Otitis Media: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Otitis media is middle ear inflammation commonly affecting children. Peak incidence is between 6-12 months, with bacterial and viral causes. Risk factors include immune suppression, family history of OM, and anatomical abnormalities. Types include acute, with effusion, and chronic suppurative otitis media. Clinical features include earache, hearing loss, and tympanic membrane bulging.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Introduction Introduction Otitis media refers to inflammation of the middle ear.
Epidemiology Epidemiology The peak incidence of otitis media occurs between six and twelve months of life and declines after age five. Approximately 80% of all children will experience a case of otitis media during their lifetime, and between 80% and 90% of all children will experience otitis media with an effusion before school age
Etiology Etiology Bacterial causative agents are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae , and Moraxella catarrhalis. In case of chronic suppurative otitis media, the causative agents are Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Proteus species, Klebsiella pneumonia, and diphtheroids . Viral causative agents are respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), coronaviruses, influenza viruses, adenoviruses, human metapneumovirus, and picornaviruses
Pathophysiology Pathophysiology Blockage of eustachian tube by any cause results into negative pressure build up in the middle ear space which causes inflammation of the mucosa membrane resulting into excessive production of exudates that causes bulging of the tympanic membrane.
Risk factors Risk factors Immuno suppression in condtitions Family history of OM Anatomic abnormalities of the palate and tensor veli palatini Cochlear implants Vitamin A deficiency Allergies
Types Types Acute otitis media lasting for 6 weeks or less. Otitis media with effusion, is a condition in which there is fluid in the middle ear, but no signs of acute infection. Suppurative Chronic otitis media is a stage of ear disease in which there is an on-going chronic infection of the middle ear associated with perforated tympanic membrane. It lasts for more than 6 weeks.
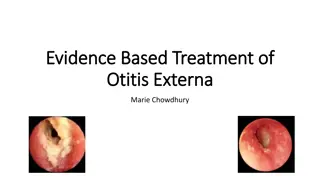
Clinical features Clinical features Earache Hearing loss Pyrexia Tender ear Purulent ear discharge Bulged tympanic membrane
Evaluation Evaluation FBP Pus for culture and sensitivity
Treatment Treatment Acute otitis media Antibiotics Analgesics In case of chronic suppurative otitis media: Aural toileting Ear wicking regularly, with a dry cotton wick at home Antibiotics Hydrogen peroxide 3% or Boric acid ear drops Surgical repair of the ear drum (Mastoidectomy, Endoscopic tympanoplasty, Tympano-mastoidectomy, Ossiculoplasty)
Complications Complications Intratemporal complications Hearing loss Tympanic membrane Chronic suppurative otitis media Mastoiditis Inner ear infection Intracranial complications Meningitis,Subdural empyema, Brain abscess,Extradural abscess,Lateral sinus thrombosis, Otitic hydrocephalus.
Prevention Prevention Proper ear hygiene Proper treatment of URTI Early repair of nasal anomalies Healthy eating Early diagnosis and treatment