Study on Elbasvir/Grazoprevir with or without Ribavirin in HCV Patients
The C-EDGE.experienced Study investigated the use of Elbasvir/Grazoprevir with or without Ribavirin in patients who failed prior therapy with PEG-IFN and Ribavirin. The study had 105 participants and aimed to achieve an SVR12 rate of over 95%. Results showed high SVR12 rates in both treatment arms, demonstrating the efficacy of Elbasvir/Grazoprevir in HCV patients with previous treatment failure.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
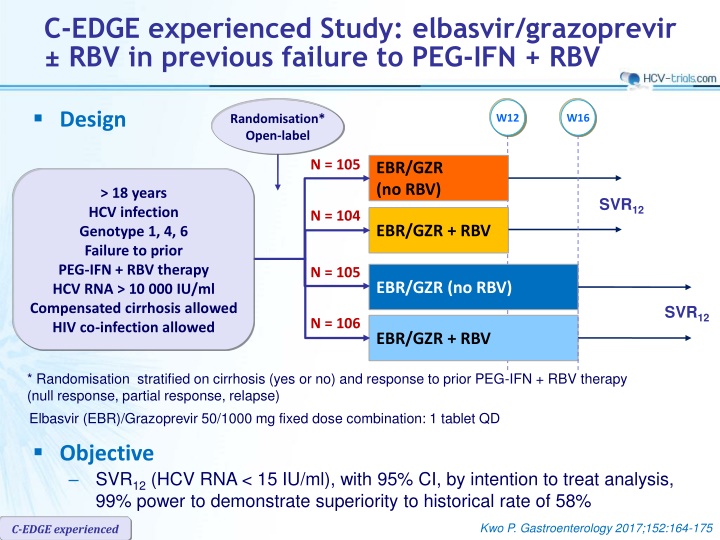
C-EDGE experienced Study: elbasvir/grazoprevir RBV in previous failure to PEG-IFN + RBV Design Randomisation* Open-label W12 W16 N = 105 EBR/GZR (no RBV) > 18 years HCV infection Genotype 1, 4, 6 Failure to prior PEG-IFN + RBV therapy HCV RNA > 10 000 IU/ml Compensated cirrhosis allowed HIV co-infection allowed SVR12 N = 104 EBR/GZR + RBV N = 105 EBR/GZR (no RBV) SVR12 N = 106 EBR/GZR + RBV * Randomisation stratified on cirrhosis (yes or no) and response to prior PEG-IFN + RBV therapy (null response, partial response, relapse) Elbasvir (EBR)/Grazoprevir 50/1000 mg fixed dose combination: 1 tablet QD Objective SVR12(HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml), with 95% CI, by intention to treat analysis, 99% power to demonstrate superiority to historical rate of 58% Kwo P. Gastroenterology 2017;152:164-175 C-EDGE experienced
C-EDGE experienced Study: elbasvir/grazoprevir RBV in previous failure to PEG-IFN + RBV Baseline characteristics and disposition EBR/GZR 12 weeks No RBV N = 105 56 37 63 / 22 EBR/GZR 16 weeks No RBV N = 105 55 34 69 / 9 + RBV N = 104 56 31 67 / 23 + RBV N = 106 55 40 74 / 14 Age, median years Female, % Race : White / Black, % Genotype, % 1a 1b or other genotypes 1 4 6 HIV co-infection, % Cirrhosis, % Prior treatment response, N (%) Null response Partial response Relapse Treatment discontinuation, N Adverse event / virologic failure Follow-up discontinuation (virologic failure) 58 33 9 0 6 35 58 28 14 0 5 34 46 46 5 4 6 36 55 36 8 2 4 35 49 (47) 21 (20) 35 (33) 1 1 / 0 9 (3) 44 (42) 22 (21) 38 (37) 1 1 / 0 6 (6) 46 (44) 21 (20) 38 (36) 7 0 / 3 5 (4) 43 (41) 23 (22) 40 (38) 5 4 / 0 3 (0) Kwo P. Gastroenterology 2017;152:164-175 C-EDGE experienced
C-EDGE experienced Study: elbasvir/grazoprevir RBV in previous failure to PEG-IFN + RBV SVR12(HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml), ITT, % (95% CI) 12 weeks 16 weeks 98.1 % 94.2 92.4 92.4 (92.0-99.4) 100 (87.9-97.9) 85.5-96.7) (85.5-96.7) 80 60 40 20 105 108 105 106 0 No RBV + RBV No RBV + RBV Breakthrough Virologic rebound Relapse LTFU/Early DC 0 0 6 2 0 0 6 0 1 2 4 1 0 0 0 2 Kwo P. Gastroenterology 2017;152:164-175 C-EDGE experienced
C-EDGE experienced Study: elbasvir/grazoprevir RBV in previous failure to PEG-IFN + RBV SVR12(HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml) by subgroup, ITT, n/N (%) EBR/GZR (no RBV) 12 weeks N = 105 EBR/GZR + RBV 12 weeks N = 104 EBR/GZR (no RBV) 16 weeks N = 105 EBR/GZR + RBV 16 weeks N = 106 Overall, % 92.4 94.2 92.4 98.1 Genotype 1a 1b 1-other 4 6 55/61 (90.2) 34/34 (100) 1/1 (100) 7/9 (77.8) 0 56/60 (93.3) 28/29 (96.6) 0 14/15 (93.3) 0 45/48 (93.8) 46/48 (95.8) 0 3/5 (60.0) 3/4 (75.0) 55/58 (94.8) 36/36 (100) 2/2 (100) 8/8 (100) 2/2 (100) Hepatic fibrosis stage Cirrhosis No cirrhosis 33/37 (89.2) 64/68 (94.1) 31/35 (88.6) 67/69 (97.1) 35838 (92.1) 62/67 (92.5) 37/37 (100) 66/69 (95.7) HIV/HCV co-infection 6/6 (100) 5/5 (100) 5/6 (83.3) 4/4 (100) Kwo P. EASL 2015, Abs. P0886 C-EDGE experienced
