Exploring Change Management Models: Classic Curve, Kotter’s 8-Step, Pritchett’s & More
Unveil the intricacies of various Change Management Models including the Classic Change Curve, Kotter’s 8-Step Approach, Pritchett’s Model, ACMP Standard, and Leavitt’s Diamond. Gain valuable insights into implementing successful organizational change strategies.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
BY CHOOLS CONSULTING SERVICE www.chools.in
AGENDA Change Management Models 1. Classic Change Curve 16. Kotter s 8-Step Change Model 30. Pritchett s Change Management Model 2. ACMP Standard for Change Management 17. Leavitt s Diamond 31. Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBoK) 3. ADDIE Model 18. Lewin s Force Field Analysis 32. Prosci 3-Phase Change Management Process 4. Beckhard s Change Model 19. Lewin s 3-Stage Model 33. Prosci ADKAR Model 5. Bridges Transition Model 20. Management of Risk (M_o_R) 34. Prosci Project Change Triangle (PCT) 6. Burke-Litwin Change Model 21. Managing Successful Programmes (MSP) 35. Purpose, People and Process 7. Business Process Redesign (BPR) 22. Martec s Law of Disruption 36. Revolutionary Change Cycle 8. Change Curve 23. 7S Framework (McKinsey) 37. Rogers Tech Adoption Curve 9. Clayton s Change Curve 24. Onion Model of Resistance 38. John Shook s Change Management Model 10. Change Management Adoption Curve 25. Iceberg Model of Organizational Culture 39. Simon Sinek s Golden Circle 11. Drucker s Paradigm of Change Model 26. Organization Development Intervention Cycle 40. Six Sigma DMAIC Improvement Cycle 12. Change Management Iceberg Model 41. Transtheoretical Model 27. Osgood-Schramm Model of Communication 13. Johari Window 42. Szpekman s Communication Framework 28. Deming Cycle/PDCA Cycle 14. Katgar Model for Change 43. Theory of Change 29. PRINCE2 Project Management 15. Kirkpatrick Model www.chools.in
AGENDA Change Management Models 44. Training Needs Analysis Model 58. EFQM Model 73. Project Management Change Process 45. Xerox Benchmarking Model 59. Galpin s Model 74. Nudge Theory 46. Change Delta Framework 60. GE Change Acceleration Process 75. Stephen Covey s Model 47. Beckhard & Harris Change Management Process 61. Judson s 5-Phase Model 76. Virginia Satir Change Management Model 48. Bullock & Batten s Planned Change Model 62. LaMarsh Global Managed Change 77. Chip & Dan Heath s Switch Framework 49. Carnall s Change Management Model 63. Lipitt, Watson and Westley Model 78. K bler-Ross Model 50. CHAMPS2 Business Change 64. Nadler/Tushman Congruence Model 79. Stages of Change (MacDonald & Boyd Associates) 51. Change Leader s Roadmap Methodology 65. People-Centered Implementation 80. Personal Change Model 52. Change Management Body of Knowledge 66. PMI Change Life Cycle Framework 81. Otto Scharmer s Theory U 53. Conner Partners Change Execution Methodology (CEM) 67. Senge s Five Disciplines 82. Spiral Dynamics Change State Indicator 68. Viral Change Model 83. Prochaska & DiClemente Model 54. Cooperrider s Appreciative Inquiry 69. Teece s Dynamic Capabilities 84. 4 Stages of Learning 55. Cummings/Worley s Change Management Model 70. Weisbord s Six Box Model 56. Delta V 71. William Bridges Model 57. Edwin Cornelius Model 72. Change Communication Huddle www.chools.in
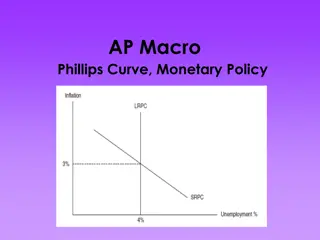
1. CLASSIC CHANGE CURVE Change Management Models Trus t Understand Accept Commit Behavior Engagemen t Shorter duration possible Tim e www.chools.in
2. ACMP STANDARD FOR CHANGE MANAGEMENT Change Management Models Implement change management planning ACMP focuses on a comprehensive definition of change management, as well as the standard elements involved in its execution. Complete change process Published in September 2014, the ACMP Standard Procedure for Change Management is a collection of established change management practices. Evaluate impact of change and organizational willingness to change Develop change management plans Formulate change management strategy www.chools.in
3. ADDIE-MODEL Change Management Models A systematic analysis of the current and target situation. The difference determines the performance gap. If a performance gap is identified, the design phase will define performance objectives. The information gathered during the analysis and design phases is then used to develop the performance solution. The performance solution is implemented by the company. Evaluation: Have the objectives been met using the performance solution? www.chools.in
4. BECKHARDS CHANGE MODEL Change Management Models familiar letting go of the old unknown, risky comfortable accepting the new lack of control manageable making many changes new roles distinct allocation of roles feelings of: loss, depression, gain, elation www.chools.in
