Understanding Cellular Respiration Through Investigation
Explore the key concepts related to cellular respiration, including the substances needed, products produced, sources of substances, the respiration equation, effects of exercise, and comparison with photosynthesis. Engage in practical activities like investigating the factors affecting respiration using germinating peas. Understand the energy release process and how it impacts various bodily systems during different activities.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
At the end of this unit you should: 1. Be able to identify the substances needed for respiration to take place. 2. Be able to identify the products of respiration. 3. Be able to explain where the substances needed for respiration come from. 4. Be able to recall and understand the equation for respiration. 5. Be able to explain what happens the products produced in respiration. 6. Be able to recognise the similarities and differences between photosynthesis and respiration. 7. Be able to investigate the factors that affect respiration through exercise.
absorbed energy aerobic glucose anaerobic lactic acid biological mitochondria carbon dioxide oxygen chemical products contract respiration
RESPIRATION Respiration: The controlled release of energy from food.
(a) This body cell circle represents what goes in and out of a body cell. Copy and complete the circle using all the words in the list: Oxygen; Food; Carbon Dioxide; Water Vapour; Energy Carbon Dioxide Oxygen Water Vapour Food Energy
(b) Make a list of the ways you think we use the energy released in respiration. Any activity or exercise, e.g. sleeping, walking, eating, talking, running, playing a sport.
(c) You have just finished playing a game of basketball. You used more energy playing the game than you did when you were watching television, as your body systems had to work harder than normal. (i) Describe what happened to your circulatory system and your breathing system during and after the game. Heart rate and breathing rate increased.
(c) You have just finished playing a game of basketball. You used more energy playing the game than you did when you were watching television, as your body systems had to work harder than normal. (ii) Explain why the events in part (i) happened. The body requires more oxygen to be delivered to the cells so that respiration can occur to release energy.
Investigation 05.02.01: Showing that respiration takes place Equipment: A handful of germinating peas, two flasks, two thermometers, some cotton wool, a beaker, a tripod, some wire gauze, some water, a pair of tongs, a sieve or filter paper, two labels. Instructions: 1.Label one flask 'treated' and the other 'untreated'. 2.Split the peas into two batches. Put half into the beaker, place on gauze on tripod and boil for three minutes. (This will kill the peas) 3.Remove the beaker from the tripod using the tongs. 4.Using the sieve or filter paper, remove the peas from the water after they have cooled down. 5.Place un-boiled/treated peas into one flask and the boiled/treated peas into the other.
Investigation 05.02.01: Showing that respiration takes place Instructions: 6. Place a thermometer into each flask and cotton wool at the top around the thermometer to stop heat from escaping. 7. Record the temperature after one minute of the peas being in both flasks. 8. Monitor the temperature within the flasks over a day or until next class. 9. Record results.
1. What is the control in your investigation? Boiled peas.
2. Why do you think a control is necessary? To prove that respiration does happen in living things and the control can then be used to compare the results between a living and a non-living thing.
3. What do you predict will be the result of the investigation? The untreated/un-boiled peas will respire and the temperature within the flask will increase. The flask with the treated/boiled peas will have no temperature change from the start of the investigation.
LIGHTBULB QUESTION Water vapour can be seen when one breathes on a cold surface such as a window or a mirror.
Investigation 05.02.02: Showing that respiration demands affect heart and breathing rates Equipment: You and a partner, results table, stopwatch. Instructions: 1. Students to measure heart rate and breathing rate. 2. For heart rate instructions, see Investigation 03.03.01: How exercise affects your body (p.61). 3. For breathing rate instructions see Investigation 03.04.02: How do different levels of exercise affect breathing rate? (p70).
Copy and Complete In this unit I learned that respiration is the release of energy from foods. It happens in our body cells. The food we take into our body gets broken down and we take in oxygen from the air. The food, which is called glucose, and the oxygen both travel to the cells in the blood. In the cells a chemical reaction takes place and energy is released as it happens. After the reaction the cell releases carbon dioxide and water vapour. The carbon dioxide and water vapour are released from the body when we breathe out.
Copy and Complete Plants use the carbondioxide that we release when they make food during photosynthesis. There are two types of respiration: aerobic is the release of energy using oxygen; anaerobic is the release of a small amount of energy without using oxygen. In order for the body to get more oxygen to the muscles to make energy, it must breathe quicker to take in more oxygen and the heart must pump blood faster as it transports this oxygen to the muscles.
1. Describe what happens during respiration. Food and oxygen are taken into the body cell. A chemical reaction occurs and carbon dioxide, water vapour and energy are released.
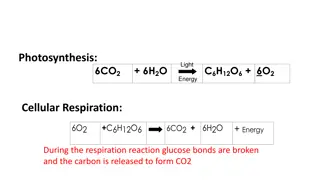
2. Write out the word equation for respiration. Food + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water vapour + energy
3. Can you explain how digested food is used by the body? It is absorbed into the blood at the small intestines and travels to the body cells. The broken-down food molecules travel in the blood to the body cells where they are taken in and used in the chemical reaction, respiration.
4. How do you think the glucose and oxygen needed for aerobic respiration get to all the body s cells? Both glucose and oxygen travel in the blood to get to the body's cells for aerobic respiration.
5. Describe how our breathing rate changes when we exercise. The breathing rate increases during exercise which increases the amount of oxygen taken in and the amount of carbon dioxide that is removed.
6. State what the two types of respiration are. Explain what is involved in each. Aerobic respiration involves the release of energy from cells using oxygen. Anaerobic respiration involves releasing energy from the cells without using oxygen.
7. The equations for photosynthesis and respiration are shown below. Spend a few minutes looking at both. Make a list of any similarities and differences between them. Similarities: A gas is taken in for both reactions to occur, both produce a gas during the reaction, energy is involved in both reactions. Differences: The gases involved are different, In photosynthesis energy is trapped and along with the gas used to produce food, in respiration energy is released by the reaction between the food and the gas.