Investigating the Effect of Light Intensity on Photosynthesis Using Pondweed
Explore the impact of light intensity on photosynthesis rates by conducting a practical experiment with aquatic plants like pondweed. Learn about the factors influencing photosynthesis and how to measure its rate effectively through counting oxygen bubbles produced. Follow a step-by-step guide to set up the experiment, identify variables, and make improvements for accurate results.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Photosynthesis RP DNA 1. Define: Independent variable Dependent variable Control Variable
Progress Indicators Good Progress Identify the equipment used to measure the rate of photosynthesis Outstanding Progress Plan a practical to measure the rate of photosynthesis
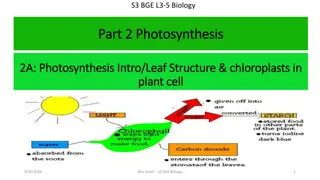
Photosynthesis Required Practical Investigate the effect of a factor on the rate of photosynthesis using an aquatic organism such as pondweed. Investigating the effect of light intensity on photosynthesis in pondweed Plants use carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose and oxygen. This process is called photosynthesis. The rate of photosynthesis is affected by many factors, such as: light intensity light wavelength. Aquatic plants produce visible bubbles of oxygen gas into the surrounding water when they photosynthesise. These bubbles can be counted as a measure of the rate of photosynthesis. Pondweed is an example of an aquatic plant.
Task: Watch the video and fill in the following boxes https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=id0aO_OdFwA Aim Method Equipment Variables Improvements that could be made Independent: Dependent: Control:
Task: Watch the video and fill in the following boxes https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=id0aO_OdFwA Aim To see how light intensity affects the rate of photosynthesis in pond weed bubbles per minute. 7. Repeat steps 1 7 with the test tube rack and boiling tube at distances of 20 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm from the light source. Method 1. Set up a clamp stand holding a boiling tube at a distance of 10 cm away from the light source Fill the boiling tube with the sodium hydrogen carbonate solution. Put the piece of pondweed into the boiling tube with the cut end at the top. Leave the boiling tube for 5 minutes. Start the stop watch and count the number of bubbles produced in one minute. Repeat the count twice more. Then use the data to calculate the mean number of 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Variables Equipment Boiling tube Pondweed Light Ruler Stop watch Clamp stand Independent: Light Intensity Improvements that could be made Dependent: Number of bubbles Use LED lamp/ heat shield Use a gas syringe to measure volume of gas produced Control: Temperature, amount of pondweed, carbon dioxide concentration
Photosynthesis Required Practical Task: Calculate the mean for each distance (remember to look out for anomalies) Round any answers to 2dp where necessary. Distance between pondweed and light source in cm 10 20 30 40 Number of bubbles per minute 1 2 3 Mean 16 12 8 10 18 12 9 3 17 11 8 2
Photosynthesis Required Practical Task: Calculate the mean for each distance (remember to look out for anomalies) Round any answers to 2dp where necessary. Distance between pondweed and light source in cm 10 20 30 40 Number of bubbles per minute 1 2 3 Mean 17 11.67 8.33 2.5 16 12 8 10 18 12 9 3 17 11 8 2
Photosynthesis Required Practical Marks can be given for: Carbon dioxide comes from the air Water comes from the ground Plants need sun light to photosynthesise (to carry out photosynthesis) There is daylight between dawn and dusk As the plant carries out photosynthesis it takes in carbon dioxide from the green house so the concentration of carbon dioxide goes down When it is dark the plants stop photosynthesising and start respiring which produces carbon dioxide Describe what the plant needs for photosynthesis, where these things come from and concentration of carbon dioxide changes over 24 hours. To answer this question you will need to use and discuss photosynthesis equation. So the concentration of carbon dioxide rises why the increasing concentration of gas the 0 6 12 18 dusk 24 mid night mid night dawn midday
Investigate the effect of a factor on the rate of photosynthesis using an aquatic organism such as pondweed.. Reliability & Reproducibility Reliability: the degree to which the result of a measurement, calculation, or specification can be depended on to be accurate. Task 1. How do we know if results are reliable? 2. How do we know if results are reproducible? 3. How could we improve our method to make it more reliable & reproducible? Reproducibility : The ability of an entire experiment or study to be duplicated, either by the same researcher or by someone else working independently. Reproducing an experiment is called replicating it.
Investigate the effect of a factor on the rate of photosynthesis using an aquatic organism such as pondweed.. . Photosynthesis Required Practical Things to remember when answering 6 mark exam questions: 1.Try and remember everything you can about what the question is asking before you start answering it 2.Make at least 6 points 3.Write in full sentences starting with capital letters and ending with full stops 4.Try and answer the question in around five minutes 5.Check your answer to make sure you have not left anything out 6.Remember to use key words when appropriate
Plenary Complete the exam style questions