Understanding Phagocytosis, Inflammation, and Granulomas in Tuberculosis
Phagocytosis is a crucial process where cells engulf and digest pathogens. Inflammation responses involve various immune cells like neutrophils, plasma cells, lymphocytes, and macrophages. Granulomas, typical in diseases like tuberculosis, are mass accumulations in chronic inflammation. Tuberculosis, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, primarily affects the lungs but can spread to other body parts. The disease progresses through various stages like early tubercles in lymph nodes to caseating tuberculosis and chronic fibrocasious tuberculosis in the lungs.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
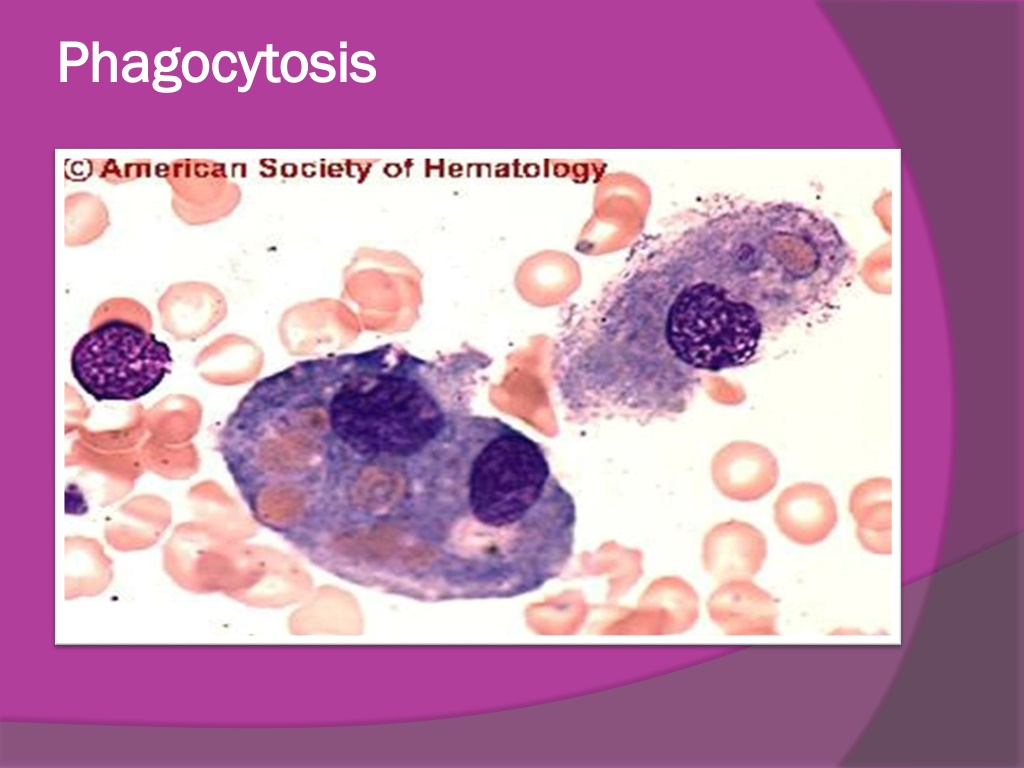
Phagocytosis Phagocytosis
PMNLs Plasma cells Macrophage inflammation: seen here are mainly neutrophils, but there are also plasma cells, lymphocytes, and macrophages lymphocyte
CONT. INFLAMMATION GRANULOMA
Granuloma: : -It s a type of chronic specific inflammation, characterized by accumulation of tumor like masses. -types: 1-infective, 2-non-infective.
Granuloma Granuloma: : The single tubercle composed of : 1-central necrotic tissue, 2-epithellioid cells, 3-lymphocytes and plasma cells, 4-langhans cell .
Tuberculosis -Tuberculosis , MTB or TB (short for tubercles bacillus) is infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis -It is usually attacks the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body. - It is spread through the air when people who have active MTB infection cough, sneeze, or spit
1- Early T.B in lymph node: -Pale pink rounded tubercles among blue lymphoid tissue. -the tubercle is formed of : epithelioid cells, langhans gient cells &lymphocytes.
2 2- - Caseating Caseating T. T.B in LN B in LN -Caseous is a form of biological tissue death. Necrosis (death) Tuberculosis - it is characterized by acellular pink areas of necrosis surrounded by a granulomatous inflammatory process
3 3- - Chronic Chronic fibrocasious fibrocasious T. T.B in lung B in lung: -large irregular areas of caseation appearing homogenous pink surrounded by tubercles reaction an fibrous tissue.
Bilharziasis Bilharziasis -It is a parasite infection by a trematode worm acquired from infested water. Also known as (schistosomiasis). - it is can produce in liver, bladder, and gastrointestinal problems
4- Bilharziasis in rectum: Bilharzia ova deposited mainly in the submucosa -ova appear rounded or oval and yllowish refractile shell,degenerated ova are pink , while clascified ova are blue. -ova are surrounded by macrophages ,plasma cells, esinophils,lymphocytes & foreign body giant cells.
5- Bilharziasis in Urinary Bladder: -Bilharzia ova deposited mainly in the submucosa with less degree in other layers . -The ova surrounded by bilharzial rxn
6- Bilharziasis in liver: Bilharzias ova deposited in the portal tract. The ova surrounded by bilharzial rxn formed capilleries & new bile ducts.