Reference Emission Level in REDD
REDD (Reducing Emission from Deforestation and Forest Degradation) involves a system for producing carbon credits, including steps like setting baseline emission levels, devising deforestation reduction strategies, monitoring changes, managing carbon credit sales, and distributing income. Organizational infrastructure plays a vital role in establishing Reference Emission Levels (REL) based on historical data to measure emission reductions accurately. The interconnected elements of the REDD supply chain and governance framework are crucial for successful implementation.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
REL IN REDD (Reference Emission Level in Reducing Emission from Deforestation and Forest Degradation) Wandojo Siswanto Staf Ahli Menteri Kehutanan Bidang Kemitraan E-mail: wandojos@yahoo.co.id
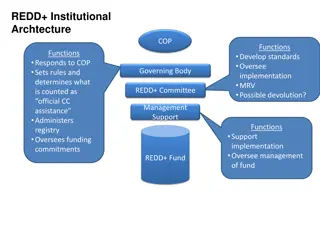
1. INTRODUCTION The production of a REDD carbon credit requires implementation of a system consisting of a series of steps. This system is referred to as a REDD carbon credit supply chain (IFCA Study, 2008). Four elements of the REDD carbon credit supply chain: A. Development of an organizational infrastructure B. Identification of organizations to achieve emission reduction C. Development of a carbon market system D. Forest governance to ensure law enforcement The relationship among elements is illustrated in FIGURE 1.
A. The organizational infrastructure should be capable of: 1. Set a baseline/reference emission level (REL) 2. Set a strategy to reduce deforestation/degradation 3. Monitor the changes 4. Management of the sale of carbon credits 5. Distribute income from carbon credits The relationship among elements is illustrated in FIGURE 1.
Relationship among four elements of REDD Forest cover and carbon stock changes, National registry National approach, sub-national implementation Responsibilities and benefits Historical emission /future scenario Attractiveness, Source of fund MARKET SYSTEM $ 1 3 4 5 2 INFRASTRUCTURE Reference Emission Level Market/ Funding Strategy Monitoring Distribution IFCA Recommendation 2007 : REDD strategy in 5 landscape types : production forest, conservation forest, plantation forest, peat land, oil palm/estate crops. Awareness raising Capacity building Access to data Access to technology Stakeholders communication WG-FCC REDDI Guideline REDDI Committee GOVERNANCE
2. REFERENCE EMISSION LEVEL (REL) REL is the first component in the organizational infrastructure The SB 28 decision (ref) describes Reference Emissions Levels (REL) as follows: Means to establish reference emission levels, based on historical data, taking into account, inter-alia, trends, starting dates and the length of the reference period, availability and reliability of historical data, and other specific national circumstances.
A REL/BASELINE (IFCA Study, 2008): A projection of emissions from deforestation and forest degradation A reference for measuring reductions in emissions from deforestation and forest degradation
SCALE OF REL: Local - individual project/sub national Leakage ? National - whole country Leakage ? Global - several countries in the system Leakage ?
3. CHALLENGES/ISSUES related to the draft of Permenhut REL: What approach to establish REL Do we need to set REL at National, Sub- national and Project Levels? By whom? What is the mechanism? How to deal with leakage Data availability, uncertainty
4. POLICIES in REDD implementation Regional Autonomy/Decentralization Sustainable forest management Participation of people around the forests Stakeholders Involvement pro job, pro poor, pro growth
Ministry of Forestry of the Republic of Indonesia