5. BRIDGES TRANSITION MODEL Change Management Models Rejectio Enthusias m n Apprehensio Trus t Denial Commitment n Shoc Relie f Hop e k Resignatio n Ange r Fea r Confusio n Frustration Impatienc e Acceptanc e Feeling of Loss Creativit y High Stress Level Resistance Exploration Conflic t Aimless Energy www.chools.in
5. BRIDGES TRANSITION MODEL Change Management Models Grief Growth Status Quo Advocacy Backing off Denial Agreement Backing off Resistance Acceptance Backing off Backing off Pleading Tolerance Flame out Skepticism www.chools.in
5. BRIDGES TRANSITION MODEL Change Management Models Enthusias m Trus t Denia Excitemen t l Fea Relief / Anxiety r Shoc Hope / Skepticism k Confusio Impatienc e n Resignatio Acceptanc e nAnge Feeling of Loss rAvoidanc High Stress Level Aimless Emery e Resistanc Conflic t Creativity e www.chools.in
5. BRIDGES TRANSITION MODEL Change Management Models Understanding the reasons for success and failure "Changes aren t necessary" Assimilating new skills and behavior patterns Backing off/blocking Forming new behaviors and habits False capability Self-Perceived Capability "Changes are necessary" Understanding the limitations of one's own capabilities Testing new concepts/skills Practice/attempt to do things differently Surprise, and in extreme cases, panic and crippling fear Feedback on outcomes, successes, and failures Discrepancy between expectations and reality can adversely affect self- confidence "Changes are necessary" Letting go of old habits and attitudes Beginning of Transition Phase Tim e www.chools.in
6. BURKE-LITWIN CHANGE MODEL Change Management Models Individual Needs and Values Culture Systems External Environment Management practices Work Climate Leadership Motivation Performance Synergy Between Job/Skills Vision and Strategy Structures www.chools.in
7. BUSINESS PROCESS REDESIGN (BPR) Change Management Models 1. Define Scope and Objective 2. Redesign Process Structure 3. Establish Management 4. Implement & Integrate Signs of a need for change: Key elements: Key elements: Key elements: performance requirements management tools Establish management through conflicts performance measurement Apply change management in meetings critical success factors through unstructured communication efficiency learning process compensation in strategic dialogue www.chools.in
8. CHANGE CURVE Change Management Models Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Stage 1 Inform Stage 4 Encourage Self-Confidence, Work Ethic & Effectiveness Current Situation Disruption Exploration Rebuilding Process Impact Stage 2 Support Stage 3 Guide Ti me Ti me Looking to the Past Looking to the Future www.chools.in
8. CHANGE CURVE Change Management Models Accelerating Change Impact Managed Change Processes Unmanaged Change Reducing Negative Consequences Ti me www.chools.in
8. CHANGE CURVE Change Management Models Impact Tim e Stage Status Status Quo Disrupt Explore Rebuild Reaction Shock, Denial Anger, Fear Acceptance Commitment www.chools.in
9. CLAYTONS CHANGE CURVE Change Management Models Reaction Acceptance Resentment Sadness Frustration Emotional Focus Anger Rational Focus Resistance Discovery Negative Stage Positive Stage www.chools.in
10. CHANGE MANAGEMENT ADOPTION CURVE Change Management Models Relative % of Customers Time Customers want new technology and performance Customers want solutions and convenience www.chools.in
11. DRUCKERS PARADIGM OF CHANGE MODEL Change Management Models 3. Transformation 2. Transitional 1. Traditional What is the company like now? Traditional What will the Company be like? Transitional What should the company be like? Transformation al www.chools.in
12. CHANGE MANAGEMENT ICEBERG MODEL Change Management Models Qualit y Logical Rational Aware Know-How Cost s Tim e Issue Essential External Facts Management Positiv e Suppor ters Emotional Instinctive Potenti al Suppor ters Hidden Oppon ents Immaterial Internal Social Skills Oppon ents Management of perceptions and convictions Management of power and politics Negativ e www.chools.in
13. JOHARI WINDOW Change Management Models Known by Feedback Others Feedback Known by Others Disclosure Disclosure Self- Self- Share Unknow n by Others Self- Discovery Self- Unknow n by Others Discovery I don t know I don t know I know I know Ask www.chools.in
14. KATGAR MODEL FOR CHANGE Change Management Models state of central awareness understanding of external environment and internal repercussions ready for action willingness to share information answering questions before they are asked input not output Manage- ment focus on the individual employees must change before the organization vision direction passion reinforcing what s already working flexibility & details recognizing success having fun at all levels customer understanding internal & external reflection www.chools.in
