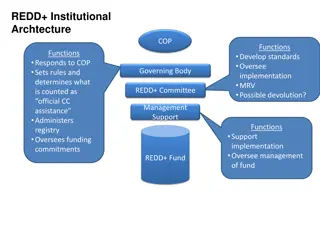
UN-REDD Support on Safeguards and Safeguard Information Systems
The UN-REDD Programme assists countries in addressing social and environmental issues through the development of national approaches to safeguards. The programme's approach emphasizes the importance of safeguarding national REDD+ systems to manage potential negative impacts and enhance benefits. Structured support is provided in areas such as developing frameworks, identifying safeguards, and structuring Safeguard Information Systems. Key tools like the SEPC and BeRT guide the formulation and implementation of UN-REDD National Programmes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
UN-REDD support to countries on Safeguards and Safeguard Information Systems Aki Kono Regional Technical Advisor UNDP/UN-REDD REDD+ SES Exchange and Learning Event Bogor, Indonesia 1-3 July, 2013
Objectives of UN-REDD Work on Safeguards The objectives of the UN-REDD Programme s work on safeguards are: 1. To address social and environmental issues in UN- REDD National Programmes and other UN-REDD funded activities 2. To support countries in developing national approaches to safeguards in line with the UNFCCC
The UN-REDD Programmes Approach to Safeguards Support provided: Ensures that the tools and guidance that have been developed by the UN-REDD Programme and that are relevant to safeguards are presented and used in a coordinated way that responds to country needs Highlights the importance of safeguards for national REDD+ systems to ensure that potential negative impacts are assessed, identified and managed and that multiple benefits of REDD+ can be enhanced and optimized Reflects the UN REDD Programme s responsibility to UN conventions, treaties and declarations
Structuring of UN-REDD Support on Safeguards/SIS Three main functional areas identified for UN-REDD safeguards work: 1. Provision of a framework for overarching country approaches to safeguards Clarifying the role of all existing UN-REDD tools linked to safeguards Support on identification of relevant safeguards to be addressed/respected Developing approaches to help countries to assess their existing policies and compare these to the UNFCCC Cancun safeguards Development and Structuring of Safeguard Information Systems (SIS) Develop approaches to help countries to assess their existing systems that may already fulfill some of the functions of a REDD+ SIS 2. 3.
Social and Environmental Principles and Criteria (SEPC) The SEPC provides a guiding framework: In the formulation, review and implementation of UN-REDD National Programmes To help support countries in developing national approaches to REDD+ safeguards in line with UNFCCC provides more detailed criteria that can be used to "unpack" the UNFCCC safeguards particularly useful at the stage of a country defining the objectives of its approach to safeguards The accompanying Benefits and Risks Tool (BeRT) is currently being revised to better suit this purpose
UN-REDD Tools to Support National Approaches to Safeguards (1) Step UN-REDD tools Explanation of how the tools can contribute to the activity Detailed activities Objective setting Defining goals of the country safeguards approach SEPC Provides more detailed criteria that can be used to unpack the Cancun safeguards UN-REDD/FCPF Stakeholder Engagement Guidelines Provides guidance on how participation of stakeholders can be ensured in UN- REDD activities, including how to apply the principle of FPIC; could be used by countries in the development of REDD+ PLRs and adapted to national context if necessary UN-REDD FPIC Guidelines Provides a framework for applying the principle of FPIC at community, sub- nation and national levels; primarily designed for UN-REDD activities but could be adopted in REDD+ PLRs and adapted to national context
UN-REDD Tools to Support National Approaches to Safeguards (2) Step UN-REDD tools Explanation of how the tools contribute to the activity Detailed activities BeRT Defining or developing safeguard policies, laws and regulations Gap analysis of existing PLRs Provides a list of questions across a broad range of issues in order to assess existing PLRs Provides a process for participatory evaluation of governance systems relevant to REDD+ Provides a more detailed framework (compared to BeRT) for assessing corruption risks in REDD+ PGA Draft Guidance on Conducting REDD+ Corruption Risk Assessment FPIC Guidelines Development of new PLRs (if necessary) Provides a framework for applying the principle of FPIC at community, sub-national and national levels; primarily designed for UN-REDD activities but could be adopted in REDD+ PLRs and adapted to national context Provides guidance on how to assess and strengthen existing PLRs and institutional capacity to address REDD+ related grievances Provides a participatory approach for formulating legal and policy reforms and drafting new PLRs in response to REDD+ Guidelines on Strengthening/Establishing National-Level Grievance Mechanisms Participatory Law Development (LEG- REDD+)
UN-REDD Tools to Support National Approaches to Safeguards (3) Step UN-REDD tools Explanation of how the tools contribute to the activity Detailed activities PGAs SIS Indicators Provides an overall approach for developing governance indicators for REDD+ schemes through a participatory approach Provides a tool for designing robust and comprehensive sets of governance indicators Framework for assessing and monitoring forest governance Draft Guidelines for monitoring the impacts of REDD+ on biodiversity and ecosystem services Methodologies for collection of information Provides draft guidelines that could be used by government in establishing aspects of the SIS that are relevant to biodiversity Draft manual on the collection of forest governance data Provides a range of practical considerations, methods and available resources for collecting governance data
Examples of UN-REDD support to countries on safeguards and SIS in National Programmes Ecuador Development of a proposal for a multiple benefits monitoring system as part of a national System of Information and Monitoring for Safeguards and Multiple Benefits Tanzania Working on Linkages between the national forest inventory and the development of spatial analyses to inform REDD+ environmental safeguards and development of a SIS DRC Inputs to framework strategy on environmental REDD+ safeguards Feedback provided on the DRC national standards based on the SEPC as a guiding framework Technical consultations on the development of an SIS Bhutan Workshop on multiple benefits and environmental safeguards, covering national approaches to safeguards, gap analysis of national policies, laws and regulations, and SIS
Examples of UN-REDD support to countries on Safeguards/SIS: Targeted Support Costa Rica Design of a single safeguard information system that takes into account different safeguard approaches (e.g. UN-REDD, FCPF, REDD+ SES) Argentina Design of a single safeguard information system that takes into account different safeguard approaches (e.g. UN-REDD, FCPF, REDD+ SES). Consultations in four different regions are taking place. Peru Design and initial implementation of a participatory monitoring approach as part of the SIS; Capacity-building for indigenous communities to collect safeguard information
Key Messages The UN-REDD Programme aims to support countries: in accordance with their national context and requirements to implement the UNFCCC guidance on safeguards and SIS ensuring the promotion of multiple social and environmental benefits from REDD+ and avoidance of risks By providing relevant tools and guidance to help meet country needs
Thank You Website: http://www.un-redd.org