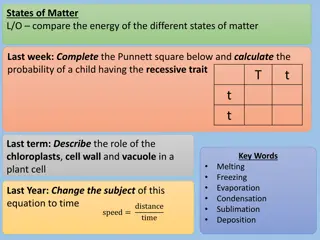
Understanding States of Matter: Energy and Changes
Explore the energy differences between the states of matter, learn about the properties of solids, liquids, and gases, and understand how energy affects state changes through melting, freezing, evaporation, condensation, sublimation, and deposition. Discover the roles of chloroplasts, cell walls, an
0 views • 10 slides
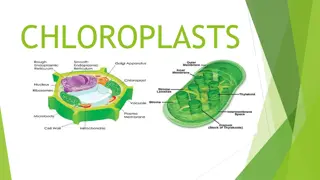
Understanding Chloroplast: The Green Powerhouse of Plant Cells
Chloroplasts, key organelles in plant cells, contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis, producing food and oxygen. They are absent in animal cells, housing their own DNA and capable of independent reproduction. The structure includes grana and stroma, each serving vital roles in energy production withi
0 views • 11 slides
Plant Mitochondrial and Chloroplast DNA Replication Mechanisms
Plant mitochondria and chloroplasts have intricate DNA replication processes. Mitochondrial DNA replication is independent of the plant cell cycle and is associated with specific proteins in nucleoid complexes. Plant mtDNA contains more genes than animal mtDNA, with a complex structure involving int
1 views • 16 slides
Understanding Chloroplasts: Structure, Function, and Marker Enzymes
Chloroplasts are vital organelles in plant cells responsible for photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy. They contain chlorophyll pigments for light absorption and play a crucial role in synthesizing foodstuffs. Marker enzymes such as RUBISCO, NADP-Reductase, and ATP synthase a
1 views • 7 slides
Bryophyta Thallus Structure and Reproduction in Hepaticopsida
The Bryophyta group includes structures like thalli and reproductive organs, particularly in the class Hepaticopsida. These plants have simple or foliose body structures with distinct characteristics such as aseptate rhizoids, ventral scales, and chloroplasts without pyrenoids. The gametophyte is st
1 views • 20 slides
Understanding Chloroplasts in Plant Cells
Chloroplasts are vital organelles in plant cells responsible for photosynthesis. They contain pigments like chlorophyll, absorbing light energy and converting it into chemical energy. This process is what makes plants green, as chloroplasts reflect green light. The structure of chloroplasts, includi
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding the Calvin Cycle in Photosynthesis
The Calvin cycle, also known as the light-independent reactions, is a crucial part of photosynthesis where carbon dioxide is converted into glucose. This cycle occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts and utilizes ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions to produce sugars for plants. It consists
5 views • 15 slides
The Biosynthesis and Role of Salicylic Acid in Plants
Salicylic acid (SA), a phenolic derivative widely present in plants, plays a crucial role as a regulator in various physiological and biochemical processes. Originally isolated from willow trees, SA is synthesized through the shikimate pathway via metabolic routes involving enzymes like PAL and BA2H
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Photosynthesis and Cycling of Matter in Living Systems
Photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into chemical energy, and the cycling of matter through carbon, nitrogen, and water cycles are crucial aspects of living systems. Chloroplasts and chlorophyll play key roles in photosynthesis, while the carbon cycle highlights the essentia
0 views • 20 slides
Classification and Characteristics of Phylum Protozoa
Phylum Protozoa comprises unicellular, microscopic, eukaryotic organisms found mostly in aquatic habitats. They exhibit diverse locomotory structures such as cilia, flagella, or pseudopodia. These protists may possess a cellulose cell wall and various membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria and
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Photosynthesis: A Comprehensive Overview
Photosynthesis is the fundamental process through which plants produce food in the form of glucose. This intricate process involves the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose using sunlight as the energy source. The key player in photosynthesis is chlorophyll, a green compound found in
0 views • 13 slides
Exploring Cellular Structures in Quizbowl Biology
Biology in quizbowl competitions often focuses on understanding cellular structures, from organs to organelles. Players encounter questions about various organelles like mitochondria, ribosomes, chloroplasts, and the Golgi body. Ribosomes, though not classified as organelles, play a critical role in
0 views • 27 slides
Comparison of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells in Cell Biology
Cells are the fundamental units of life, but viruses are an exception as they lack cells. Eukaryotic cells have a defined nucleus with a nuclear membrane housing chromosomes, while prokaryotic cells lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other organelles. Eukaryotic cells are larger, containing membrane-
0 views • 9 slides
Cellular Processes and Functions Explained
The cytoplasm is essential for cell function, housing organelles like chloroplasts and vacuoles unique to plants. Mitochondria facilitate cellular respiration, while amino acids form proteins. Enzymes are proteins, and carbohydrates consist of simple sugars. Basic pH numbers range from 8 to 14. Star
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Cell Structure: Key Organelles and Functions
Explore the intricate world of cell structure as we delve into the functions of essential organelles such as chloroplasts, mitochondria, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, vacuoles, lysosomes, and the nucleus. Uncover the significance of each organelle in maintaining the cell's processe
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Photosynthesis: The Process of Energy Conversion in Plants
Photosynthesis is a vital process where plants, algae, and cyanobacteria convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This energy conversion involves the absorption of light by chlorophyll molecules in chloroplasts, leading to the generation of ATP and the formation
0 views • 12 slides
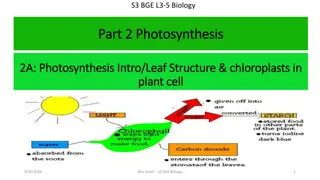
Understanding Leaf Structure and Photosynthesis in Biology
Green plants use photosynthesis to make their own food by converting light energy into starch and oxygen through chlorophyll in the chloroplasts of their cells. Learn about the structure of a leaf and how to test for starch in this informative presentation.
