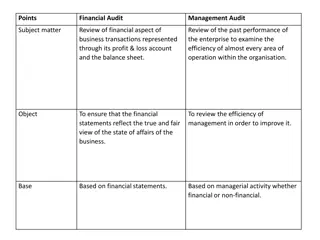
Post-Audit Activities in CNS Oversight: Overview and Procedures
The post-audit activities in CNS oversight involve completing administrative details, producing audit reports, evaluating corrective action plans, ensuring full plan implementation, and formal closure of audits. Audit teams conduct meetings, analyze data, validate observations, submit reports, archive records, and follow up with service providers. Corrective Action Requests (CAR) are issued, and findings are classified per regulations. Effective record-keeping systems are crucial for oversight activities.
Uploaded on Sep 24, 2024 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CHAPTER 3 CNS Oversight-Post Audit Activities
Overview Post- Audit/Inspection & follow-up Phase Post-Audit/Inspection activities include completion of administrative details and production of the Audit/Inspection report. Audit/Inspection follow-up includes: Evaluation and acceptance of the CNS provider s corrective action plans (CAPS); verification of full implementation of that plan; and, formal closure of the Audit/Inspection.
Post-Audit Activities After physical or virtual surveillance, audit teams conduct a post- audit meeting to consolidate and analyze data. Once conclusions have been drawn, audit teams are expected to conduct a validation meeting with the Head of the inspectorate (Depends on CAA applicable procedures) and finally to complete and submit an audit report to the CNS service provider. Audit teams are expected to track and follow-up on CNS service provider responses to the audit report, as well as any corrective actions. Audit records should be archived. Note: The CAA should implement an effective and efficient system for record-keeping and filing of records for all oversight activities.
Post-Audit Activities Post audit activities include: collating and analyzing data collected from all audited facilities and services; validating observations; writing and submitting an audit report; archiving audit records; and follow-up with the service provider(s).
Corrective Action Requests (CAR) The audit report transmitted to the audited entity will be accompanied with individual Corrective Action Requests for each finding identified during the audit/inspection CAR should contain: - The regulation/requirement breached - The details of the finding including any evidence(s)
Classification of Findings Audit findings need to be classified; PQ 7.395- Has the State established a mechanism/system with time frame for the elimination of deficiencies identified by CNS inspectors? Advisory Circular CAA-AC-ANS007, May 2018 lays down the mechanism for elimination of shortcomings and deficiencies identified within the framework of APIRG and those identified by the inspectors. However, the deficiencies identified is not classified in accordance with the provisions of the circular and no evidence provided on the follow-up of corrective action plans submitted by the service provider The CAA will review the CAR forms to be line with the contents of Order CAA-O-GEN 016B
Classification of Findings Findings can be classified in three classes namely: Serious Finding (Level I) Major Deficiency (Level II) Minor Deficiency (Level III)
Serious Finding (Level I) A deficiency posing a very serious safety risk to aviation safety Requires immediate action by the ANSP to resolve it Involves imposition of operating restrictions till the safety concern has been addressed or resolved No certificate/licence or authorization should be issued or renewed till the deficiency is resolved or eliminated.
Major Deficiency (Level II) A deficiency in the service provider s system and posing a serious safety risk which should be resolved within 10 days Requires a CAP from the ANSP detailing plans and timelines to resolve the deficiency The Authority can impose operating restrictions to ensure the ANSP resolves the deficiency Certificate/licence/authorization action till an acceptable CAP is received is an example of operating restrictions
Minor Deficiency (Level III) A non-compliance that could lower safety standards Poses less serious safety risk and concerns isolated incidents which will not necessarily have a direct impact on safety on its own Required development of a CAP by the ANSP with a maximum implementation period of 90 days A certificate/licence/authorization may be issued/renewed subject to submission of an acceptable CAP by the ANSP
Minor Deficiency (Level III) The CNS Service provider shall inform the CAA in writing on completion of corrective actions for all deficiencies identified. The CNS Service provider can apply for exemption while providing suitable mitigation measures where the deficiency cannot be resolved within 90 days Exemptions shall be granted for a period not exceeding that specified in the regulations Handout 3.1
Parallel Findings Findings against the CAA Involves deficiencies in or misapplication of Civil Aviation legislation, policies and procedures Findings against the CAA will be described in a parallel report The parallel report is forwarded to the CAA by the audit manager with notes identifying the problem, cause, responsibility and recommended solutions. The CAA deficiencies shall neither be included nor referenced in the audit report
Parallel Finding Follow-Up Parallel finding items shall be forwarded to Head of Oversight, who will assign an appropriate office for co- ordination and follow-up of those deficiencies The CAA is responsible for resolving these inconsistencies and advising the auditee of any required action
Observation May be negative or positive They must not include information suggesting non- compliance with Civil Aviation Regulations and/or procedure No regulatory action is required to be taken in the case of observation; Service providers are however urged to take observations seriously for purposes of improving their operations.
