Production Possibilities Curve and Economic Growth
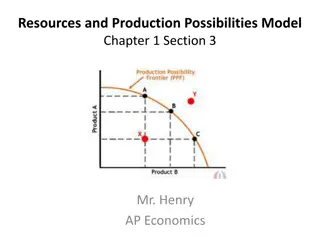
The Production Possibilities Curve illustrates trade-offs in an economy producing two goods, showing possible combinations using available resources. Efficiency on the curve means no way to make some better off without others worse off. Opportunity cost is the given-up production when increasing one good at the expense of another. Economists argue that Opportunity Costs are not constant, leading to the Law of Increasing Costs. Economic Growth occurs with resource or technology increases, shifting the curve outward for increased production.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
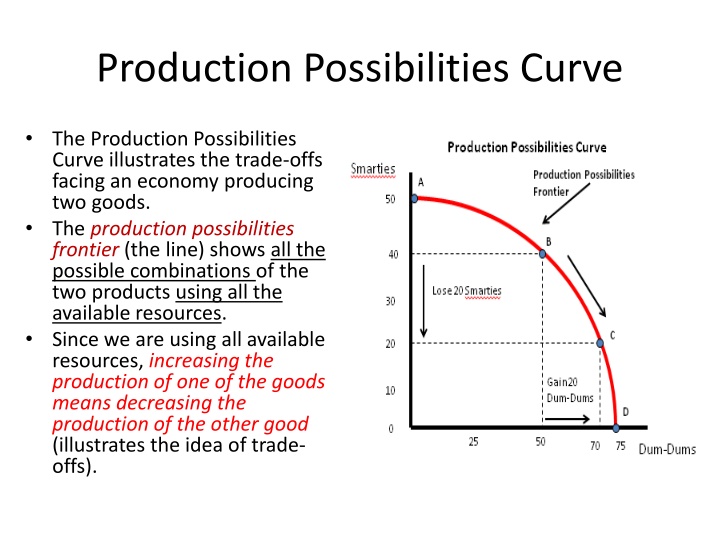
Production Possibilities Curve The Production Possibilities Curve illustrates the trade-offs facing an economy producing two goods. The production possibilities frontier (the line) shows all the possible combinations of the two products using all the available resources. Since we are using all available resources, increasing the production of one of the goods means decreasing the production of the other good (illustrates the idea of trade- offs).
Efficiency Production is efficient if there is not a way to make some people better off without making other people worse off. All points on the frontier are efficient. Any point inside of the frontier is inefficient and shows an underutilization of resources. It represents unemployment within a business or within a country. Production is allocatively efficient if the mix of goods is what people want to consume.
Opportunity Cost As production of one good is increased, production of the second must be decreased This loss of production is the opportunity cost: what must be given up. If the cost is constant the production possibilities curve will be a straight line.
Increasing Opportunity Cost However, economists believe that opportunity costs are not constant along the frontier. As resources are moved from the production of Smarties to Dum-Dums, increasingly larger amounts of Smarties must be given up to get decreasingly smaller amounts of Dum- Dums. This happens because resources are not equally suited to the production of both goods. This is known as the Law of Increasing Costs.
Economic Growth Production outside of the frontier is not possible with current available resources. However, if there is an increase in land, labor or capital OR technology then the frontier will shift outwards. A shift out means that more of both products can be produced. This shift represents economic growth