The Human Ear: Structure, Function, and Adaptations
Explore the intricate structure of the human ear, its role in hearing, and adaptations for sound absorption. Learn about the functions of different ear parts, from the pinna to the auditory nerve, in converting sound waves into nerve impulses for interpretation by the brain.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
ASSET TUTORING REVISION 2020 HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM 4: THE EAR For each section please read the exam guidelines first before going on to the content. Learn all the content in this presentation
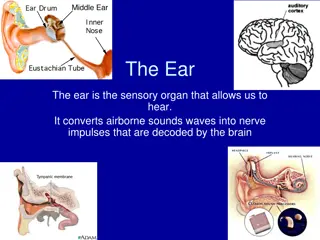
The Ear structure 2 learn, be able to label and give functions of all or parts of the ear
Functioning of the human ear in: Hearing (include the role of the organ of Corti without details of its structure) Pinna traps and directs sound waves in the air along auditory canal Sound waves hit tympanic membrane causing it to vibrate This causes ossicles to vibrate, first the hammer, then the anvil and finally the stirrup Stirrup causes membrane of the oval window to vibrate This creates pressure waves in the perilymph of cochlea The Organ of Corti in the cochlea is stimulated Stimulus is turned into nerve impulse Auditory Nerve sends impulses to Cerebrum to be interpreted as sounds.
Adaptations of parts of the ear for hearing Pinna is large and projected out of head to capture sound waves Cerumen (wax) and hairs in auditory canal trap small organisms preventing entry and prevents drying out of the auditory canal Hammer is attached to tympanic membrane so it can vibrate along with the tympanic membrane Stirrup is attached to oval window NB When the ossicles vibrate, they amplify the sound NB The tympanic membrane is much larger than the oval window membrane, this amplifies the sound waves Oval window also vibrates creating pressure waves in the perilymph of the vestibular canal Eustachian tube allows air to be released out of, or taken into, thus equalizing pressure between middle and outer ear (prevents tympanic membrane bursting. Round window acts as a cushion absorbing the pressure coming from the waves Cochlea contains the organ of Corti which is the receptor picking up the stimulus of sound Auditory nerve arising from the cochlea transmits sound to the cerebrum of the brain
Functioning of the human ear in: Balance (include the role of maculae and cristae without details of their structure)
Middle ear infections and Treatment 1
Middle ear infections and treatment 2 Middle Ear Infection Most common cause of earaches. Caused by viruses and bacteria Fluid build up results in increased pressure and inflammation Treated using medication (antibiotics) or grommets, which are tiny plastic buttons with a fine hole in the middle. These are inserted into eardrum allowing air to enter giving time for the eustachian tube to recover with all the fluid build up.
Deafness and treatment 1
Deafness and treatment 2 Deafness Can be caused by: Fluid in the middle ear, damage to ear drum, hardened wax in the ear, hardening of ear tissue, age, injuries to parts of the ear, nerves or brain responsible for hearing. Treatment depends on the cause, not all cases are treatable. Hearing aids make sound louder so that person can listen and communicate. Cochlear Implants can also be used to treat deafness. These don t work by amplifying sounds but rather by stimulating the auditory nerve in side the cochlear as the organ of corti would normally do
Go to Q & A on Human Nervous System Good luck with your studying for the finals

 undefined
undefined