C-EDGE experienced Study: elbasvir/grazoprevir RBV in previous failure to PEG-IFN + RBV SVR12(HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml) by subgroup, ITT EBR/GZR (No RBV), 12 weeks EBR/GZR + RBV, 12 weeks All EBR/GZR (No RBV), 16 weeks EBR/GZR + RBV, 16 weeks % 100 100 100 100 98 98 97 95 100 100 94 94 93 93 92 92 91 91 91 90 80 80 60 60 40 40 20 20 N 35 37 38 39 67 64 66 62 59 207 51 52 57 47 213 54 52 48 0 0 Prior relapse Prior partial or null response < 2 M > 2 M Baseline HCV RNA (IU/ml) Kwo P. Gastroenterology 2017;152:164-175 C-EDGE experienced
C-EDGE experienced Study: elbasvir/grazoprevir RBV in previous failure to PEG-IFN + RBV SVR12(HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml) by subgroup, Per-protocol, n/N (%) Overall Overall 390/408 (95.6) Genotype 1a 1b 4 6 207/218 (95.0) 143/145 (98.6) 32/36 (88.9) 5/6 (83.3) Hepatic fibrosis stage Cirrhosis No cirrhosis 135/144 (93.8) 255/264 (96.6) Baseline HCV RNA 2 Million IU/ml > 2 Million IU/ml 202/207 (98) 188/201 (94) The per-protocol analysis excluded 12 patients who discontinued for administrative reasons Kwo P. Gastroenterology 2017;152:164-175 C-EDGE experienced
C-EDGE experienced Study: elbasvir/grazoprevir RBV in previous failure to PEG-IFN + RBV Resistance-Associated Variants Presence of NS3 RAVs at baseline in genotype 1 by population sequencing: 33.2% (123/170) NS3 variants at positions 36, 54, 55, 56, 80, 107, 122, 132, 155, 156, 158, 168, 170, and 175, considered for the analysis SVR12rates: 97.2% (240/247) and 94.3% (116/123) if baseline NS3 RAVs absent or present, respectively The slightly higher rate of virologic failure among patients with baseline NS3 RAVs is likely explained by the co-existence of baseline NS5A RAVs in these patients. Of the 14 virologic failures in genotype 1, 12 had baseline NS5A RAVs, and of the 2 failures who were wild-type for NS5A, only 1 had a baseline NS3 RAV NS5A RAVs at positions 28, 30, 31 and 93 assessed by population sequencing (limit of detection: 25%) and NGS (limit of detection: 1% and 15%) The lower-sensitivity assays (population sequencing and NGS 15%) offer the highest precision in identifying patients with baseline RAVs at risk of virologic failure Kwo P. Gastroenterology 2017;152:164-175 C-EDGE experienced
C-EDGE experienced Study: elbasvir/grazoprevir RBV in previous failure to PEG-IFN + RBV Impact of baseline NS3 variants on SVR12in genotype 1, n/N (%) NS3 variants not detectable 240/247 (97.2) 57/59 (96.6) 58/62 (93.5) 70/71 (98.6) 55/55 (100) 107/112 (95.5) 27/29 (93.1) 33/36 (91.7) 26/26 (100 21/21 (100) 133/135 (98.5) 30/30 (100) 23/26 (96.2) 44/45 (97.8) 34/34 (100) - NS3 variants detected 116/123 (94.3) 32/35 (91.4) 26/27 (96.3) 21/24 (87.5) 37/37 (100) 104/111 (93.7) 28/31 (90.3) 23/24 (95.8) 19/22 (86.4) 34/34 (100) 11/11 (100) 4/4 (100) 3/3 (100) 2/2 (100) 2/2 (100) 1/1 (100) Overall efficacy Overall genotype 1 in RAP * 12W, no RBV 12W + RBV 16W, no RBV 16W + RBV Overall