of data in driving business success. Dive into common dashboard metrics, the role of data in decision-making, and how technology supports these processes.
- Dashboard Metrics
- Business Management
- Data-driven Decisions
- Technology Support
- Key Performance Indicators
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Its all about the data, Today s economy, communications, social interaction, politics you name it, is driven by the internet The internet is driven by data Search/ SEO, recommenders, curated content, ML and AI It s no surprise that money follows the metrics And technology enables the metrics that drag the money along One of the most valuable assets in today s world is data, and the people who manage the data, access to the data and know how to use the data are equally valuable
What companies are interested in Companies are typically risk-averse They want to know what is going on today so they can plan the safest (and most lucrative) direction for tomorrow I m not saying that is the most effective or socially conscious way but it is a reality And even socially conscious decisions are informed by data So we will look at some ways companies look at data to get a grounding in how data can be presented and how technology supports the work
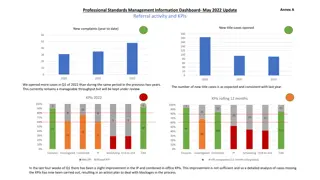
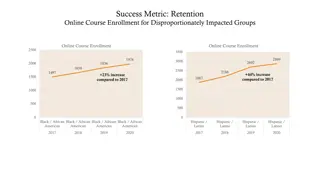
Common metrics Dashboard metrics are tools and measurements you can use to create digital displays of data that you've gathered These displays may include charts, graphs, tables and percentages to help you better understand a specific area of a company. Dashboard tools typically operate software or web applications that collect data, either through extracting it from other sources or receiving it from manual inputs and transform that data into visual forms. Businesses often use these dashboard tools to track and measure key performance indicators (KPIs) in each section of the company. 17 Dashboard Metrics Examples (With KPIs for Each Type) | Indeed.com
HR Metrics # Active employees Tenure Vacation usage Absences Geographic distribution of personnel Employee performance
Manufacturing Safety Production (items built, stored) Rate of production Rate of shipment Quality (# built, # rejected)
Business and Finance Budget Expenses People Buildings, operation expenses Profit/ loss (Quarterly, Annual) Productivity per dept. Products growth/ success # Products sold; YOY change
Dept. Operations Projects Slip rate Employee productivity People per project per project (How many people it takes for each project) Department size, growth, budget Product quality Complaints/ bugs/ recalls (like missing doors :P )
Sales # Products # Sales Sales/ product Sales/ month (quarter, year) YOY change Sales/ customer # customers
Dashboard basics Core metrics (for a particular department) Displays in basic formats Pie chart Line chart Bar chart Line/ Bar charts will typically allow for changes in timescale
Typical landmines The data needed is often across different areas E.g. you may need data from HR, Manufacturing, Sales Decisions How to merge and harmonise the data Live pull/ transform? Time-based pull/ transform/ store? On demand? Combo? Constraints You can t change the source of the data (i.e. no-one wants you to fiddle with THEIR process)
Common dashboards 18 Best Dashboard Examples for Any Business [Free Templates Included] | Databox Blog
Charting packages Many JS packages are available for simplifying data visualization There are completely generic ones (e.g. D3.js) There are many built to match another UI framework s design pattern Some are specific to types of visualizations e.g. financial, trees, nodes For MUI and React some examples are: X-charts React-google-charts Highcharts React-chartjs Recharts
recharts We will use recharts (why not) npm install recharts And then import { PieChart, Pie, Cell, Legend, Tooltip, BarChart, CartesianGrid, XAxis, YAxis, Bar, Rectangle } from 'recharts'; Obviously, include what you need
Example PieChart <strong style={{ paddingLeft: "10%", fontSize: "20px" }}># Workers by classification</strong> <PieChart width={400} height={400}> <Pie dataKey="value" data={chartData} cx={200} cy={200} innerRadius={40} outerRadius={80} fill="blue" label /> <Tooltip /> </PieChart>
Example PieChart custom labels <PieChart width={400} height={400} > <Legend></Legend> <Pie data={chartData} cx="50%" cy="50%" labelLine={false} label={renderCustomizedLabel} outerRadius={80} fill='black' dataKey="value" > {chartData.map((entry, index) => { return( <Cell key={`cell-${index}`} fill={COLORS[index % COLORS.length]} ) } )} </Pie> </PieChart> const renderCustomizedLabel = ({ cx, cy, midAngle, innerRadius, outerRadius, percent, index }) => { const radius = innerRadius + (outerRadius - innerRadius) * 0.5; const x = cx + radius * Math.cos(-midAngle * RADIAN); const y = cy + radius * Math.sin(-midAngle * RADIAN); console.log(x,y, index) return ( <text x={x} y={y} fill="white" textAnchor={x > cx ? 'start' : 'end'} dominantBaseline="central"> {`${(percent * 100).toFixed(0)}%`} </text> ); /> };
Bar Charts <BarChart width={500} margin={{ height={300} data={barData} top: 50, right: 30, left: 20, bottom: 5, }} <CartesianGrid strokeDasharray="3 3" /> <XAxis dataKey="name" /> <YAxis /> <Tooltip /> <Legend /> <Bar dataKey="averageWage" fill="#8884d8" activeBar={<Rectangle fill="pink" stroke="blue" />} /> </BarChart> >
Additional info Recharts https://recharts.org/en-US/examples Recommendation 1. Decide what data you want to display 2. Select appropriate chart(s) 3. Decide organization of data 4. Design API to get data from DB in the closest form possible to easily populate the charts You will need to have some specialized APIs to do things like grouping, aggregation etc.