Understanding Hitler's Aims and Nazi Economic Policies
Explore the relationship between Hitler, the SA, and Nazi economic policies. Learn about Hitler's objectives, the role of the SA, and how the Nazis addressed unemployment in Germany. Delve into the impact on society and analyze whether Hitler met his aims effectively.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Flip Learning - Source Work?
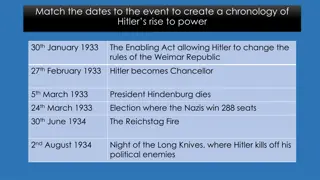
True or False Recap Look at the statements you have been given Sort them into true and false columns based on the information you gained last lesson Think about who the SA were and Hitler s objectives
True False The SA had protected Hitler from harm and beaten up his opponents Hitler didn t mind the SA/Rohm having power- they gave him protection Hitler did not need to please the army. The SA was his own private army The leader of the SA was named Ernst Rohm Hitler was worried that Rohm was becoming too powerful SA members did not want more pay now Hitler was in power they were happy with what they had The SA already had more members than the German Army Hitler was a man who wanted power equally shared. He did not just want it in his hands Hitler needed the army more than the SA Hitler needed the army to get back the land Germany had lost in the Treaty of Versailles
Great learning: Explain what sections of society this affected Even better: Analyse whether Hitler met his aims Good learning: Describe how the Nazis reduced employment
1. Economy The state of a country in terms of the production/consumption of goods and services/supply of money. 2. Nazi Economic Policies Actions that the Nazi government took in an attempt to improve the economy
Over six million Germans were out of work when Hitler came to power in 1933. What did the Nazis do about this? Option B OPTION A OPTION B OPTION C The Nazis set up a number of schemes, programmes and organisations to get Germans back to work. Absolutely nothing. The Nazis had gained power now so it did not matter if people were unemployed They promised to use radical methods to solve the countries 2 main problems. Desperate unemployment and a crisis in German farming The Nazis set up a number of schemes, programmes and organisations to get Germans back to work Set up schemes to help the unemployed but only focused on big business 20 10 30
https://www.bbc.com/bitesize/guides/zw6s7p 3/video Make notes to the questions on the handout
Hitler wanted Hitler wanted 1. Drag Germany out of the world recession 2. Make Germany an autarky self sufficient (the Nazis to control the economy and direct all manufacturing, agricultural and industrial production 3. Get rid of Jewish industrialists and give their businesses to pure German men 4 Transform the economy to focus on rearmament and war
The Nazis set up a number of schemes, programmes and organisations to get Germans back to work
Public Work Schemes - A new network of autobahns (motorways) to link Germany s major towns and cities was built - This gave work to nearly 100,000 people New schools and hospitals were built, creating even more jobs - - Railways were extended or built from scratch The National Labour Service (RAD) - - All men aged between 18 and 25 had to spend six months in the RAD - They planted forests, mended hedges and dug drainage ditches on farms - They wore uniforms and lived in camps but were given free meals and a small wage Invisible unemployment The Nazis used a variety of other methods to reduce unemployment figures Women who gave up work to have a family did not count in the official figures - Part-time workers were counted as full-time - The Nazis created jobs by sacking people, such as Jews, and giving their jobs to non-Jews. These out of work Jews were not counted in jobless figures -
Rearmament - The Nazis ordered the rearmament of Germany to rebuild its armed forces - New tanks, battleships, fighter planes and guns were built, creating thousands of jobs - Huge government arms contracts made factory owners and industrial bosses a fortune - Conscription was introduced in 1935. All males aged between 18 and 25 had to join the armed forces for at least two years. Within fives years, the army grew from 100,000 to 1,400,00 creating even more jobs
The economy under Hjalmar Schacht Respected banker- directed German economic policy Believed in steady growth and a stable currency He realised that imports of raw materials, such as iron, steel, rubber and wood, were needed to build more weapons He signed deals with countries in South America and south-east Europe to supply raw materials in return for German goods For a short time, things went well weapons production increased and unemployment fell But Germany was still dependent on foreign raw materials and the changes were too slow for the impatient Hitler Schact was sacked and replaced by Hermann Goering
The economy under Goering In 1936 Goering introduced a Four Year Plan to increase military production High targets were set (and met) in industries like steel and the production of explosives However, targets were not met in other key industries like oil production Germany still needed foreign raw materials so Goering tried to make Germany self-sufficient Why would rearmament boost national pride?
Goerings 4 Year Plan Goering s 4 Year Plan Speed up rearmament and make Germany ready for war German Military spending 1933 1939 1.9 million marks 32.3 million marks Make Germany self sufficient in raw materials autarchy by developing home grown substitutes*.
What were the results of this? What were the results of this? The size of the German army grew massively Hitler became more confident and started to openly break the Treaty of Versailles.
Was the 4 year Plan a success? Was the 4 year Plan a success? Unemployment dropped quickly 4.8 million in 1933 to 0.5 million in 1938 Wages rose slightly but were still lower in 1938 than they had been in 1928 Working hours went up to 49 hours per week in 1939 52 hours in 1943 to over 60 hours per week by 1945 There were fewer consumer goods - personal and household goods Food also cost more than it used to. Germany was trying to be self- sufficient and not rely on foreign imports. So with less food in the shops shopkeepers charged more because of high demand
The Nazis hoped to stop being reliant on foreign goods by making Germany self sufficient. They would find alternatives to the things the country needed, or develop artificial substitutes Self-sufficiency German scientists found ways to make . Image result for cartoon scientist Petrol from coal Makeup from flour
6 5 4 Unemployment (Millions) 3 2 1 0 1937 1933 1932 1934 1936 1935 1938
Flip Learning Make a spider diagram/mind-map/notes (whichever format you prefer) summarising the key points from this lesson Include: - What Hitler s aims were - What schemes/organisations/policies the Nazi s introduced to try and get Germans back to work - Key concepts such as the Four-Year Plan (what it means to be self sufficient) - Anything else that is useful ready for Fridays session on benefits & drawbacks!