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding Photosynthesis: Process and Importance in Plants
Photosynthesis is a vital process in green plants where they use carbon dioxide and water to produce sugar and oxygen, facilitated by chloroplasts. Limiting factors such as light, water, and temperature can impact photosynthesis rate. Green plants are producers that make their own food through photo
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Photosynthesis: Role of NADP and Division into Light and Dark Stages
In photosynthesis, NADP plays a crucial role in carrying hydrogen into the dark stage for carbon dioxide reduction. The process is divided into light and dark stages where different components like chlorophyll, chloroplasts, and electron transfer mechanisms are involved. This division ensures effici
0 views • 50 slides
Understanding Photosynthesis and Photophosphorylation Processes
Photosynthesis is a vital process where autotrophic organisms trap solar energy to convert it into chemical energy in the form of food. Non-cyclic photophosphorylation involves the transfer of phosphate groups and ATP synthesis utilizing light energy. This process takes place at photosystem II in ch
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Photosynthesis: The Importance and Mechanism
Photosynthesis is a vital process in plants, utilizing sunlight to produce energy for life on Earth. It occurs in chloroplasts, primarily in leaves, where chlorophyll captures light for the process. The green pigment in plants is due to chloroplasts containing photosynthetic pigments. This process i
0 views • 41 slides
Regulation of Photosynthesis in Arabidopsis Chloroplasts
Balancing photosynthesis with chloroplast metabolism is crucial for plant growth. Thioredoxins play a key role in regulating photosynthesis reactions in Arabidopsis chloroplasts. This study investigates the interplay between ferredoxin-dependent and NADPH-dependent thioredoxin systems in response to
0 views • 5 slides
Understanding Cells: Structure, Function, and Evolution
Explore the world of cells, the basic units of life, from their structure and function to the history of cell theory. Learn about prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, the cytoskeleton, and key organelles. Dive into differences between animal and plant cells and the critical role of chloroplasts in ener
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding the Functions of Cell Organelles
Explore the vital functions of different cell organelles such as the cell membrane, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, cytoplasm, ribosomes, vacuole, cell wall, chloroplasts, and chlorophyll in a cell. Learn how each organelle plays a unique role in maintaining
0 views • 38 slides
Understanding Plant Cell Physiology and Functions
Plant cells are the fundamental units of life in the Plantae kingdom, comprising various organelles like the nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria. These cells perform essential functions such as photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and storage. Differentiated by their unique cell walls, chloropl
1 views • 24 slides
Understanding Mitochondria, Plastids, and Chloroplasts in Cells
Mitochondria, known as the powerhouse of the cell, generate ATP for energy production through cellular respiration. Plastids, such as leucoplasts, store various compounds like starch and proteins. Chloroplasts conduct photosynthesis in plants, utilizing chlorophyll and performing light-dependent rea
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Plant Cell Components: Nucleus, Cell Wall, Mitochondria, Cytoplasm, Chloroplasts
Plant cells consist of various components like the nucleus, cell wall, mitochondria, cytoplasm, and chloroplasts, each serving specific functions essential for the plant's growth and survival. The nucleus houses genetic information, the cell wall provides support, mitochondria produce energy, cytopl
0 views • 18 slides