Understanding States of Matter and Changes in State
Explore the characteristics of solids, liquids, and gases, along with their particle arrangements and movements. Learn how heat energy influences changes in states of matter such as melting, evaporation, boiling, and sublimation. Discover the importance of adding or subtracting heat energy to transition between different states of matter.
Uploaded on Oct 02, 2024 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
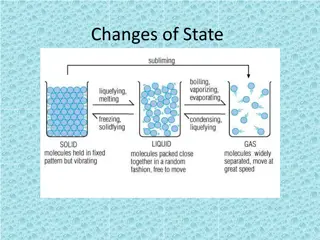
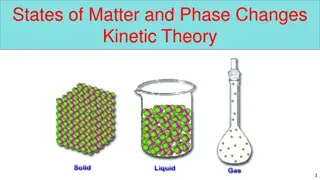
STATES OF MATTER AND CHANGES OF STATE
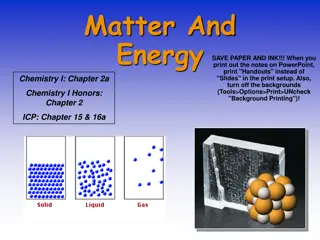
1. PARTICLES ARE TIGHTLY ARRANGED. NO SPACE BETWEEN ATOMS SOLID 2. DEFINITE SHAPE 3. DEFINITE VOLUME 4. PARTICLES VIBRATE NEXT TO EACH OTHER
1. PARTICLES HAVE SOME SPACE BETWEEN. 2. DEFINITE VOLUME LIQUID 3. NO DEFINITE SHAPE 4. PARTICLE MOVEMENT IS A SLIDING ACTION PAST EACH OTHER
1.PARTICLE SPACING IS VERY FAR APART 2. NO DEFINITE SHAPE 3. NO DEFINITE VOLUME 4. PARTICLE MOVEMENT IS VERY FAST AND MAY OR MAY NOT COME IN CONTACT WITH EACH OTHER GAS
IN ORDER FOR A SOLID, LIQUID OR GAS TO CHANGE ITS STATE OF MATTER HEAT ENERGY IS EITHER ADDED OR SUBTRACTED
HOW DOES A SOLID, LIQUID OR GAS CHANGE ITS STATE HEAT ENERGY HAS TO BE ADDED OR SUBTRACTED
HEAT ENERGY ADDED TO A SOLID-MELTING OCCURS KITCHEN MELTING POINTS 97 F/16 C MELTED GOLD
HEAT ENERGY ADDED TO A LIQUID EVAPORATION OR BOILING WATER EVAPORATING MOLECULE MOTION IN EVAPORATION AND BOILING BOILING WATER
SUBLIMATION A SOLID CHANGES INTO A GAS WITHOUT BECOMING A LIQUID FIRST DRY ICE SNOW SUBLIMATION DRY ICE
WHEN HEAT ENERGY IS REMOVED A GAS BECOMES A LIQUID CONDENSATION WATER VAPOR CONDENSING ON SODA LITER WATER VAPOR CONDENSING ON GLASS WATER VAPOR CONDENSING ON PLANTS
REMOVAL OF HEAT ENERGY FROM A LIQUID FREEZING THERE IS A SPECIFIC TEMP AT WHICH LIQUIDS FREEZE
THE LOWEST TEMPERATURE THAT IT IS POSSIBLE TO REACH (O K, -273.15 C, -459.67 F) IS CALLED ABSOLUTE ZERO
DEPOSITION WHEN HEAT ENERGY IS REMOVED AND WATER VAPOR CHANGES DIRECTLY INTO A SOLID FROST SNOW FROST
WATER HAS A FREEZING POINT OF 0C AND A MELTING POINT OF 0 C HOW IS THIS POSSIBLE???