Understanding the Mole Concept in Chemistry
Delve into the world of chemistry with the Mole Concept, exploring molar mass, Avogadro's number, representative particles, and more. Learn how to determine molar mass for compounds and grasp the significance of a mole in chemical calculations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
X Chemistry Unit 7 The Mole Problem Solving involving Chemical Compounds
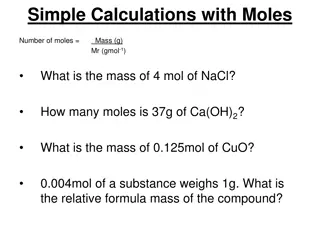
Vocab: Molar Mass- the mass of 1 mole of a substance Equal to the atomic mass for elements For a compound, the sum of the atomic masses for all the atoms in a compound Units = grams/mole = g/mol Mole - the amount of substance that is equal to 6.02x1023particles of that substance
Vocab: Representative particle- the smallest particle of a substance; defined by the type of substance: Element = atom Covalent compound = molecule Ionic compound = formula unit Charged atom = ion
Vocab: Avogadro s Number- the number of particles in 1 mole of any substance Avogadro s # = 6.02x1023 Molar Volume- the volume of 1 mole of ANY gas at STP (Standard Temperature and Pressure = 0 C and 1atm), 22.4 Liters
What is a Mole? Amedeo Avogadro (Italian Mathematician) used Carbon as the basis for the masses of the other elements devised a counting relationship between grams and moles 1 mole = 6.02x1023atoms of any element 1 mole of carbon = 12.0 g Carbon (matches the atomic mass on the P.T.)
What is a Mole? Although the amount of particles is the same, the weight is not necessarily the same!! (REAL WORLD EXAMPLE) Relationships: 1 dozen = 12 donuts just like 1 mole = 6.02x1023atoms BUT: 1 dozen feathers = 0.015 grams and 1 dozen bricks = 32,400 grams!
What is a Mole? The mass of 1 mole of any element will be different than 1 mole of any other element!! What are the masses of 1 mole of the following elements? Magnesium = 24.31 g/mol Nitrogen = 14.01 g/mol These values come from the periodic table!!
Determining Molar Mass for a Compound: Write the symbols of the elements in the formula down the left hand side of the paper. 1. Count the number of each atom of each element present. 2. Multiply the number of each atom by the molar mass of the corresponding element from the periodic table rounded to the tenths place. 3. Sum the products from step 3. 4. The units on your final answer are g/mol (grams per mole). 5.
Determining Molar Mass: Examples: CO2 (NH4)2SO4
Mole Conversions Moles! Use molar mass Use Avogadro s # (6.02 x 1023 particles per 1 mole) ( __ grams / 1 mole) Mole Conversions Representative particles Mass (atoms, molecules, formula units, ions)
Mole Conversions Always start with the number given in the problem If mass appears anywhere in the problem, you must use molar mass as a conversion! If particles (atoms, molecules, ions) appear anywhere in the problem, you must use Avogadro s number as a conversion! Cross out units that cancel Stop when you get to the unit asked for in the problem!
Converting between Moles and Mass (Grams): Dimensional Analysis!! Use molar mass as conversion factor! Moles to grams: # ?? ????? ????? ???? ? = # ?? ????? 1 ???? Grams to moles: 1 ???? # ?? ????? ????? ???? (?)= # ?? ?????
Converting between Moles and Mass: Examples: How many moles of CCl4 are there in 523.4 g?
Converting between Moles and Mass: Examples: (cont.) How many grams of Na are there in 12.3 moles of Na?
Converting between Moles and Particles: Dimensional Analysis!! Use Avogadro s number as conversion factor! Moles to particles: # ?? ????? 6.02 ? 1023 = # ?? ????????? 1 ???? Particles to moles: 1 ???? 6.02 ? 1023= # ?? ????? # ?? ?????????
Conversions Between Moles & Particles: Use Avogadro s Number!! Examples: How many atoms of carbon are contained in 0.230 moles of C?
Conversions Between Moles & Particles Examples: How many moles of sodium chloride are contained in 8.73 x 1022 molecules (formula units) of NaCl?
Conversions Between Moles & Particles Challenge!! How many molecules of barium chloride are contained in 1.07 grams of barium chloride?
Vocab: Percent composition mass of the part divided by mass of the whole times 100 Empirical Formula the simplest whole number ratio of atoms in a compound Molecular Formula- the true whole number ratio of atoms in a compound
Percent Composition Problems: 2 types: 1. Using mass data about a specific sample to find percentage of each component in the sample (More specific) 2. Using a chemical formula to find percentage of each element in a compound (More general)
Percent Composition Problems: Type 1: (just like the separation of a mixture lab!!) % of element or component in a specific sample mass of one component total mass of sample = % composition 100%
Percent Composition Problems: Examples: If 20.55 g of sodium combines completely with 31.75 g of chlorine to form a compound, what is the % composition of each element in this compound?
Percent Composition Problems: Type 2: Mass of each element in 1 mole of a compound (1 mole use the molar mass!!) mass of element from periodic table # of atom molar mass of entire compound = % composition 100%
Percent Composition Problems: Example: What is the percent composition of each element in C12H22O11?
Empirical Formula vs. Molecular Formula Molecular Formula P3H6 Empirical Formula PH2 C6H12O6 CH2O N6F8 N3F4
Identify the following as empirical or molecular formulas Ribose, C5H10O5, a sugar molecule in RNA. Ethyl butanoate, C6H12O2, a compound with the odor of pineapple. Chlorophyll, C55H72MgN4O5, part of photosynthesis. DEET, C12H17ON, an insect repellent. Oxalic acid H2C2O4, found in spinach and tea.