Understanding Casting Defects in Metal Casting Processes
A casting defect is an undesirable irregularity in metal casting processes that may require correction or elimination. This article discusses the definition, types, remedies, causes, prevention, and conclusion of casting defects. It covers shrinkage defects, gas porosity, pouring metal defects, metallurgical defects, and more.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
StudyMafia.Org Casting Defects { Submitted To: Submitted By: Studymafia.org Studymafia.org
Table Contents Definition Introduction Types of Casting Defects Remedies of Casting Defects Causes of Casting Defects Prevention of Casting Defects Conclusion 2
Definition A casting defect is an undesired irregularity in a metal casting process. Some defects can be tolerated while others can be repaired, otherwise they must be eliminated. 3
Introduction The terms "defect" and "discontinuity" refer to two specific and separate things in castings. Defects are defined as conditions in a casting that must be corrected or removed, or the casting must be rejected. Discontinuities, also known as "imperfections", are defined as "interruptions in the physical continuity of the casting". Therefore, if the casting is less than perfect, but still useful and in tolerance, the imperfections should be deemed "discontinuities" 4
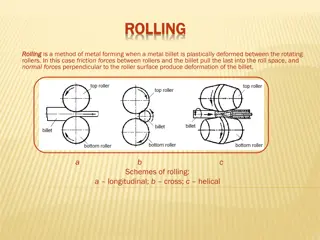
Types of Casting Defects Shrinkage defects Shrinkage defects can occur when standard feed metal is not available to compensate for shrinkage as the thick metal solidifies. Shrinkage defects will have jagged or linear appearance. Shrinkage defects usually occur in either the cope or drag portion of the casting 6
Types of Casting Defects Gas porosity Gas porosity is the formation of bubbles within the casting after it has cooled. This occurs because most liquid materials can hold a large amount of dissolved gas, but the solid form of the same material cannot, so the gas forms bubbles within the material as it cools 7
Types of Casting Defects Pouring metal defects Pouring metal defects include misruns, cold shuts, and inclusions. A misrun occurs when the liquid metal does not completely fill the mould cavity, leaving an unfilled portion. Cold shuts occur when two fronts of liquid metal do not fuse properly in the mould cavity, leaving a weak spot 8
Types of Casting Defects Metallurgical defects There are two defects in this category: hot tears and hot spots. Hot tears, also known as hot cracking, are failures in the casting that occur as the casting cools. This happens because the metal is weak when it is hot and the residual stresses in the material can cause the casting to fail as it cools. 9
Types of Casting Defects Die casting In die casting the most common defects are misruns and cold shuts. These defects can be caused by cold dies, low metal temperature, dirty metal, lack of venting, or too much lubricant. Other possible defects are gas porosity, shrinkage porosity, hot tears, and flow marks. 10
Types of Casting Defects Continuous casting A longitudinal facial crack is a specialized type of defect that only occurs in continuous casting processes. This defect is caused by uneven cooling, both primary cooling and secondary cooling, and includes molten steel qualities, such as the chemical composition being out of specification, cleanliness of the material, and homogeneity. 11
Remedies of Casting Defects Pouring of metal is done as rapidly as possible without interaction. Use vacuum degassing. Melt the metal in vacuum. Keep the temperature of mould low. Use adequate venting of moulds and cores. 12
Remedies of Casting Defects Have sufficient metal in ladel to fill the mould. Improve the gating system. Modify the casting design to avoid the thin metal section and improve runner design. Increase the metal pouring temperature 13
Remedies of Casting Defects Use extra metal while pouring to avoid the sinks. Increase the gate seal time. Increase the injection speed to decrease viscosity and allow more backing pressure. Relocate gates to problem areas. Increase the cooling time of metal. 14
Causes of Casting Defects Increased metal concentration at specific region. Complexity in casting geometry. Pressure of metal is too low. Poor gating and runner design. Metal is contaminated. Reduced metal volume during solidification 15
Prevention of Casting Defects Avoid pinholes, blowholes, and open holes by making sure the molding sand is dry and permeable. It should be noted that the coarser sand is, the more permeable it is. Even using sand that is too fine can prevent optimal permeability. Additionally, sand molds that have been rammed too much lose their permeability, so it s important not to overdo it. 16
Prevention of Casting Defects Make sure that molds and cores are dry before use and stored under dry conditions as well, and be sure that there s enough venting in the molds to allow gases to escape. You should also use good melting practices by melting the material in a vacuum, around low- solubility gases, or under a flux, which prevents air from touching the molten metal. 17
Conclusion Casting is a process which carries risk of failure occurrence during all the process of accomplishment of the finished product. Hence necessary action should be taken while manufacturing of cast product so that defect free parts are obtained. Mostly casting defects are concerned with process parameters. 19
References Google.com Wikipedia.org Studymafia.org Slidespanda.com
Thanks To StudyMafia.org