Essential Information on Naming Compounds, Cations, and Anions
Learn about the essential elements, symbols, and polyatomic ions you need to know for naming compounds correctly. Understand rules for naming compounds when elements combine, including diatomic molecules, halogens, oxygen, and sulfur. Explore polyatomic ions with different charges and their names to enhance your chemistry knowledge.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Naming Compounds, cations and anions
Elements and symbols that you should know: Part 1 The obvious ones: 1) Hydrogen 2) Helium 3) Lithium 4) Beryllium 5) Boron 6) Carbon 7) Nitrogen H He Li Be B C N 8) Oxygen 9) Fluorine 10)Neon 11) Magnesium 12)Aluminium 13)Silicon 14)Phosphorus O F Ne Mg Al Si P
Some more obvious ones: S Cl Ar 15)Sulphur 16)Chlorine 17)Argon 18) Calcium 19) Zinc Ca Zn The less obvious ones: Na K Fe Cu Ag 1) Sodium 2) Potassium 3) Iron 4) Copper 5) Silver 6) Tin 7) Gold 8) Mercury 9) Lead Sn Au Hg Pb
Polyatomic ions (-1 charge) H2PO4 C2H3O2 HSO3 HCO3 NO2 NO3 CN OH MnO4 ClO ClO2 ClO3 ClO4 DiHydrogen phosphate Acetate Hydrogen Sulfite Hydrogen Carbonate Nitrite Nitrate Cyanide Hydroxide Permanganate Hypochlorite Chlorite Chlorate Perchlorate
Polyatomic ions (-2 charge) HPO4 C2O4 SO3 SO4 CO3 CrO4 Cr2O7 SiO3 Hydrogen Phosphate Oxalate Sulfite Sulfate Carbonate Chromate Dichromate Silicate
Polyatomic ions (-3 charge) PO3 PO4 Phosphite Phosphate
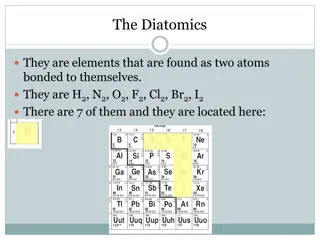
Rule 1If two identical elements combine then the name doesn t change This happens with the following elements: 4) F2 5) Cl2 6) Br2 1) H2 2) N2 3) O2 These elements always go around in pairs (diatomic molecules). For example, hydrogen looks like this:
Rule 2 When two elements join and one is a halogen, oxygen or sulphur the name ends with ____ide e.g. Magnesium + oxygen magnesium oxide 1) Sodium + chlorine 2) Magnesium + fluorine 3) Lithium + iodine 4) Chlorine + copper 5) Oxygen + iron 6) KBr 7) LiCl 8) CaO 9) MgS 10)KF
Rule 3 When three or more elements combine and two of them are hydrogen and oxygen the name ends with hydroxide e.g. Sodium + hydrogen + oxygen Sodium hydroxide 1) Potassium + hydrogen + oxygen 2) Lithium + hydrogen + oxygen 3) Calcium + hydrogen + oxygen 4) Mg(OH)2
Rule 4 When three or more elements combine and one of them is oxygen the ending is _____ate e.g. Copper + sulphur + oxygen Copper sulphate 1) Calcium + carbon + oxygen 2) Potassium + carbon + oxygen 3) Calcium + sulphur + oxygen 4) Magnesium + chlorine + oxygen 5) Calcium + oxygen + nitrogen 6) AgNO3 7) H2SO4 8) K2CO3
Covalent formulae Ionic formulae H2O CO2 NH3 H2 O2 N2 SO2 Water Carbon dioxide Ammonia Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Sulphur dioxide NaCl CaCl2 MgO HCl H2SO4 HNO3 NaOH Ca(OH)2 CaCO3 Al2O3 Fe2O3 Sodium chloride Calcium chloride Magnesium oxide Hydrochloric acid Sulphuric acid Nitric acid Sodium hydroxide Calcium hydroxide Calcium carbonate Aluminium oxide Iron oxide
This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.