Race and Ethnicity in Sociology: An Overview
This content explores the traditional definitions of race and ethnicity, discussing their biological and sociological aspects. It delves into the physical characteristics of different racial groups, such as the Caucasian race, and presents various racial classifications throughout history. The distinctions between race, based on physical attributes, and ethnicity, rooted in cultural factors, are highlighted, offering insights into the complexity of these concepts.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Race and Ethnicity Academic Focus: Sociology 1
Race and Ethnicity Reading Assignment 1 Studying Sociology from Breadth and Depth 2
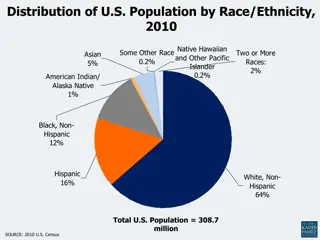
The traditional definition of raceand ethnicity is related to biological and sociological factors respectively. Race refers to a person's physical appearance, such as skin color, eye color, hair color, bone/jaw structure etc. Ethnicity, on the other hand, relates to cultural factors such as nationality, culture, ancestry, language and beliefs. 3
For example, take the Caucasian race. The physical characteristics of Caucasians were described by M. A. MacConaill, as being "light skin and eyes, narrow noses, and thin lips. Their hair is usually straight or wavy". Caucasoids are said to have the lowest degree of projection of the alveolar bones which contain the teeth, a notable size prominence of the cranium and forehead region, and a projection of the midfacial region. A person whose appearance matches these characteristics is said to be a Caucasian. However, there are many ethnicities within the Caucasian race e.g. Irish, Welsh, German, French, Slovak etc. What differentiates these ethnic groups from each other is their country of origin, language they speak, cultural heritage and traditions, beliefs and rituals. 4
Over time many different racial classifications have existing numbering anywhere between 6 and several hundred. Below are a few of these: Khoid (Hottentot) race Sanid (Bushmen) race Central Congoid race (Geographic center and origin in the Congo river basin) Bambutid race (African Pygmies) Aethiopid race (Ethiopia, Somalia) Mediterranid race (from Mediterranean areas) Dinaric race (predominant in western Balkans [Dinaric Mountains] and northern Italy) Alpine race 5
Ladogan race (named after Lake Ladoga; indigenous to Russia; includes Lappish subrace of arctic Europe) Nordish or Northern European race Armenid race (Armenia, Syria, Lebanon and northern Iraq) Turanid race (Kazakhstan, Hungary and Turkey) Irano-Afghan race (Iran and Afghanistan, Iraq, Turkey) Indic or Nordindid race (Pakistan and northern India) Dravidic race (India, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka) Veddoid race (remnant Australoid population in central and southern India) Melanesian race (New Guinea, Papua, Solomon Islands) 6
Australian-Tasmanian race (Australian Aborigines) Northeast Asian or Northern Mogoloid race (China, Manchuria, Korea and Japan) Southeast Asian or Southern Mongoloid race (China, Indochina, Thailand, Myanmar [Burma], Malaysia, Indonesia and the Philippines) Micronesian-Polynesian race Ainuid race (remnants of aboriginal population in northern Japan) Tungid race (Mongolia and Siberia, Eskimos) Amerindian race (American Indians) 7
What is the Academic Word List? Some words appear over and over again in academic reading. These words appear academic disciplines, from textbooks in sociology and world history to articles in business and computer science, so they are important words to learn and remember. Common academic words are marked in the reading selections in this textbook with dotted underlines. 8
Using the Academic World List A useful vocabulary learning strategy is to keep a reading and vocabulary journal. Reminders could include a definition, synonym, translation, or the word in a phrase. 9
Reading for purpose One important skill of a good reader is to read selections more than one time. Every time you read a selection, read it for a different purpose. Previewing The first time you read a passage look for an overview of the topic. Try to understand the general subject area and get a quick indication of the main idea of the selection. 10
Requirements for B.A. in European Languages and Literature Student s must complete 128 credit hours to earn a B.A. in European Languages and Literature distributed as follows. 26 credit hours of Foundation year requirements 9 credit hours of University requirements 78 credit hours of Department requirements 9 credit hours of requirement from other departments 6 credit hours of electives 11
Scanning What Is Scanning? It is very high-speed reading that you do when you are looking for a specific piece of information. When you scan, you have a question in mind. You do not read every word, only key words that will answer your question. 12
It is a technique you often use when looking up a word in the telephone book or dictionary. You search for key words or ideas. In most cases, you know what you're looking for, so you're concentrating on finding a particular answer. Scanning involves moving your eyes quickly down the page seeking specific words and phrases. Scanning is also used when you first find a resource to determine whether it will answer your questions. Once you've scanned the document, you might go back and skim it. 13
When scanning, look for the author's use of organizers such as numbers, letters, steps, or the words, first, second, or next. Look for words that are bold faced, italics, or in a different font size, style, or color. Sometimes the author will put key ideas in the margin. 14
Understanding Patterns of Academic Writing: Repetition, Explanation, and extension Authors use patterns when writing academic texts. By understanding these patterns, we can understand their texts. The authors of Introduction to Sociology use a pattern several times to introduce a concept and the give an explanation about the concept. 15
The pattern has two sentences. In the first sentence, the authors introduce the concept In the second sentence, the authors use synonyms and pronouns to give more information about the subject and the concept The authors may also extend the concept with an additional phrase. 16
What is summarizing? Summarizing is the process of retelling the important parts of a reading selection in a much shorter form. Summarizing is the restating of the main ideas of the text in as few words as possible. 17
Summarizing is how we take larger selections of text and reduce them to their bare essentials: the gist, the key ideas, the main points that are worth noting and remembering. Webster's calls a summary the "general idea in brief form"; it's the distillation, condensation, or reduction of a larger work into its primary notions. Summarizing helps students to understand and remember what they have read. 18