Plate Tectonics and Earth's Structure for 5th Grade Science
Delve into the world of plate tectonics with a focus on Earth's layers, crust, mantle, and core. Understand how tectonic plates move and learn about continental drift and the concept of Pangea. Explore evidence of Pangea, sea floor spreading, and the fascinating geological processes that shape our planet.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
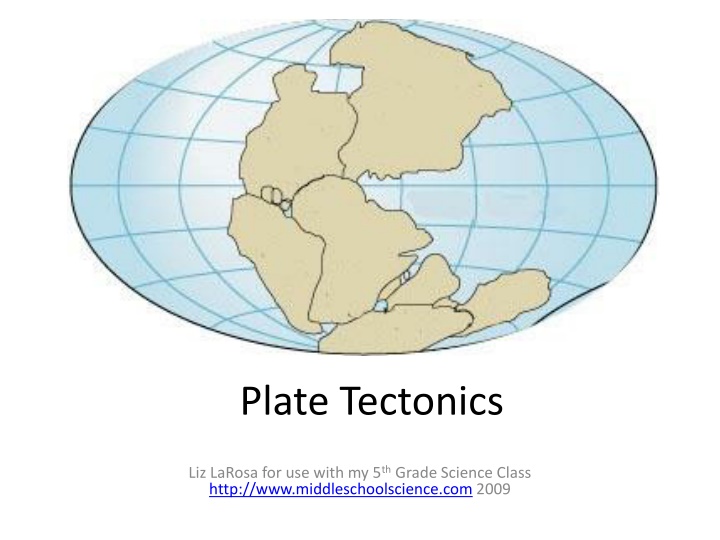
Plate Tectonics Liz LaRosa for use with my 5thGrade Science Class http://www.middleschoolscience.com 2009
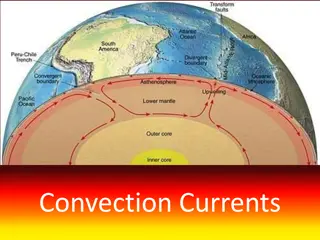
Earths Layers The Earth's rocky outer crust solidified billions of years ago, soon after the Earth formed. This crust is not a solid shell; it is broken up into huge, thick plates that drift atop the soft, underlying mantle.
The Crust http://members.enchantedlearning.com/ogifs/outerlayersearth.GIF Outermost layer 5 100 km thick Made of Oxygen, Silicon, Aluminum
The Mantle Layer of Earth between the crust and the core Contains most of the Earth s mass Has more magnesium and less aluminum and silicon than the crust Is denser than the crust http://members.enchantedlearning.com/ogifs/outerlayersearth.GIF
The Core Below the mantle and to the center of the Earth Believed to be mostly Iron, smaller amounts of Nickel, almost no Oxygen, Silicon, Aluminum, or Magnesium
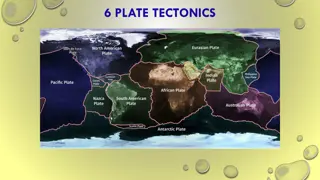
Plate Tectonics Greek tektonikos of a builder Pieces of the lithosphere(Earth s crust) that move around Each plate has a name Fit together like jigsaw puzzles Float on top of mantle similar to ice cubes in a bowl of water
Continental Drift Alfred Wegener 1900 s theory that Continents were once a single land mass that drifted apart. Fossils of the same plants and animals are found on different continents Called this supercontinent Pangaea, Greek for all Earth 245 Million years ago Split again Laurasia & Gondwana 180 million years ago http://members.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/astronomy/planets/earth/Continents.shtml
Sea Floor Spreading Mid Ocean Ridges underwater mountain chains that run through the Earth s Basins Magma rises to the surface and solidifies and new crust forms Older Crust is pushed farther away from the ridge http://members.enchantedlearning.com/sgifs/Seafloorspreading.GIF
How Plates Move http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/unanswered.html
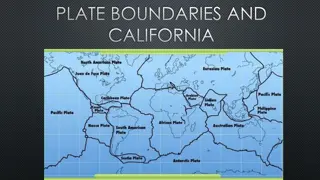
Different Types of Boundaries http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html
Divergent Boundary Arabian and African Plates Red Sea
Divergent Boundary Iceland http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html
Divergent Boundary - Oceanic http://www.geology.com
Divergent Boundary - Continental http://www.geology.com
Convergent Boundary Indian and Eurasian Plates The red marker identifies the Himalaya Mountains
Convergent Boundary Oceanic & Continental http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html & http://www.geology.com
Convergent Boundary Oceanic & Oceanic http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html & http://www.geology.com
Convergent Boundaries - Continental http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html & http://www.geology.com
Transform Boundary San Andreas Fault www.geology.com
Review Name the 3 main layers of the Earth What is a tectonic plate? What was Pangea? What is Sea-Floor spreading? Name the three different types of plate boundaries and one location on Earth for each one