The Functions of Cell Organelles
Explore the vital functions of different cell organelles such as the cell membrane, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, cytoplasm, ribosomes, vacuole, cell wall, chloroplasts, and chlorophyll in a cell. Learn how each organelle plays a unique role in maintaining the cell's health and function, from controlling movement of materials to producing energy and supporting cell structures.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
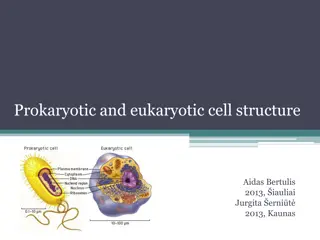
THE CELL Organelle Functions
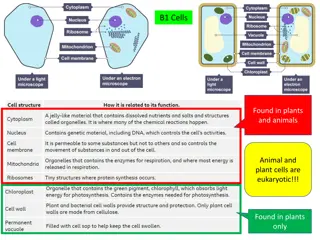
Cell Membrane Controls the movement of material in and out of the cell.
Nucleus Controls the actions of the cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Connects the parts of the cell. Allows for transportation of material around the cell.
Lysosomes Cleans the cell of waste.
Golgi Apparatus Packages nutrients for delivery throughout the cell.
Mitochondria Produces energy from eaten food.
Cytoplasm Jelly-like substance in the cell
Ribosomes Makes proteins for the cell
Vacuole Contains water and dissolved materials
Cell Wall (Plants Only) Shapes and supports the cell
Chloroplasts (plants only) Food for the plant is made here (photosynthesis)
Chlorophyll(plants only) Traps sun light for photosynthesis
Do Now What is a theory?
A Theory Widely accepted Supported by experimental evidence and observations
Cell Theory Every living thing is made of one or more cells Cells carry out the functions needed to support life Cells come only from other living cells
Pasteur Experiment Confirmed the cell theory Did not support spontaneous generation-the idea that living things formed from non-living things
Classification of Cells Archaea- ancient usually found in extreme environments. Prokaryotic cells Bacteria-prokaryotic cells Eukarya- are eukaryotic cells, more complex, includes all multicellular organisms and some unicellular organisms (protists and paramecium)
Multicellular Organism Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems
Carbohydrates Provides the cell with energy by breaking down sugar
Lipids Are fats and oils that are used for energy and for making organelles in the cell Lipids can t mix with water important for the cell
Proteins Made up of amino acids and are used by the cell for proper cell functioning proteins help the cell transport materials in and out of the cell
Nucleic Acids Provide the cell with the instructions for the maintenance, growth, and reproduction of the cell.
Cell Membrane Made up of fats, provides a barrier between materials inside the cell and outside the cell. Selectively permeable (semi- permeable)-only some things are allowed in/out of the cell.
Importance of Cell Membrane Allow needed materials into the cell Prevents unwanted materials from getting into the cell Lets unneeded materials out of the cell Cell Membrance animation
Passive Transport When molecules move freely across the cell membrane. No energy is required from the cell.
Diffusion Movement of material from an area of high concentration (crowded) to an area of low concentration (uncrowded).
Osmosis Diffusion of water across a membrane Diffusion Osmosis
Active Transport When the cell uses energy to move material across the cell s membrane.
Endocytosis When the cell uses energy to move large molecules into the cell.
Exocytosis When the cell uses energy to move large molecules out of the cell.
How does this picture represent Active Transport?
Photosynthesis Plants use energy from the sun to make food Takes place in the chloroplasts by the chlorophyll Materials needed: 1. Water (H2O) 2. Carbon dioxide (CO2) Materials produced: 1. Glucose-sugar (C6H12O6) 2. Oxygen (O2 )
Photosynthesis H2O + CO2 C6H12O6 + O2
Respiration Process where a plant uses the sugar made during photosynthesis. The use of sugar release energy Takes place in the mitochondria Produces waste: 1. Carbon dioxide 2. Water
Respiration C6H12O6 + O2 H2O + CO2