Cell Structure and Function: A Comprehensive Overview
Delve into the world of cells, exploring the distinct features of animal and plant cells, the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, the significance of organelles, and the fascinating processes such as stem cell differentiation and cell adaptation. Discover how substances move across cell membranes and the role of osmosis in plant physiology. Uncover the wonders of cell biology through concise explanations and engaging visuals.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
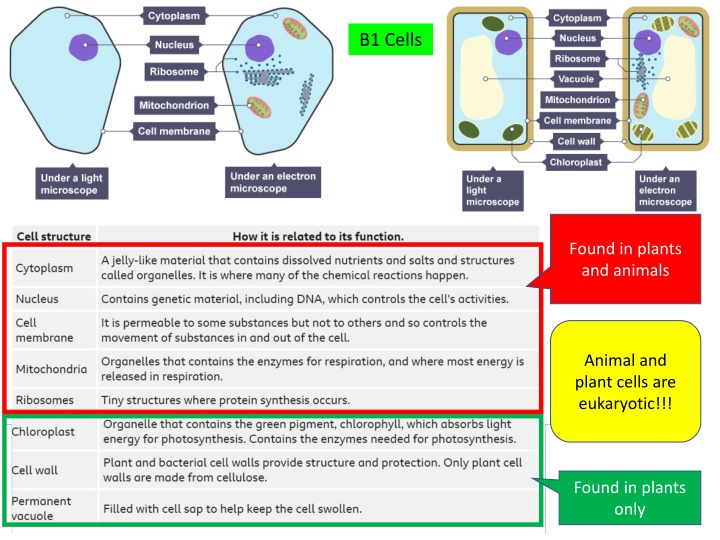
B1 Cells Found in plants and animals Animal and plant cells are eukaryotic!!! Found in plants only
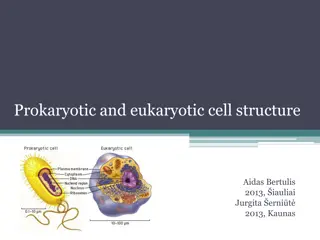
Bacteria cells are prokaryotic!!! Prokaryotic vs eukaryotic Prokaryotic cells have a cell wall Feature prokaryote eukaryote Nucleus No Yes Where DNA found? Free floating in cytoplasm In nucleus Plant cells have a cell wall But Animal cells do not size Smaller than eukaryote Larger than eukaryote Organelles e.g. mitochondria No Yes Ribosomes Yes - smaller Yes - Larger Cell membrane yes yes Cytoplasm yes yes
Change objective lens changes magnification Focusing knobs makes the image clear and in focus Do not write zoom!!! Order of magnitude 10 x bigger order of magnitude 101 100 x bigger order of magnitude 102 Changing mm to m x1000 Changing mm to m 1000 High resolution high magnification Dead things only can be viewed Low resolution Low magnification Living things can be viewed
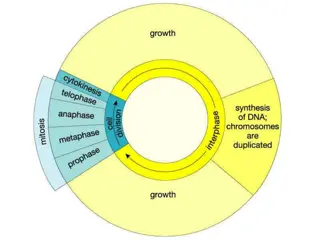
Stem cell undifferentiated cell Specialised cell cell with a specific function Embryonic stem cells Differentiate into any type of cell Adult stem cells From bone marrow Can only differentiate into limited cells Painful process Plant stem cells * Found in meristem Cell cycle use divide not split!!! Cell Adaptation Muscle Many mitochondria Nerve Myelin sheath Stage 1: DNA and organelles replicate State 2: Each set of chromosomes move to opposite poles Stage 3: Cytoplasm and membrane divides Root hair Large surface area Red blood No nucleus and haemoglobin
Substance moves against the concentration gradient- energy is needed!!! Substance moves down the concentration gradient- from a high to a low concentration Water moves down the water concentration gradient-from a high water to a low water concentration through a selectively permeable membrane RP - osmosis https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zs6 3tv4/revision/5 Water moves into the plant by osmosis and the mass increases Where line crosses x axis is the concentration of sucrose in plant tissues Independent: concentration of sugar solution Dependent: % change in mass Control: length and width of potato, volume of solution Water moves out of the plant by osmosis and the mass decreases % change in mass used as different starting masses