Plant Cell Growth Mechanisms
Explore the fascinating world of plant cell growth with a focus on specialized cells like guard cells for gas exchange, meristematic cells for differentiation, and apical meristems for plant growth. Learn how stomata function to regulate water loss and support photosynthesis, and uncover the key processes involved in cell division, elongation, and maturation in apical meristems. Discover the essential role of lateral meristems in promoting plant width expansion.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
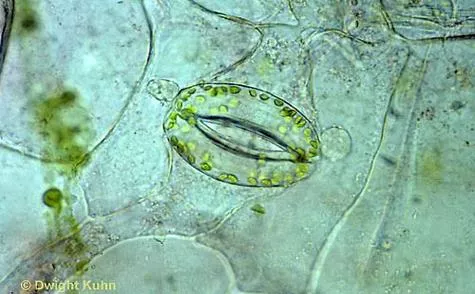
Specialized Cells Guard Cells Guard cells create openings in the cuticle which allow gases (CO2) to enter the leaf for use in photosynthesis. These openings are called stomata. Guard cells can change their shape to open and close the opening.
Specialized Cells The majority of stomata are located on the underside of leaves to reduce water loss (through evaporation) and allowing the upper surface of the leaf to be used for photosynthesis.
Meristematic Cells Animals have stem cells that can differentiate into all the cells in our bodies. Plants have a similar type of cell called meristematic cells. These cells have the ability to differentiate into specialized tissues.
Meristematic Cells Meristematic cells are the only cells in plants that will continue to divide throughout the life of the plant. These cells are only located in a few spots in the plant The apical meristem tissue The lateral meristem tissue
Apical Meristems Apical meristem tissue is located at the tip of the roots and shoots. This type of tissue allows the plant to grow taller.
Apical Meristems Apical meristem cells go through a 3 step process: Cell division Elongation Maturation
Apical Meristems As these cells elongate and mature the root is pushed further into the ground or the shoot grows further from the stem.
Apical Meristems As the cells elongate they will differentiate into different types of cells in dermal, ground or vascular tissue.
Lateral Meristems located in the roots and shoots allows the plant to grow wider
Lateral Meristems Two rings of lateral meristem tissue run the length of roots and shoots The outer ring produces new epidermal tissue called cork and the inner ring produces new xylem towards the inside of the stem and phloem towards the outside. The cork and phloem form the bark of trees and the xylem produces the rings we use to tell how old a tree is.
Plant Reproduction Because of meristematic tissue, some plants have developed a method of reproduction that does not require pollination of the ovule.
Vegetative Reproduction A plant can produce genetically identical clones by sending out new shoots or roots from meristematic tissue, that will grow new roots and an entire new plant Example. Strawberry plants
Vegetative Reproduction Poplar Trees
Vegetative Reproduction If you cut a stem, root or leaf of a plant and place it in water, it can eventually grow new roots and produce a new plant with identical genetics