Understanding Photosynthesis and Limiting Factors
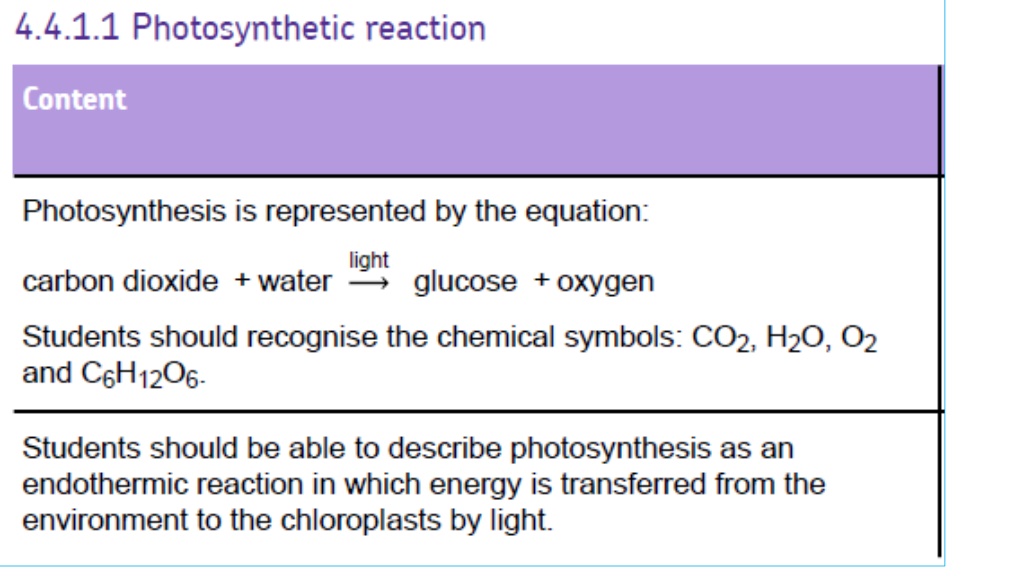
Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction that takes in energy from its surroundings. The law of limiting factors explains how various factors such as light intensity, temperature, and CO2 concentration can impact the rate of photosynthesis. Additionally, the concept of the inverse square law helps understand the relationship between light intensity and distance in photosynthesis experiments.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
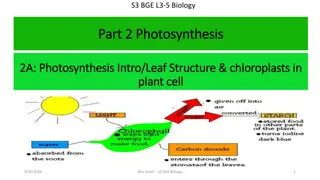
Photosynthesis Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is an ENDOTHERMIC reaction what does this mean? Takes energy IN from it s surroundings
What are limiting factors? What are limiting factors? The law of limiting factors states that: At any given moment, the rate of a physiological process is limited by the factor that is at its least favourable value. This factor is called a limiting factor because it limits the rate at which the process can take place. Changing the levels of other factors will not alter the rate of the process. Factors that can limit the rate of photosynthesis include: light intensity temperature CO2 concentration.
Key Words rate of photosynthesis, light, temperature, concentration of carbon dioxide, increase, decrease, stays the same, limiting factor Challenge 1 Describe what is happening in each graph in section 1 and section 2 Challenge 2 Explain what is happening in each graph in section 1 and section 2
Think about Independent variable Dependent variable Control variables
The inverse square law The inverse square law When you double the distance from a light source, the light intensity falls by a factor of four. This is the inverse square law: Relative light intensity = 1 distance from light source2 Relative light intensity does not have a unit
Effect of light distance on rate of photosynthesis 90 Relative light intensity = 1 80 distance from light source2 70 Number of bubbles per minute 60 50 Effect of light intensity on rate of photosynthesis 40 90 30 80 20 Number of bubbles per minute 10 70 RLI Number of bubbles per minute 0 60 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 100 84 Distance of light (cm) 50 40 44 84 Redo this table with relative light intensity instead of distance . You will need to use the inverse square law 30 25 76 20 6.25 52 10 0 4 26 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 Relative light intensity
Glucose is produced during photosynthesis and is used by the plant to make: Cellulose - which strengthens the cell wall Glucose is stored by plants as starch, fats and oils. Proteins - such as enzymes and chlorophyll
Aerobic respiration Aerobic respiration Respiration is an EXOTHERMIC reaction GIVES energy to the surroundings
Why do we respire? Why do we respire? Plants build s______ & n_______ into a______ a______ which then build p_______ Used to make _________ contract RESPIRATION Build up large molecules from small molecules Maintain constant body _________
Why do we respire? Why do we respire? Plants build sugar & nitrates into amino acids which then build proteins Used to make muscles contract RESPIRATION Build up large molecules from small molecules Maintain constant body temperature
Anaerobic Anaerobic Anaerobic = Without Oxygen O2
Anaerobic Respiration Anaerobic Respiration The incomplete breakdown of glucose. Releases less energy than aerobic respiration. Temporary process.