genotype 1a in RAP * 12W, no RBV 12W + RBV 16W, no RBV 16W + RBV Overall genotype 1b in RAP * 12W, no RBV 12W + RBV 16W, no RBV 16W + RBV Genotype 1-other RAVs assessed by population sequencing; limit of detection approximately 25% 356/370 (96.2) 89/94 (94.7) 84/89 (94.4) 91/95 (95.8) 92/92 (100) 211/223 (94.6) 55/60 (91.7) 56/60 (93.3) 45/48 (93.8) 55/55 (100) 144/146 (98.6) 34/34 (100) 28/29 (96.6) 46/47 (97.9) 36/36 (100) 1/1 (100) * RAP = resistance analysis population excludes patients who discontinued for administrative reasons or did not have sequence data Kwo P. Gastroenterology 2017;152:164-175 C-EDGE experienced
C-EDGE experienced Study: elbasvir/grazoprevir RBV in previous failure to PEG-IFN + RBV Impact of baseline NS5A variants on efficacy in genotype 1-infected subjects SVR12(%) Overall efficacy in subject with sequence in RAP* NS5A variants with < 5-fold shift to EBR NS5A variants with > 5-fold shift to EBR NS5A variants not detectable Overall genotype 1 in RAP 355/369 (96.2%) 317/319 (99.4%) 10/10 (100%) 28/40 (70.0%) By Genotype and Subtypes 1a 211/223 (94.6%) 190/192 (99.0%) 10/10 (100%) 11/21 (52.4%) 1b 143/145 (98.6%) 127/127 (100%) 0 16/18 (88.9%) 1-other 1/1 (100%) 0 0 1/1 (100%) RAVs assessed by population sequencing; limit of detection approximately 25% * RAP = resistance analysis population excludes patients who discontinued for administrative reasons or did not have sequence data n/a = not applicable Kwo P. EASL 2015, Abs. P0886 C-EDGE experienced
C-EDGE experienced Study: elbasvir/grazoprevir RBV in previous failure to PEG-IFN + RBV Impact of baseline NS5A variants on SVR12in genotype 1a No baseline NS5A RAVs n/N Baseline NS5A RAVs n/N % % Population sequencing (LDD 25%) Overall 12W, no RBV 12W + RBV 16W, no RBV 16W + RBV NGS, LDD 15% Overall 12W, no RBV 12W + RBV 16W, no RBV 16W + RBV NGS, LDD 1% Overall 12W, no RBV 12W + RBV 16W, no RBV 16W + RBV The same 10 virologic failures are identified by all 3 assays as having baseline NS5A RAVs 7 of the 10 patients with baseline NS5A RAVs who experienced virologic failure received a 12-week regimen 190/192 49/50 50/51 42/42 49/49 99 98 98 100 100 21/31 6/10 6/9 3/6 6/6 67.7 60 66.7 50 100 190/192 48/49 50/51 43/43 49/49 99 98 98 100 100 21/31 7/11 6/9 2/5 6/6 67.7 63.6 66.7 40 100 168/170 41/42 45/46 40/40 42/42 98.8 97.6 97.8 100 100 43/53 14/18 11/14 5/8 13/13 81.1 77.8 78.6 62.5 100 Kwo P. Gastroenterology 2017;152:164-175 C-EDGE experienced
C-EDGE experienced Study: elbasvir/grazoprevir RBV in previous failure to PEG-IFN + RBV Impact of baseline NS5A variants on SVR12in genotype 1b No baseline NS5A RAVs Baseline NS5A RAVs n/N % n/N % Population sequencing (LDD 25%) Overall 12W, no RBV 12W + RBV 16W, no RBV 16W + RBV 117/117 30/30 24/24 35/35 28/28 100 100 100 100 100 28/30 4/4 4/5 11/12 9/9 93.3 100 80 91.7 100 NGS, LDD 15% Overall 12W, no RBV 12W + RBV 16W, no RBV 16W + RBV 39/40 11/11 9/10 11/11 8/8 97.5 100 90 100 100 9/10 2/2 1/1 3/4 3/3 90 100 100 75 100 NGS, LDD 1% Overall 12W, no RBV 12W + RBV 16W, no RBV 16W + RBV 36/36 11/11 8/8 11/11 6/6 100 100 100 100 100 12/14 2/2 2/3 3/4 5/5 85.7 100 66.7 75 100 Kwo P. Gastroenterology 2017;152:164-175 C-EDGE experienced
