Understanding Production Management in the Context of Manufacturing
Production management plays a crucial role in converting inputs into outputs efficiently by utilizing various processes. It involves controlling manufacturing costs, ensuring product quality, maintaining production schedules, and more. The ultimate objectives include managing costs and ensuring product quality, while intermediate objectives focus on machinery, manpower planning, and other related aspects. The significance of production management lies in designing products, executing plans, and benefiting various stakeholders such as consumers, investors, employees, suppliers, and the community.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
1. 2. 3. Name of the staff : Dr.A.Krithika Designation : Assistant professor Name of the college: Aiman College of Arts & Science for women Semester : IV Subject Title : Production Management Paper code : 16ACBB4 Mobile number : 8883851529 4. 5. 6. 7.
MEANING AND DEFINITION OF PRODUCTION MANAGEMENT Production management is a branch of management which is related to the production function. It may be referred to as the process concerned with the conversion of inputs into output with the help of certain processes. While management is the process of exploitation of these factors of production in order to achieve the desired results.
Production management is concerned with those processes which convert the inputs into outputs. The inputs are various resources like raw materials, men, machines, methods etc., and the outputs are goods and services. H.A.Harding
Ultimate objectives Controlling manufacturing costs Proper quality of products Keeping manufacturing schedule II. Intermediate objectives Maintaining proper machinery and equipment Proper manpower planning Adequate manufacturing services Materials Methods 1. a. b. c. a. b. c. d. e.
Designing the products and packages Production administration Execution of plans, policies and decisions Dependent services Importance of Production Management Benefits of operation management to organization Consumer investors employee Suppliers Community Nation
Functions of Production Management Production planning Quality control Purchasing Manufacturing Inventory control Work measurement Production control Industrial engineering Plant engineering Method analysis Plant layout and materials handling
It is a set of interrelated component or subsystem which receives the inputs from the environment, transform it into desirable outputs. It includes all the functions required to design, produce, distribute and service to manufacture a product. Production system is a regularly interacting or interdependent group of items forming a unified whole. Webster
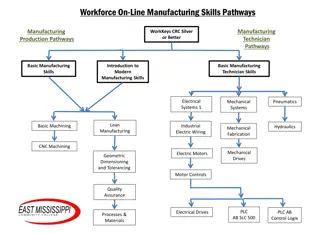
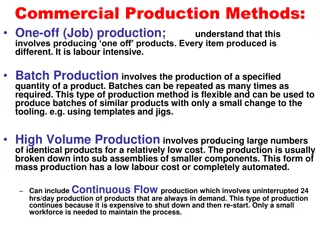
I. Flow or Continuous production A. Mass production B. Process production- I. Synthetic II. Analytic C. Assembly lines II. Intermittent Production A. Project B. Job shop production C. Batch production
Plant Location means establishment of a particular industrial unit at a particular place. It is the function of determining where the industrial plant shall be located for maximum operating economy and effectiveness. The function of determining the plant should be located for maximum operating economy and effectiveness. Prof. R.C.Davis
Adequate supply of raw materials Availability of skilled and qualified workforce Competitive advantage Reduced transportation expenditure Improved efficiency
I. Dominant Factors Availability of raw materials Favorable Labor climate Integration with other parts of the organization Proximity to markets Quality of Life Proximity to supplier and resources Safety requirements Availability of services II. Secondary Factors Room for expansion Construction costs Community attitude etc.,
A layout refers to the arrangement of machinery, equipment and other industrial facilities. According to Shubin, Plant arrangement and location of production machinery, work centers and auxiliary facilities and activities for the purpose of achieving efficiency in manufacturing products or supplying consumer services . Layout is the
Integrate the production place Reduce material handling Effective utilization of available space Worker convenience and job satisfaction Flexibility Quick disposal of work Avoids industrial accidents
Product Layout Fixed Layout Group technology Layout Process Layout Flexible Manufacturing system Combined Based Layout
Economies in Handling Effective use of available area Minimization of production delays Improved quality controls Minimum equipment investment Avoidance of bottlenecks Better production control Better supervision Improved utilization of labor Avoidance of unnecessary and costly changes