Anaerobic Respiration in animals Anaerobic Respiration in animals Glucose Lactic Acid + Energy Where does this occur? Cells
Anaerobic Respiration in plants Anaerobic Respiration in plants Glucose ethanol + carbon dioxide Where does this occur? Used in bread making and alcohol
What does the body need for releasing energy? The body s energy-releasing process depends on the digestive system and the breathing system. What are the substances supplied by these systems? glucose is the fuel supplied by the digestive system oxygen is supplied by the breathing system ? ?
During exercise, the muscle cells respire more than they do at rest. This means that: Oxygen and glucose must be delivered to them more quickly Waste carbon dioxide must be removed more quickly This is achieved by increasing: volume of breathing rate of breathing heart rate
What are the mistakes What are the mistakes Your body needs more energy because your muscles are contracting less. Energy is produced in respiration. Respiration needs carbon dioxide and glucose. Oxygen is taken in through the lungs and transported around the body in the blood. Glucose is absorbed in the large intestines and also transported around the body in the blood. Your muscles are using oxygen and glucose quicker and as a result your heart rate increases to deliver more oxygen and glucose to the cells that are respirating quicker. This also means more glycogen is removed too. It is also important as heat is carried away, the blood carries heat away.
What are the mistakes What are the mistakes Your body needs more energy because your muscles are contracting more. Energy is released in respiration. Respiration needs oxygen and glucose. Oxygen is taken in through the lungs and transported around the body in the blood. Glucose is absorbed in the small intestines and also transported around the body in the blood. Your muscles are using oxygen and glucose quicker and as a result your heart rate increases to deliver more oxygen and glucose to the cells that a respiring quicker. This also means more carbon dioxide is removed too. It is also important as heat is carried away, the blood carries heat away.
Recovery Recovery What do you think is needed to get rid of lactic acid? O2
O2 Recovery with oxygen Recovery with oxygen Oxygen can be used to break down the lactic acid into carbon dioxide and water. This gets rid of it. The muscles recover from their fatigue Lactic Acid + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + Water
Oxygen Debt Oxygen Debt the amount of oxygen that is the amount of oxygen that is needed to oxidise the lactic acid needed to oxidise the lactic acid Lactic acid builds up during anaerobic respiration. Lactic Acid Lactic Acid Lactic Acid Lactic Acid Lactic Acid Lactic Acid
Oxygen Debt Oxygen Debt the amount of oxygen that is the amount of oxygen that is needed to oxidise the lactic acid needed to oxidise the lactic acid Oxygen can break the lactic acid down, at a fixed rate. Lactic Acid Lactic Acid Lactic Acid Lactic Acid Lactic Acid Lactic Acid
What gas was made when oxygen and lactic What gas was made when oxygen and lactic acid reacted? acid reacted? Carbon dioxide
Oxygen debt is paid off during Oxygen debt is paid off during r recovery time ecovery time Oxygen debt depends on how much lactic acid was produced. Which depends on how long anaerobic respiration was going for. Complete the sentence in your book The more lactic acid produced the greater the Oxygen debt, therefore the greater the recovery time.