REDD+ Financing in India: A Comprehensive Overview
The presentation discusses REDD+ financing in India, highlighting the roadmap for implementation and the sources of funding. It covers domestic funding mechanisms, such as government grants and the contribution of state governments, as well as international funding sources from agencies like JICA and the World Bank. The strategies outlined aim to meet India's target of additional CO2 sequestration through forestry by 2030. Various funding channels, including tax devolution and convergence schemes, play a crucial role in achieving these objectives.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
REDD+ Financing: The Case from India 11th October 2017 UN- REDD Meeting Bangkok Dr. T.P. Singh Conservator of Forests India
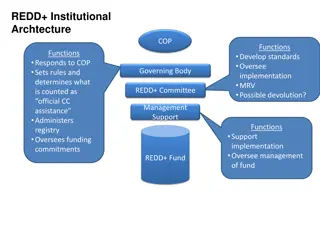
Roadmap for REDD+ in India Phase 1 National Strategy and Action Plan Development (MoEFCC) Phase 2 Readiness and Initial Action Phase 3 Results based Implementation Under implementation India has a target of 2.5 3.0 Billion tonnes of additional CO2 sequestration from forestry by 2030 (Paris Agreement) Which needs huge Forestry investments
REDD+ Finance in India Inbuilt in Forestry Sector Funding Primarily Domestic Funding International Finance Convergence of Forestry with other sectors like Rural Development and Agriculture Devolution of Taxes also encourage fulfilling of REDD+ Objectives No dedicated funding for REDD+ Only for a few pilot projects amounting to US$ 10 Million
Domestic Funding contributing to REDD+ Central Government Funding US $ 720 M per year Through Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change US $ 300 M Green India Mission, National Afforestation Programme, Forest Development Agencies etc. Given to States for afforestation / allied activities State Governments contribute matching 40% Grant of US $ 220 M Compensatory Afforestation (CAMPA) has a Corpus Fund of US $ 2.0 Billion. Annual Interest used for afforestation US $200 M State Governments own Funding US $ 400 M
Domestic Funding through Convergence Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MNREGA) Scheme of Ministry of Rural Development One of the biggest schemes of rural employment in the World converges various sectors including forestry Annual funding of US $ 7.0 Billion. Annual allotment for NRM is US $ 1.0 Billion out of which afforestation is US $300 M Missions under National Action Plan on Climate Change (Agriculture, Himalayas, Knowledge) also converge
Tax Devolution 14th Finance Commission Award 42% of the taxes collected by National Government are given to the States Following Criteria and weights (%): Introduced in 2015 Meets objectives of REDD+, as incentivizes conservation
International Funding Mainly from JICA , the biggest forestry portfolio of US$ 300 M per year But comes as a loan! World Bank US$ 200M EU Bilaterals like GIZ, NORAD etc. Total International Funding around US$ 500 M per year
Way Forward for REDD+ Finance in India India spend more than 2.0 Billion US$ per year on Forestry activities 1.5 B from Domestic and 0.5 B from international resources Look forward to Results based payments from GCF for these efforts