The Anatomy of the Ear
The ear is a complex sensory organ that enables us to hear by converting sound waves into nerve impulses processed by the brain. It consists of the outer, middle, and inner ear, each playing a crucial role in the hearing process. Changes in air pressure can affect the ear, causing discomfort that can be alleviated through simple actions like yawning or swallowing. Explore the intricate structures of the ear, such as the cochlea and auditory nerve, to gain a deeper understanding of how we perceive sound.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
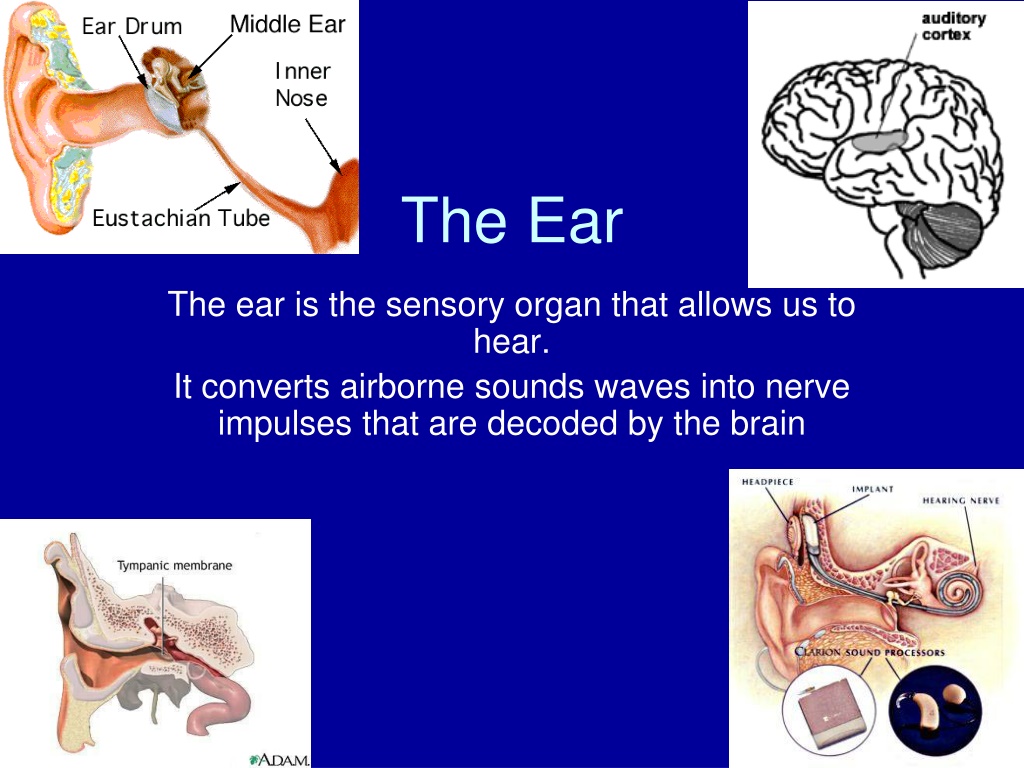
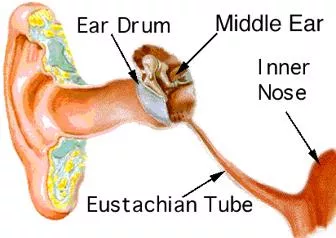
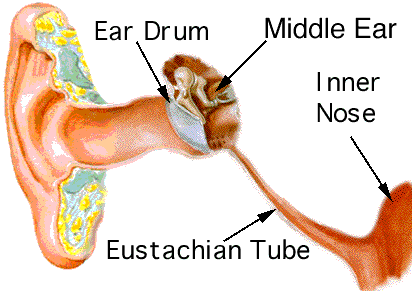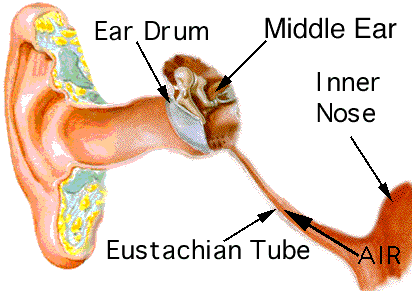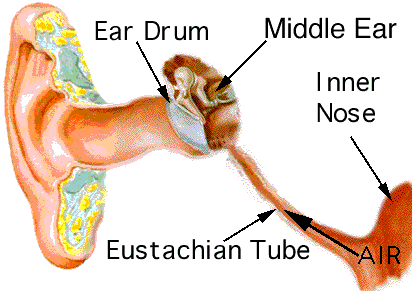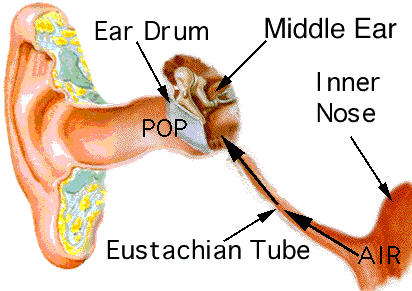
The Ear The ear is the sensory organ that allows us to hear. It converts airborne sounds waves into nerve impulses that are decoded by the brain
Parts of the ear Outer ear (external) Auricle or Pinna - This is the visible part of the ear. 2) The auditory canal - It gathers sound waves from the environment and directs them along the auditory canal is 3.75 cm long Has walls lined with hairs and glands that secrete wax these prevent foreign particles from entering the ear Ends at the tympanic membrane or eardrum
2) The middle ear The eardrum or tympanic membrane Three small bones or ossicles (maleus - hammer, incus- anvil, stapes- stirrup) It is linked to the Eustacian tube which serves to equalize the air pressure on the two sides of the eardrum 3) The inner ear a fluid filled cavity in the temporal bone Contains the semicircular canals and the cochlea
For your information The takeoff or landing of an airplane, the acceleration of an elevator, deep-sea diving, or driving up a steep hill in a car all bring about changes in air pressure which may be experienced as discomfort in the ears. This feeling is the result of increased pressure being exerted on the eardrum, which causes it to bulge on one side or the other, depending where the pressure is higher. Usually the act of yawning, swallowing, or sneezing opens the Eustachian tube, equalizing the pressure on the two sides of the eardrum and relaxing this membrane.
