Understanding Molar Mass and Conversions in Chemistry
Explore the concept of molar mass, moles of atoms, and conversions between mass and moles in chemistry through an engaging lesson on toxins, stoichiometry, solution chemistry, and acids and bases. Learn how to calculate molar mass, describe the magnitude of a mole of a substance, and conduct simple conversions between mass and moles. Dive into discussions on mass relationships, gas volumes, and the significance of molar mass in compound conversions, all designed to deepen your understanding of fundamental chemistry principles.
Uploaded on Oct 09, 2024 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Living By Chemistry SECOND EDITION Unit 4: TOXINS Stoichiometry, Solution Chemistry, and Acids and Bases
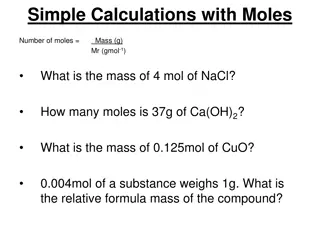
Lesson 77: What s in a Mole? Molar Mass
ChemCatalyst Consider 12 nickels, 2 empty aluminum cans, and a balloon full of carbon dioxide gas. a. Which has the greatest mass? b. Which has the greatest number of atoms? c. Which has the greatest number of moles of atoms? Explain the reasoning behind your answers.
Key Question How can you convert between mass and moles?
You will be able to: calculate the molar mass of compounds describe the approximate magnitude of a mole of a substance complete simple conversions between mass and moles
Prepare for the Lab Work in groups of four.
Discussion Notes You can figure out the mass of 1 mole of any element or compound using a periodic table. A mole of atoms or molecules of a solid or a liquid is an amount you usually can hold in your hand. A mole of any gas, if it is at standard temperature and pressure, always has a volume of 22.4 L.
Wrap Up How can you convert between mass and moles? The molar mass of a compound is the sum of the atomic masses of the atoms in the compound. The molar mass of a compound allows you to convert between moles of the compound and grams of the compound.
Wrap Up (cont.) One mole of a solid or a liquid is an amount that you usually can hold in your hand. One mole of a gas occupies a volume of 22.4 L. This is larger than the volume of 1 mol of a liquid or a solid because of the space between gas molecules.
Check-In You have 1 mol of oxygen molecules, O2, and 1 mol of carbon dioxide molecules, CO2. Which has more mass? Which has a larger volume at room temperature?