15. KIRKPATRICK MODEL Change Management Models The extent to which the targeted goal has been achieved thanks to training events and additional consolidating efforts. The extent to which participants apply what they have learned after returning to their jobs. The extent to which participants gain knowledge, skills, and attitudes based on their participation. The extent to which participants react positively to the training event. www.chools.in
16. KOTTERS 8-STEP CHANGE MODEL Change Management Models Sustain Change Stimulate Change Create Quick Wins Empower Employees to Participate in Change Communicate Vision for Change Develop Vision Form Leadership Coalition Establish Urgency www.chools.in
16. KOTTERS 8-STEP CHANGE MODEL Change Management Models Sustain Change Stimulate Change Empower Employees to Participate in Change Create Quick Wins Communicate Vision for Change Develop Vision Form Leadership Coalition Establish Urgency www.chools.in
16. KOTTERS 8-STEP CHANGE MODEL Change Management Models Sustain Change Establish Urgency Form Leadership Coalition Stimulate Change The text demonstrates how your own text will look when you replace the placeholder with your own text. Create Quick Wins Develop Vision Empower Employees to Make Changes Communicate Vision for Change www.chools.in
16. KOTTERS 8-STEP CHANGE MODEL Change Management Models Create Change Culture The text demonstrates how your own text will look when you re- place the placeholder with your own text. Stimulate Change Create Quick Wins Remove Obstacles Develop and Communicate Vision Form Leadership Coalition Establish Urgency www.chools.in
16. KOTTERS 8-STEP CHANGE MODEL Change Management Models Communicate the rationale, as well as a business scenario, for change 1. Establish Urgency Highlight the connection between the new approach and the company s success. Integrate a new corporate style into management development and 8. 2. Build a team with power and influence within the company to lead the change process Standardize Corporate Change Form Leadership Coalition succession planning. Leverage credibility to change policies and processes that are not in line with the vision. Recruit and promote employees who can implement the 7. 3. Create a persuasive vision of the future to steer the direction of change Consolidate progress Develop Vision vision. 6. 4. Plan tangible and quick wins. Integrate employees into the process, recognize and reward them. Use all opportunities to communicate the vision. Exemplify new behaviors. Plan and Create Quick Wins Communicate Vision 5. Empower Employees to Participate in Change Eliminate any obstacles. Change systems or structures that jeopardize the vision. www.chools.in
17. LEAVITTS DIAMOND Change Management Models Leavitt s Diamond is based on the principle that every company has four major components that are interdependent. Any change or redesign of one component affects the other three components. www.chools.in
18. LEWINS FORCE FIELD ANALYSIS Change Management Models Operational Efficiency (%) Output 120 110 100 90 80 Time Pre-Change Equilibrium Change Process Post-Change Equilibrium www.chools.in
19. LEWINS 3-STAGE MODEL Change Management Models Determine what needs to be changed Communicate regularly Integrate changes in corporate culture Dispel rumors Ensure there is support Develop ways to maintain change Facilitate action Communicate the need for change Provide training and support Involve employees in the process Celebrate achievements Address doubts and concerns www.chools.in
20. MANAGEMENT OF RISK (M_O_R) Change Management Models M_o_R Principles Assess & Embed M_o_R is used to identify, analyze, and manage risks. Risk Management M_o_R Method Process Guide www.chools.in
21. MANAGING SUCCESSFUL PROGRAMMES (MSP) Change Management Models The MSP method for program management enables companies to coordinate, direct, manage, and implement a portfolio of projects. Sponsoring Group Owner Sponsor Program Manager Business Change Manager Program Office Deliver Output Incorporate Changes Project Team Service Team www.chools.in
22. MARTECS LAW OF DISRUPTION Change Management Models Change Technologies change exponentially, while companies absorb change logarithmically. With this limited absorption capability in mind, management must make a strategic decision as to which technological changes should, and can, be adopted. Technology grows exponentially Companies change at a logarithmic rate Time www.chools.in
23. 7S FRAMEWORK (MCKINSEY) Change Management Models Placeholder. Placeholder. This text can be replaced with your own text. This text can be replaced with your own text. Placeholder. Placeholder. This text can be replaced with your own text. This text can be replaced with your own text. Placeholder. Placeholder. This text can be replaced with your own text. This text can be replaced with your own text. Placeholder. Placeholder. This text can be replaced with your own text. This text can be replaced with your own text. www.chools.in
