Understanding Photosynthesis and Photophosphorylation Processes
Photosynthesis is a vital process where autotrophic organisms trap solar energy to convert it into chemical energy in the form of food. Non-cyclic photophosphorylation involves the transfer of phosphate groups and ATP synthesis utilizing light energy. This process takes place at photosystem II in chloroplasts and involves electron transport chains, proton gradients, and ATP production. The continuous supply of water molecules is crucial for electron flow and NADP reduction. Understanding the intricate mechanisms of photosynthesis and photophosphorylation sheds light on how plants harness energy from sunlight to produce vital nutrients.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
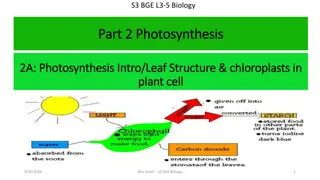
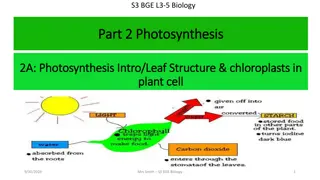
PHOTOSYNTHESIS It is a process where solar is trapped by autotrophic organisms and converted in to chemical energy in the form of food .
PHOTOSYNTHETIC PHOSPHORYLATION Photosynthetic phosphorylation or photophosphorylation is the process of phosphate group transfer According to chemiosmotic hypothesis (Mitchell 1961) the ATP is synthesized on ATPase complexes into ADP to synthesize energy rich ATP molecule making use of light as external energy source. located on the non appressed portions of thylakoid membranes particularly towards margins.
NON CYCLIC PHOTOPHOSPHORYLATION PRIMARY ACCEPTOR , Q PROTON GRADIENT PRIMARY ACCEPTOR , X 2e- 2e- PQ Fd ADP+Pi CYTOCHROME COMPLEX ATP NADP + 2e- P680 PC H2O NADPH + H+ 1/2O2 2H+ P700
Non cyclic photophosphorylation takes place at Non cyclic photophosphorylation takes place at photosystem photosystem II or PS II which includes P 680 II or PS II which includes P 680 along with pigments molecule which absorb at or along with pigments molecule which absorb at or below 680 nm in the below 680 nm in the grana grana of chloroplasts. of chloroplasts.
PROCESS: 1. After trapping solar energy (2 photons), excited 2e- are ejected from P680. These excited 2e- flow down an electron transport chain to P700. 2. During flow of electrons from P680 to P700 through electron transport chain , there is synthesis of ATP. 3. The oxidised P68O regains its electron by the photolysis of water into 2H+,2e- and oxygen. The O2 is given out by the plant.
4. 2e- are accepted by the PS II centre. 5. The protons H+ accumulate inside the Thyllakoid membrane , resulting in a Proton Gradient . The energy released by the protons , when they diffuse across the thyllakoid membrane into stroma , is used to produce ATP. 6. The electrons lost by P680 do not come back to it. There is a need of constant supply of water molecule for photolysis to supply lost electron to P680 and protons to reduce NADP. This process is called non cyclic photophosphorylation.
CYCLIC PHOTOPHOSPHORYLATION PROTON GRADIENT ADP + Pi PRIMARY ACCEPTORS,X ATP Fd PQ CYTOCHROME COMPLEX ADP + Pi PC ATP P700
Cyclic photophosphorylation occurs at reaction Cyclic photophosphorylation occurs at reaction centre or photo system I P700 or Ps along with centre or photo system I P700 or Ps along with pigment molecules which absorb at or below 700 pigment molecules which absorb at or below 700 nm. nm. Photo System I (P700 )is located in the Photo System I (P700 )is located in the Thyllakoid Thyllakoid membranes of the chloroplast. membranes of the chloroplast.
PROCESS: P700 after trapping 2 photons ejects electron which undergo electron transport chain, losing the energy at each step. The energy released is utilised in the synthesis of ATP. The 2e- after losing energy are accepted back by the P700. This process with P700 and the ultimate acceptor of the de-energised electron is also accepted back by P700.Thus the process is a cyclic one.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN CYCLIC AND NON CYCLIC PHOTOPHOSHORYLATION