Otitis Externa: Overview, Risk Factors, and Treatment
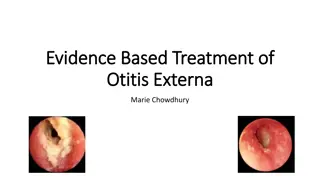
Otitis externa, also known as swimmer's ear, is an inflammation of the external auditory canal. It can be acute or chronic and is common among individuals aged 7-14 years. The main causative organisms include Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Risk factors include swimming in pools, humid environments, trauma to the ear canal, and immunocompromised states. Clinical features include otorrhea, hearing loss, and ear pain. Diagnosis involves otoscopy and ear swabs for culture. Treatment includes aural toileting, topical and systemic antibiotics, and analgesics. Complications can range from canal stenosis to osteomyelitis of the temporal bone. Prevention strategies include avoiding unsafe waters, using ear protectors when swimming, and timely surgical repair for anatomical anomalies. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing otitis externa.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Introduction Introduction Otherwise called a swimmers disease, is an inflammation of the of the external auditory canal. It can be acute or chronic based of duration of inflammation.
Epidemiology Epidemiology It is common at the age of 7-14 years. Approximately 10% of people will develop otitis externa during their lifetime, and the majority of cases (95%) are acute.
Etiology Etiology Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus (most common) Diphtheroids Proteus vulgaris Escherichia coli Streptococcus faecalis Aspergillus niger Candida albicans
Risk factors Risk factors Swimming in pools or bath tabs Humid environmental conditions Trauma or foreign body into the ear canal Dermatologic conditions Anatomical anomalies of ear canal Ear canal obstruction Radiotherapy or chemotherapy Immuno-incompetence.
Clinical features Clinical features Otorrhea Fullness sensation Hearing loss Itchy, dry and scaly ear canal Ear pain
Evaluation Evaluation Otoscopy Ear swab for culture and sensitivity
Treatment Treatment Aural toileting Topical antibiotics Systemic antibiotics Analgesics
Complications Complications Canal stenosis Hearing loss Malignant otitis externa Periauricular cellulitis Myringitis Perichondritis Facial cellulitis Osteomyelitis of the temporal bone
Prevention Prevention Avoid swimming in unsafe waters Wearing ear protectives when swimming Avoid unnecessary foreign objects into ears Ear surgical repair in case of anatomical ear canal anomalies. Early diagnosis and treatment Avoid ear unnecessary pricking