Understanding Electronic Spectra and Transition Metal Complexes
Explore the world of electronic spectra, absorption bands, and transition metal complexes through various diagrams and explanations covering topics like d-d transitions, free ions, microstates, and charge transfer transitions. Discover the reasons behind the coloring of octahedral compounds despite Laporte forbidden transitions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
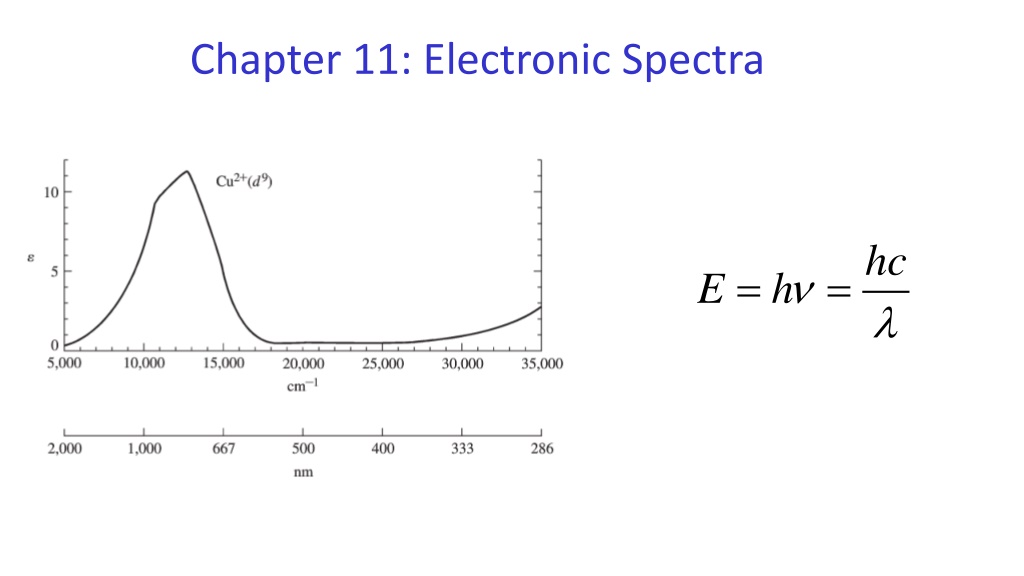
Chapter 11: Electronic Spectra hc = h = E
Why are absorption spectra bands instead of lines? Ground and excited state energy wells. Electronic, vibrational, rotational and solvent transitions.
Electronic states of free ions. Quantum numbers of multielectron atoms. Microstates. Draw all microstates for a p2 configuration. (15 of them) ml +1 0 -1 +1 0 -1 ml
Electronic states of free ions. Quantum numbers of multielectron atoms. Microstates.
Since octahedral compounds all seem to have only d-d transitions that must be Laporte forbidden, why are they colored?
Correlation diagram for free ions and complexes. Example: d2 ion
Tanabe-Sugano Diagrams Example: d2
Why is: 1. Mn2+(aq) colorless 2. Cu2+(aq) less deeply blue colored than Cu(NH3)42+ 3. Zn2+(aq) colorless 4. MnO4- deeply colored 5. W(CO)6 colorless
Mn2+(aq) MnO4-
Photophysics vs. Photochemistry Ru(bpy)32+ vs. Ru(py)2(bpy)22+