C-EDGE experienced Study: elbasvir/grazoprevir RBV in previous failure to PEG-IFN + RBV RAVs in patients with genotypes 1 and 1b and virologic failure (all relapses) NS3 RAVs NS5A RAVs Response to prior Rx GT Cirrhosis BL Af failure At FW24 BL Af failure At FW24 1a Yes Null Q80K Q80K, A156T, D168A Q80K L31M Q30R, L31M Q30R, L31M Y56H, Q80K, R155I/R, D168V Y56H, Q80K 1a Yes Null Q80K Y93Y/N Y93Y/N Y93Y/N 1a 1a 1a 1a 1a 1a 1a 1a No Yes No Yes No No No Yes Null Null Null Null Null Partial Partial Partial WT V107I V107I WT Q30H, Y93H Q30H, Y93H WT WT WT L31L/M Q30R, L31M Q30R, L31M WT A156T/A WT L31L/M Q30R, L31M Q30R, L31M I170I/V R155K/R WT L31M Q30R, L31M Q30R, L31M Q80K Q80K, D168Y Q80K WT Q30R, Y93H Q30R, Y93Y/H Q80K Q80K, D168A Q80K L31L/M Q30R, L31M Q30R, L31M WT WT WT Y93N M28T, Y93S M28T, Y93S WT A156T, V158A NA Q30H Q30H NA V36L, Q80K 1a No Partial Q80K V36L, Q80K, D168A Q30H M28T, Q30H M28T, Q30H 1a 1b 1b No No Yes Partial Relapse Null I170V A156T, I170V I170V M28T M28T, Q30R M28T, Q30R WT WT WT Y93H L28M, Y93H L28M, Y93H WT WT WT L31L/M L31M, Y93H L31M, Y93H Kwo P. Gastroenterology 2017;152:164-175 C-EDGE experienced
C-EDGE experienced Study: elbasvir/grazoprevir RBV in previous failure to PEG-IFN + RBV Adverse events, N (%) EBR/GZR (no RBV) 12 weeks N = 105 41 (39.0) 1 (1.0) 0 4 (3.8) 0 EBR/GZR + RBV 12 weeks N = 104 67 (64.4) 1 (1.0) 1 (1.0) * 3 (2.9) 0 EBR/GZR (no RBV) 16 weeks N = 105 46 (43.8) 0 0 3 (2.9) 0 EBR/GZR + RBV 16 weeks N = 106 81 (76.4) 5 (4.7) 2 (1.9) ** 4 (3.8) 0 Drug-related adverse event Discontinued study medication due to AE Drug-related Serious adverse event Death Most common adverse events Fatigue Headache Nausea Hemoglobin < 10 g/dl Total bilirubin > 5 x baseline Late ALT/AST > 5 x ULN 20 (19.0) 22 (21.0) 9 (8.6) 0 0 0 28 (26.9) 21 (20.2) 15 (14.4) 9 (8.7) 0 1 (1.0) 17 (16.2) 20 (19.0) 4 (3.8) 0 0 3 (2.9) 32 (30.2) 20 (18.9) 18 (17.0) 22 (20.8) 0 0 * Emotional lability D35 ; ** palpitations, suicidal ideation Kwo P. Gastroenterology 2017;152:164-175 C-EDGE experienced
C-EDGE experienced Study: elbasvir/grazoprevir RBV in previous failure to PEG-IFN + RBV Summary In patients who failed prior PEG-IFN + RBV therapy 12 weeks of EBR/GZR without RBV achieved SVR12in 100 % of patients with history of relapse to prior PEG-IFN + RBV 12 weeks of EBR/GZR without RBV achieved SVR12in 100% of genotype 1b 16 weeks of EBR/GZR + RBV achieved SVR12of 100% with no virologic failure regardless of prior treatment history or cirrhosis status or NS5A RAV There was no difference in response rates between patients with and without cirrhosis, irrespective of therapy duration and with or without the addition of RBV Of the 12 genotype 1a with virologic failure, 10 had a baseline NS5A RAV EBR/GZR FDC was generally safe and well tolerated Virologic failure was seen in 5.8% of patients treated with 12W of EBR/GZR To maximize SVR rates, genotype 1a or 4-infected patients with a prior history of null or partial response to PEG-IFN + RBV may benefit from the addition of RBV and extension of therapy to 16 weeks, alternatively, baseline RAV testing of genotype 1a-infected patients may be used to identify the small subset of patients who can benefit from the addition of RBV and extension of therapy to 16 weeks Kwo P. Gastroenterology 2017;152:164-175 C-EDGE experienced