Corrective Action Plan (CAP) The CNS service provider is required to develop acceptable corrective action plans (CAPs) for each finding The CAPs should be submitted to the CAA for evaluation within the specified timelines Corrective actions to be taken by the ANSP shall be determined in accordance with the levels of the respective findings Handout 3.2
Evaluation of Corrective Action Plans CNS inspectors evaluate CAPs for their ability to resolve identified deficiencies For deficiencies that pose imminent safety risks, there may be no time for providing and accepting a written CAP. In such cases the operator/service provider may proceed to implement corrective action and notify the Authority of the action taken Handout 3.3
Acceptance of CAPs An acceptable CAP must have: Relevant: CAP addresses the issues and requirements related to the finding. Comprehensive: CAP is complete and includes all elements or aspects associated with the finding. Detailed: CAP outlines implementation process using step-by-step approach.
Acceptance of CAPs An acceptable CAP must have: Specific: CAP identifies who will do what, when and in coordination with other entities, if applicable. Realistic: In terms of contents and implementation timelines. Consistent: In relation to other CAPs and with the service providers procedures. Handout 3.5
Acceptance of CAPs CAPs not meeting the requirement will be rejected and the ANSP so informed The ANSP shall be required to provide a new CAP Failure by a service provider to submit an acceptable CAP may result in the deficiency being referred for enforcement action and/or imposition of sanctions Where the CAP is acceptable the ANSP will be informed as such Handout 3.3
Corrective Action Plan follow-up Accepted CAPs should be implemented within the stipulated timelines The CAA shall keep track of all CAPs submitted by service providers and follow up on their implementation In preparation for surveillance activity and/or ad-hoc audits, inspectors shall review all pending CAPs for the concerned ANSP and assess their level of implementation Handout 3.3
Follow-up process Post-Inspection/Audit surveillance During Inspection/Audit follow-up, surveillance is the only means to ensure that organizations with non- conformances comply with regulatory requirements and respond satisfactorily to Inspection/Audit findings. Post- Inspection/Audit surveillance can be conducted administratively, by inspection or as a more structured follow-up Inspection/Audit.
Follow-up process Where the inspection/audit findings are of a minor nature and no direct threat to aviation safety exists an administrative follow-up may be acceptable All other findings require on-site follow-up Progress will be monitored as the service provider completes inspection/audit finding corrective actions Long-term corrective actions will be followed-up through routine surveillance activity
Follow-up process For Acceptance of long term CAPs, the CNS inspector must; determine that the service provider has developed a reasonable timetable for long-term corrective action accept the CAP in co-ordination with the head of inspectorate and appropriate team leader and/or team members determine for each corrective action plan item whether the follow-up is to be administrative or on-site complete a risk assessment study. If the risk assessment confirms that the proposed period of time is justified, an exemption should be issued and the CAP accepted
Tracking of CAPs and Audit/ inspection Closure monitoring the progress of the corrective action plan by maintaining the follow-up section of the corrective action form ensuring that all completed CAP forms and corrective action tracking forms, together with any supporting documentation are stored advising the head of inspectorate when all corrective actions have been completed
Tracking of CAPs and Audit/ inspection Closure A CAP can be closed once corrective action has either been completed or assessed to the point whereby an exemption could be issued. The CNS inspector will confirm that all follow-up actions have been completed and entered in records or database and will recommend for closure The CNS service provider should be informed that the CAP(S) has/have been closed.
Updating CAPs ensure to continuously update CAPs by indicating the: progress level for each action item as it is implemented; and the date of completion for each completed action item. If the initial effective implementation date (EID) of an action item has passed and the action has not completed yet, the ANSP should provide a new EID Handout 3.4
Post-Audit/Inspection Review The ANS-CNS audit team and the audited/inspected party may jointly conduct post-audit/inspection reviews with the following objectives: To monitor the progress on the implementation of a CAP, and To verify the effectiveness of the corrective actions Follow-up reviews may be held at a mutually agreeable dates with the service provider