The Rise of Hitler in Germany: Events and Impact
Explore the rise of Hitler in Germany through posters, historical events, and critical questions. Understand how Hitler and the Nazi Party evolved, the significance of the Munich Putsch, reasons for Hitler's chancellorship, and the influence of the Depression and threat of Communism.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
WARNING! Remember these answers are not full answers but are just suggestions of points that you could include!
Why was this poster published in Germany in 1932? What is the main message ? The artist of the cartoon wants me to think Why was the source published? I think the cartoon was published because What was happening at the time to explain why the source was published? I know at this time A poster published in Germany in 1932. It says, Our last hope: Hitler .
The message of the source is to tell people that Hitler will help them and that they should look to him if they are to improve their lives. The German people were going through a depression. Many had lost their jobs, were homeless and starving. The government had done little to help them and Hitler was their last hope. The purpose of the poster was to persuade people to vote for, and support, Hitler. If they voted for Hitler employment would increase and the economic problems of the Weimar would be solved. Employment would be increased. I know at this time, there were 2 elections in 1932 and supporters of the Nazis would be using propaganda in order to gain them votes.
4 mark questions Describe Hitler s role in the Nazi Party before 1923. Describe the development of the Nazi Party from 1924 to 1928. In what ways did Hitler and the Nazis change tactics following the Munich Putsch? Describe the Munich Putsch of 1923.
6 mark questions Explain why Hitler attempted the Munich Putsch. Explain why few people voted for the Nazis before 1930. Explain why the Munich Putsch was not a complete disaster for the Nazis.
10 mark questions The Munich Putsch of 1923 was a disaster for Hitler and the Nazi Party. How far do you agree with this statement? Explain your answer. The effects of the Depression were the main reason why Hitler became Chancellor of Germany by 1933. How far do you agree with this statement? Explain your answer. How far was the threat of Communism the main reason for Hitler becoming Chancellor in 1933? Explain your answer.
Describe Hitlers role in the Nazi Party before 1923. In 1920 Hitler was put in charge of propaganda. He changed the name of the Party to National Socialist German Workers Party (Nazis). In 1921 he challenged Drexler and took over the Party. His aim was to overthrow the Weimar Republic. He chose the swastika and colours. He drew up a 25-point programme showing the aims of the party. In 1921 he set about converting the Party into a mass movement and by 1922 had 3000 members. He established the SA with many Freikorps
In what ways did Hitler and the Nazis change tactics following the Munich Putsch? He realised whilst in prison that the Nazis would not be able to change power by force. They would have to work within the democratic system but once in power they could destroy that system. He began to rebuild the Nazi Party to make it acceptable to the electorate by making the party less extreme. He persuaded members of the party to adopt the original 25-point programme.
Describe the development of the Nazi Party from 1924 to 1928. It was difficult at first as the leader, Hitler, was in prison. Little progress was made initially as the Nazi Party was banned until 1925. Hitler decided to win power by legal means, but the success of Stresemann s policies meant that there was little support for extremists. In the 1928 election the Nazis won just 12 seats.
Describe the Munich Putsch of 1923 Hitler believed the German economy was on the verge of collapse and he tried to seize power. It was an attempt to overthrow the Weimar Republic. He and his supporters broke up a meeting in a Munich beer hall. He forced the Bavarian state government leaders to take part in a rebellion against the government. He allowed the Bavarians to leave and they quickly changed their minds. On the 9 November Hitler and 3000 Nazis marched on Munich and were fired on by the police. Sixteen Nazis were killed. Hitler was arrested and sentenced to five years for conspiracy.
Explain why Hitler attempted the Munich Putsch. Hitler wanted to destroy the Weimar. He believed it was an opportune time to topple the Weimar government. The government was pre-occupied with the economic crisis and hyper-inflation Hitler wanted to secure power and through his close relationship with Ludendorff believed that Ludendorff would be able to persuade the German army to desert the government and side with the Nazis. The Bavarian government was right-wing. Its leaders had been plotting against the government. Hitler felt sure they would support a putsch. There was discontent in Germany due to the effects of hyperinflation. Many nationalists still hated the Treaty and were furious when Stresemann called off the passive resistance in the Ruhr and resumed paying reparations. With this in mind Hitler thought it was the right time to seize power.
Explain why few people voted for the Nazis before 1930. Stresemann s policies were successful with Germany improving economically. There was very little support for extremist parties. The party was banned until 1925. There was more social freedom under the moderate parties. People were put off by the Munich Putsch. There was political stability in Germany in the 1920s despite the constitutions use of proportional representation. Politically the public were voting for the moderate parties such as the SPD who constantly attracted between 20% to 30% of the vote thus helping to maintain the government in office.
Explain why the Munich Putsch wasnt a complete disaster for the Nazis. It showed they would not gain power by violence. It highlighted that the Nazis needed to revisit their main beliefs. It gained Hitler enormous publicity. Prison gave Hitler time to reflect that progress for the Nazis would only come through the ballot box.
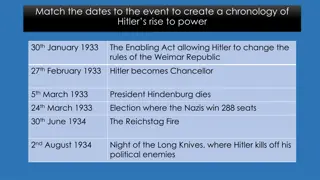
The effects of the Depression were the main reason why Hitler became Chancellor of Germany by 1933. How far do you agree with this statement? Explain your answer. As a result of the impact on American business of the Wall Street Crash American banks called in the loans they had made to Germany. Without these loans German industry could not operate. Factories closed and millions lost their jobs. Hitler promised to restore the German economy and get the men back to work. This obviously appealed to the millions out of work and in 1932 Hitler was the leader of the Party holding the largest number of seats in the Reichstag. After the July 1932 Reichstag elections, the Nazis were the largest single party. Hitler demanded the post of Chancellor but was refused it by Hindenburg who did not trust him. Papen lost most of his support in the Reichstag and in the November 1932 election there were signs that the Nazis were losing support and Hitler s claim was rejected in favour of Schleicher. He resigned within a month. To everyone s surprise Hitler was offered the post on 30 Jan 1933 as Papen and Hindenburg thought they could control Hitler.
The Munich Putsch of 1923 was a disaster for Hitler and the Nazi Party. How far do you agree with this statement? Explain your answer. The Munich Putsch was a disaster as it failed and Hitler and others received a prison sentence. This meant that at that time he was unable to fulfil his ambition to take control of Germany. Hitler had miscalculated the mood of the country and people did not rise up and support him. A ban was placed on the Nazi Party preventing it having a public voice (lifted in 1925). It was not a disaster as it gave Hitler and the Nazis the opportunity to re-evaluate policy and to implement it using peaceful means and gaining power through the ballot box. At his trial Hitler took the opportunity to make stirring speeches that got a lot of publicity. He had his sentence reduced. But was able to write the first part of Mein Kampf to outline his views and Nazi policy.
How far was the threat of Communism the main reason for Hitler becoming Chancellor in 1933? Explain your answer. The Nazi Party was anti-communist. It appealed to all those who feared what communism might bring. Industrialists were particularly fearful that a communist government would take over their businesses. By this policy he won the support of the leading industrialists, some of whom financed the Nazi Party. The Nazis needed money and votes to gain power and when in power to stay there to enable Hitler to become Chancellor. This support was gained by showing they wished to remove Communism. However, much greater was Hitler s cunning which enabled him to convince Hindenburg and Von Papen that he could be controlled and their naivety in believing this. Additionally Nazi policies were a reason but less so.