Cochlea spiral-shaped fluid-filled inner ear structure lined with cilia (tiny hairs) that move when vibrated and cause a nerve impulse to form The axons of cilia form the auditory nerve that sends auditory signals to the brain
Ear Cochlea Auditory Nerve Brain Transformer Analyzer Conductor Receiver
Match the following words with the correct term Ear Cochlea Auditory Nerve Brain Transformer Analyzer Conductor Receiver Ear Receiver Conductor Auditory Nerve Cochlea Transformer Brain Analyzer
Hearing & the ear This is the chain reaction which takes place in the hearing process: (put the following words in the appropriate order) sounds waves hearing Vibration of the eardrum auditory canal center for hearing in the brain the auricle three bones of the middle ear nerve impulse is triggered in the auditory nerve cilia move (inside cochlea)
Chain Reaction of Hearing sound waves the auricle the auditory canal vibrations the eardrum the three bones of the middle ear cilia move (inside cochlea) nerve impulse is triggered in the auditory nerve the center for hearing in the brain hearing
Hearing loss and prevention 3 Main causes of hearing loss: 1. Partial or total blocking of the auditory canal by wax Ear wax cast removed from ear
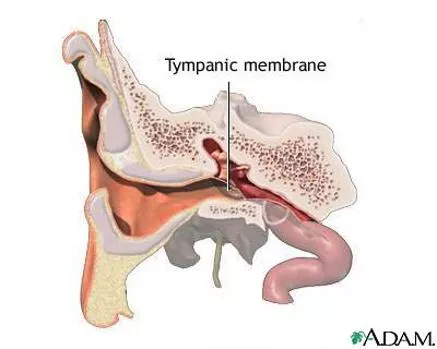
Hearing loss & prevention 3 Main causes of hearing loss: 2. Rupture of the eardrum Ear Drum or Tympanic membrane
Hearing loss & prevention 3 Main causes of hearing loss: 1. Ear wax 2. Rupture of the eardrum 3. Loss of sensitivity of the mechanical structures (eardrum, small bones of the middle ear)
Otitis Inflammation and/or infection of the middle ear Acute otitis media (acute ear infection) occurs when there is bacterial or viral infection of the fluid of the middle ear, which causes production of fluid or pus. Chronic otitis media occurs when the eustachian tube becomes blocked repeatedly due to allergies, multiple infections, ear trauma, or swelling of the adenoids.
Review Questions 1) 2) What part of the ear gathers sound waves in the air? What name is given to the structure that connects the ear to the nose? How does the ear protect itself from unwanted incoming particles? What two structures compose the inner ear? What structure contains the hearing receptor cells? Which part of the ear houses the nerve endings for hearing? When does a person experience the sensation of hearing? 3) 4) 5) 6) 7)
1) What part of the ear gathers sound waves in the air? - The auricle or the pinna What name is given to the structure that connects the ear to the nose? - Eustacian tube How does the ear protect itself from unwanted incoming particles? - The ear wax that lines the auditory canal What two structures compose the inner ear? - The semicircular canals and the cochlea 5) What structure contains the hearing receptor cells? - The cochlea 6) Which part of the hearing system houses the nerve endings for hearing? - The auditory nerve 7) When does a person experience the sensation of hearing? - When the temporal lobe of the brain receives nerve impulses from the auditory nerve 2) 3) 4)
Internet Resources Slideshow: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/tutorial s/hearingloss/htm/_no_50_no_0.htm