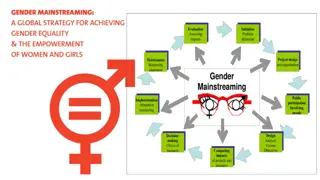
Advancing Gender Equality and Women's Empowerment in Infrastructure Development
Women's empowerment is crucial for inclusive infrastructure development. Challenges like poverty, exclusion, and discrimination marginalize women globally. In Zimbabwe, women are underrepresented in key areas. Efforts must focus on promoting women's rights, empowering them economically, and enhancing their participation in decision-making processes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
MAINSTREAMING GENDER EQUALITY AND WOMEN EMPOWERMENT TO IMPROVE INFRASTRUCTURE DEVELOPMENT IMPACT BY FIONA GANDIWA MAGAYA GENDER SPECIALIST ZIMBABWE CONGRESS OF TRADE UNIONS
INTRODUCTION: WOMEN AS AGENTS OF CHANGE Women see themselves as agents of change and this needs to be emphasized, in order to enlarge their choices and access to a broader range of activities in Economic and infrastructure Development as well as Political Spheres especially in decision making. The realization of women s rights requires countries to start investing time and resources in the implementation of some of the action points of existing instruments to which they are signatories. Research, consultation, partnership and funding are essential to promote women empowerment, especially in infrastructure development and post conflict situations.
CHALLENGES CAUSING MARGINALISATION OF WOMEN .
GENERAL STATUS OF WOMEN GLOBALLY Social Construction and Inequality Poverty exclusion Political Exclusion and Discrimination Situation of systematical disadvantages for women Ethnic Exclusi n & Discrimination Gender Roles & Responsibilities Discrimination Economic Exclusion Geographical exclusion Cultural Marginalization
Feminisation of poverty and hunger: Poverty and hunger have the face of a woman as women are the majority in the poor rural communities especially in sub Saharan Africa and women are the majority in precarious employment like Agriculture, informal economy and domestic employment. Women are under represented in decision making; Women are burdened with care work which is unpaid and not recognised as part of development of countries. Women are excluded from key infrastructure development processes; Majority of women are the most victims of violence and sexual harassment hence are more exposed to HIV and AIDs. In most underdeveloped and developing countries the following is the reality regarding girl child not accessing quality education: - a) Because of high school fees, only boys go to school b) Many adolescent girls are expected to help out at home c) Child marriage restricts girls mobility and freedom d) Girls fall pregnant at a tender age and eventually drop out of school.
ZIMBABWE CONTEXT ON WOMEN INVOLVEMENT IN INFRASTRUCTURE DEVELOPMENT .
In Zimbabwe women are underrepresented in the following areas: - Political Decision making structures even though the Electoral Act has accorded women 60 seats in Parliament and the Constitution requires 50-50 representation in Government Structures. Only 8% of the cabinet Ministers are women. Energy infrastructure projects and companies have tended to employ mainly men for both skilled and unskilled jobs with very few women electricians and a few in water management and reserve projects Construction, Cement Production and Railway Sectors are male dominated with only less than 10% women artisans in the Railways. In Mining women are involved informal mining activities which is outlawed;
Zimbabwe has also denounced the ILO Convention on Underground work for women. There has been affirmative action allowing more girls into tertiary education but this has been hampered by lack of employment and also non availability of programmes to sensitise and prevent the girl child from unwanted pregnancy There has been an increase in the reports on violence and sexual harassment affecting women and this has been a serious cause for inequalities. The social protection scheme is not inclusive and does not cover domestic and informal economy workers which are the sectors where there are more women. There is no access to clean water and sanitation and no operating space for informal economy workers where most women are. There are more women in the Agriculture sector. There has however been a few programmes on women economic empowerment and entrepreneurship skills through the ILO and Tripartite partners joint Programmes on Gender Equality. E.g. building, production of bio gas, agriculture projects and horticulture. Zimbabwe also launched a women s bank however its operations are so very polarised hence it has failed to benefit the ordinary woman.
MAINSTREAMING GENDER IN INFRASTRUCTURE DEVELOPMENT .
HOW TO MAINSTREAM GENDER EQUALITY IN INFRASTRUCTRE DEVELOPMENT Increase employment opportunities for women in sectors related to infrastructure, e.g. Water, Electricity, Construction and Mining; Invest in women and girls access to quality education and skills development Increase women representation in decision making both in corporate organisations and in political arena too; Increase women empowerment programmes and projects Sensitisation of communities, secondary and tertiary schools on gender mainstreaming and women empowerment Ensure infrastructure investments are gender sensitive, particularly by moving beyond mitigation to targeting women s economic empowerment directly.
Take a holistic approach to ending all forms of discrimination and violence against women and girls across all sectors, including:- Through initiatives designed to prevent and combat gender-based violence, To encourage and support efforts by men and boys to take an active part in the prevention and elimination of all forms of violence, especially gender-based violence, and To increase awareness of their responsibility in respect of ending the cycle of violence; Improve access to social security and financial services for women; Skills development for women and youths to increase.
WOMENS EMPOWERMENT PRINCIPLES 1. Establish high-level corporate leadership for gender equality. 2.Treat all women and men fairly at work respect and support human rights and non-discrimination. 3. Ensure the health, safety and well-being of all women and men workers. 4. Promote education, training and professional development for women.
5. Implement enterprise development, supply chain and marketing practices that empower women. 6. Promote equality through community initiatives and advocacy. 7. Measure and publicly report with gender disaggregated data on progress to achieve gender equality.
THANK YOU GENDER EQUALITY & EQUITY = KEY TO DEVELOPMENT