24. ONION MODEL OF RESISTANCE Change Management Models I don t understand why we have to change. I don t understand why this change should happen. I don t like this change. I don t like change I don t like you. www.chools.in
25. ICEBERG MODEL OF ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE Change Management Models Visible Organizational Culture Visio n The way we demonstrate how we handle things Strateg y Goal s Common Values Structure s Belief Guideline s Procedure s Common Assumptions sViewpoint s Value s Traditio n Norm s Unwritten Rules Storie Invisible Organizational Culture s Feeling s How we actually handle things www.chools.in
25. ICEBERG MODEL OF ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE Change Management Models Laws/Traditions Lifestyles Practices Doing Institutions Rituals Techniques Language Rolls Norms Thinking Convictions Ideologies Philosophy Preferences Attitudes Desires Values Feeling Expectations Presumptions Myths www.chools.in
26. ORGANIZATION DEVELOPMENT INTERVENTION CYCLE Change Management Models Wish to Change/ Improve Investigate Problem Change Becomes Necessary Evaluate Performance and Learning Explore Possible Solutions and Benchmarks Implement Measures Design Measures and Results Expectation www.chools.in
27. OSGOOD-SCHRAMM MODEL OF COMMUNICATION Change Management Models Osgood-Schramm Model of Communication (1954) Message Receiver Message Encoder Decoder Message Interpreter Interpreter Decoder Decoder Decoder Encoder Medium DISRUPT ION Interpreter Interpreter Person who understands, analyzes, and recognizes Encoder Encoder Message Message Sender Message Encoding, interpretation and decoding occur simultaneously. Each participant acts simultaneously as sender, receiver and interpreter. If the sender and receiver each have different ideas of the meaning of a message, a disruption in the communication process known as "semantic noise" occurs. www.chools.in
28. DEMING CYCLE/PDCA CYCLE Change Management Models ACT PLAN Take measures to standardize or improve the process Plan for changes Predict results CHECK DO Analyze results Execute plan, take small steps under controlled conditions www.chools.in
29. PRINCE2 PROJECT MANAGEMENT Change Management Models Ongoing Business Justification Adapt to Project Environment Define Roles &Respons- ibilities Focus on Product Learn from Experience Manage by Exception Manage in Stages www.chools.in
29. PRINCE2 PROJECT MANAGEMENT Change Management Models PRINCE2 is a process-driven project management method. Project Leadership Manage Phase Transitions Prepare a Project Launch a Project Manage a Stage Complete a Project Manage Product Delivery Plan www.chools.in
30. PRITCHETTS CHANGE MANAGEMENT MODEL Change Management Models Necessity Readiness Implementation Progress Vision and goals are presented. The project team is formed and the first commun- ication plans are developed. A road map for implementing changes is established. The project plan is implemented and monitored. Experiences during the project are assessed and achievements are disclosed.. www.chools.in
31. PROJECT MANAGEMENT BODY OF KNOWLEDGE (PMBOK) Change Management Models 1 2 3 Integration Scope Time 4 5 6 Cost Quality Personnel 7 8 9 Communication Risk Procurement www.chools.in
31. PROJECT MANAGEMENT BODY OF KNOWLEDGE (PMBOK) Change Management Models Plan Begin Project Initiate Processes Close Processes End Project Execute www.chools.in
32. PROSCI 3-PHASE CHANGE MANAGEMENT PROCESS Change Management Models PHASE 1 Prepare for Change Executive Level Change Management Strategy Middle Management PHASE 2 Manage Change Change Management Plans Front-Line Staff Change Management Specialists PHASE 3 Consolidate Change Project Resources Feedback & Upkeep A process that promotes individual competencies to facilitate the acceptance and implementation of change. www.chools.in
32. PROSCI 3-PHASE CHANGE MANAGEMENT PROCESS Change Management Models Prepare for Change Manage Change Consolidate Changes Define the change management strategy Establish change management plans Collect and analyze feedback Identify gaps and handle opposition Prepare the change management team Implement plans Implement corrective measures and acknowledge successes Develop a leadership model www.chools.in
33. PROSCI ADKAR MODEL Change Management Models www.chools.in
33. PROSCI ADKAR MODEL Change Management Models The ADKAR model provides a valuable framework for change management teams to plan and execute their work. The strategy s key components include: identifying employees' resistance to change supporting employees during the change process creating an effective plan of action for personal and professional development during change AWARENES S DESIRE KNOWLEDGE ABILITY REINFORCEMENT developing a change management plan for employees After Implement- ation Concept & Design Implement- ation Business Need www.chools.in