Study on Grazoprevir and Elbasvir in Genotype 1 with Child-Pugh B Cirrhosis
The C-SALT study evaluated the efficacy of grazoprevir and elbasvir in patients with genotype 1 chronic HCV infection and Child-Pugh B cirrhosis. The primary endpoint was achieving sustained virologic response at 12 weeks. The study included treatment-naive and pre-treated patients with IFN-based regimens. Results showed high SVR12 rates, especially in non-cirrhotic patients. Pharmacokinetic analysis demonstrated differences in drug exposure between Child-Pugh B cirrhotic patients receiving different doses. Subgroup analyses and baseline characteristics provided valuable insights into the patient population.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
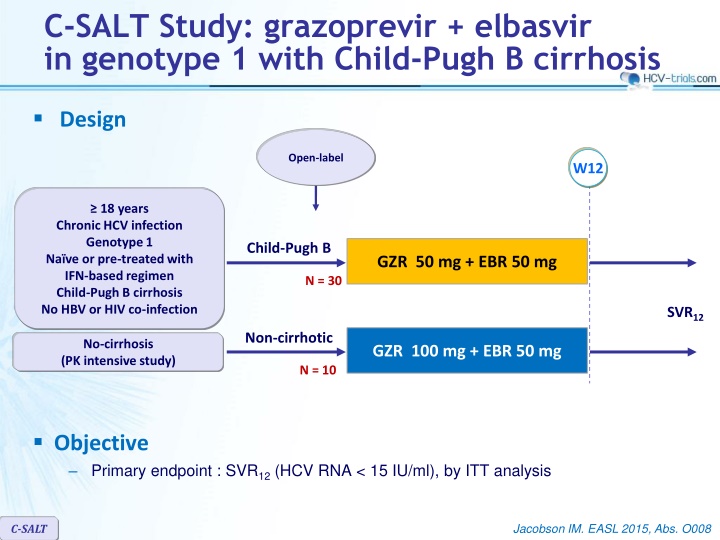
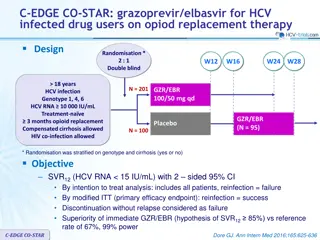
C-SALT Study: grazoprevir + elbasvir in genotype 1 with Child-Pugh B cirrhosis Design Open-label W12 18 years Chronic HCV infection Genotype 1 Na ve or pre-treated with IFN-based regimen Child-Pugh B cirrhosis No HBV or HIV co-infection Child-Pugh B GZR 50 mg + EBR 50 mg N = 30 SVR12 Non-cirrhotic No-cirrhosis (PK intensive study) GZR 100 mg + EBR 50 mg N = 10 Objective Primary endpoint : SVR12(HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml), by ITT analysis C-SALT Jacobson IM. EASL 2015, Abs. O008
C-SALT Study: grazoprevir + elbasvir in genotype 1 with Child-Pugh B cirrhosis Baseline characteristics Child Pugh-B N = 30 58.3 Non-cirrhotic (PK arm) N = 10 60.4 Mean age, years Female 43.3% 50% White Genotype 96.7% 90% 1a 1b 90% 10% 60% 40% Prior treatment status Naive Null response Partial response Relapse 60% 20% 10% 10% 63.3% 20% 0% 16.7% Child-Pugh score 7 8 9 MELD score, (mean 0 0 0 1.0 70% 23.3% 6.7% SD) 9.9 2.5 6.4 C-SALT Jacobson IM. EASL 2015, Abs. O008
C-SALT Study: grazoprevir + elbasvir in genotype 1 with Child-Pugh B cirrhosis SVR12(HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml) , % (95% CI) 100 % (69.2-100) 100 90 100 93 (73.5-97.9) 89 87 75 50 25 30 10 15 15 27 3 0 Child-Pugh B Non-cirrhotic > 1 M Genotype 1a Genotype 1b 1 M Baseline HCV RNA (IU/ml) Virologic failure Breakthrough Rebound Relapse 2 (6.7%) 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 Child-Pugh B sub-groups C-SALT Jacobson IM. EASL 2015, Abs. O008
C-SALT Study: grazoprevir + elbasvir in genotype 1 with Child-Pugh B cirrhosis Child-Pugh score change from baseline to follow-up W12 2 1 N = 18 * 0 N = 7 N = 4 -1 * -2 -3 1 died at follow-up W4 *Relapse patients (N = 2) C-SALT Jacobson IM. EASL 2015, Abs. O008
C-SALT Study: grazoprevir + elbasvir in genotype 1 with Child-Pugh B cirrhosis Pharmacokinetics Plasma samples collected over 24 hours at treatment W4 PK group (non-cirrhotic, N = 9) with GZR 100 mg Child-Pugh B (N = 9) with GZR 50 mg GMR (90% CI) Child-Pugh B / Non-cirrhotic Grazoprevir C2hr C24hr AUC0-24 Elbasvir C2hr C24hr AUC0-24 1.06 (0.53, 2.11) 1.71 (0.87, 3.33) 1.25 (0.70, 2.24) 0.93 (0.64, 1.33) 1.04 (0.67, 1.60) 0.90 (0.63, 1.60) GZR exposure was slightly higher (not significant) in patients with Child-Pugh B cirrhosis receiving 50 mg dose compared to non-cirrhotic patients receiving 100 mg dose EBR (50 mg) PK was similar in both patient populations C-SALT Jacobson IM. EASL 2015, Abs. O008
C-SALT Study: grazoprevir + elbasvir in genotype 1 with Child-Pugh B cirrhosis Adverse events, N (%) Child-Pugh B N = 30 Non cirrhotic (PK) N = 10 Discontinuation due to an AE, N (%) 0 0 Serious adverse event, N (%) 4 (13.3%)* 0 Adverse events, N (%) Fatigue Arthralgia Nausea Pyrexia Headache 30% 16.7% 10% 10% 10% 30% 20% 20% 0 50% Grade 3-4 ALT/AST elevation, N (%) 0 0 Grade 3-4 bilirubin elevation, N (%) 4 (13.3) 0 Death**, N (%) 1 (3.3) 0 * All unrelated to study treatment : hepatocellular carcinoma, N = 1; ascites and encephalopathy, N = 1 ; bacterial peritonitis, cerebral infarction and hepatic failure (**death at follow-up W4) N = 1 ; hematemesis, N = 1 C-SALT Jacobson IM. EASL 2015, Abs. O008
C-SALT Study: grazoprevir + elbasvir in genotype 1 with Child-Pugh B cirrhosis Summary High rates of virologic response were observed in Child-Pugh B patients receiving a combination of once-daily GZR 50 mg + EBR 50 mg The regimen was well tolerated with no evidence of hepatotoxicity Plasma GZR exposure was slightly higher in Child-Pugh B patients receiving 50 mg compared to non-cirrhotic patients receiving 100 mg EBR exposure was similar in both Child-Pugh B and non-cirrhotic groups This regimen was highly effective and well-tolerated in a traditionally hard-to-treat patient group with no currently approved treatment options C-SALT Jacobson IM. EASL 2015, Abs. O008