Cell Structure and Function
Explore the intricate world of cell biology through this comprehensive guide covering the definition of a cell, the characteristics of animal cells, the role of the nucleus, ribosomes, cell structure, organelles, cell membrane, and cell wall. Discover the fascinating details of eukaryotic cells and the essential functions each cell part contributes to maintaining life.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Definitionof Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capableof performing life functions.
Typical AnimalCell http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/NSC/images/cell.gif
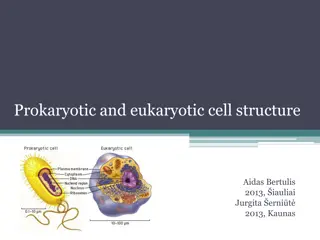
Cells cells -possess a membrane-boundnucleus -Are more complex than prokaryotic cells -compartmentalize functions within organelles and the endomembrane system -possess a cytoskeleton for support and to maintain cellular structure many cellular 4
Cells Nucleus -Stores the genetic material of the cell in the form of multiple, linear chromosomes -Surrounded by a nuclear envelope composed of 2 phospholipidbilayers -In chromosomes organized with proteins to form chromatin DNA is 6
Cells 7
Cells Ribosomes -The site of protein synthesis in the cell -Composed of ribosomal RNA and proteins -Found within the cytosol of the cytoplasm and attached to internal membranes 8
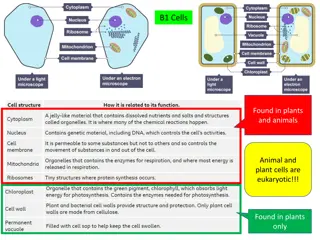
Cell Structure All Cells have: An membrane Genetic material in the form of DNA Cytoplasm with ribosomes outermost plasma
Cell Parts Organelles
CellMembrane Outer membrane of cell that controls movement in and out of the cell Double layer http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
CellWall Most commonly found in plant cells & bacteria Supports & protects cells http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Nucleus Directs cell activities Separatedfrom cytoplasm by nuclear membrane Containsgenetic material - DNA
Nuclear Membrane Surrounds nucleus Made of two layers Openings allow material to enter nucleus and leave http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Nucleolus Inside nucleus Contains RNA to build proteins http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Cytoplasm Gel-likemixture Surroundedby cell membrane Containshereditary material
EndoplasmicReticulum Moves materials around in cell Smooth type: lacks ribosomes Rough type (pictured): ribosomes embedded in surface http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Ribosomes Each cell contains thousands Make proteins Found on ribosomes & floating throughout the cell http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Mitochondria Produces energy through chemical reactions breaking down fats & carbohydrates Controls level of water and other materials in cell Recycles and decomposes proteins, fats, and carbohydrates http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
GolgiBodies Protein 'packaging plant' Move materials within the cell Move materials out of the cell http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Lysosome Digestive 'plant' for proteins, fats, and carbohydrates Transports undigested materi to cell membrane for removal Cell breaks down if lysosome structure al is disrupted. http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Vacuoles Membrane-bound sacs for storage, digestion, and waste removal Contains water solution Help plants maintain shape http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
1. Plasma Membrane All membranes are phospholipidbilayers with embedded proteins The outerplasma membrane isolates cell contents controls what gets in and out of the cell receives signals
3. Cytoplasm with ribosomes Cytoplasm fluid area inside outer plasma membrane and outside DNA region Ribosomes make proteins
Cell Structure All Cells have: an outermost plasma membrane genetic material in the formof DNA cytoplasm with ribosomes
Why Are Cells So Small? (4.2) Cells need sufficient surface area to allow adequatetransportof nutrients in and wastes out. As cell volume increases,so does the need for the transportingof nutrients and wastes.
Cells Structures in all cells Nucleus Ribosomes Endomembrane System Endoplasmic reticulum smoothand rough Golgi apparatus Vesicles Mitochondria Cytoskeleton
NUCLEUS CYTOSKELETON RIBOSOMES ROUGH ER MITOCHONDRION CYTOPLASM SMOOTH ER CENTRIOLES GOLGI BODY LYSOSOME PLASMA MEMBRANE VESICLE Fig. 4-15b, p.59
Nucleus Structure Nuclear envelope Two Phospholipid bilayers with protein lined pores Each pore is a ring of 8 proteins with an opening in the center of the ring Nucleoplasm fluid of the nucleus
Nuclearpore bilayerfacingcytoplasm Nuclearenvelope bilayerfacing nucleoplasm Fig. 4-17, p.61
Nucleus DNA is arranged in chromosomes Chromosome fiber of DNAwith proteins attached Chromatin all of the cell s DNA and the associatedproteins
Structures of the Endomembrane System Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Continuouswith the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope Two forms - smooth and rough Transport vesicles Golgi apparatus
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) The ER is continuouswith the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope There are 2 types of ER: Rough ER has ribosomes attached Smooth ER no ribosomes attached
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) -Membranes that create a network of channels throughout the cytoplasm -Attachment of ribosomes to the membrane gives a rough appearance -Synthesis of proteins to be secreted, sent to lysosomes or plasma membrane
EndoplasmicReticulum FunctionRER Proteins are modified as they move through the RER Once modified, the proteins are packaged in transport vesicles for transport to the Golgi body
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) -Relatively few ribosomes attached -functions: -synthesis of membrane lipids -calcium storage -detoxification of foreign substances
EndomembraneSystem Function SER Lipids are made inside the SER fatty acids, phospholipids, sterols.. Lipids are packaged in transport vesicles and sent to the Golgi Smooth ER (SER) Tubular membrane structure Continuous with RER No ribosomes attached
EndomembraneSystem Vacuoles -membrane-boundstructures with various functionsdependingon the cell type There are different types of vacuoles: -Central vacuole in plant cells. -Contractilevacuole of some protists. -Vacuoles for storage. 42
EndomembraneSystem Endomembranesystem -Aseries of membranes throughoutthe cytoplasm -divides cell into compartments where different cellular functionsoccur 1. endoplasmicreticulum 2. Golgi apparatus 3. lysosomes 43
EndomembraneSystem Golgi apparatus -flattened stacksof interconnected membranes -packagingand distributionof materials to different parts of the cell -synthesis of cell wall components 44
EndomembraneSystem Lysosomes -Membrane bound vesicles containing digestive enzymes to break down macromolecules -destroy cells or foreign matter that the cell has engulfed by phagocytosis 46
Golgi Apparatus GolgiApparatus Stack of flattened membrane sacs FunctionGolgi apparatus Completes the processing substances received from the ER Sorts, tags and packages fully processed proteins and lipids in vesicles
Golgi Apparatus Golgi apparatusreceives transportvesicles from the ER on one side of the organelle Vesicle binds to the first layer of the Golgi and its contents enter the Golgi