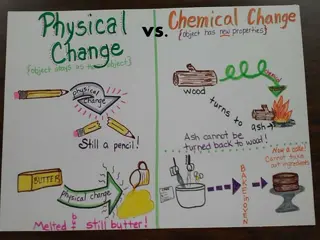Physical and Chemical Properties of Matter
Explore the distinction between physical and chemical properties of matter in Chapter 15, Section 2. Learn to classify properties such as color, flammability, odor, shape, taste, density, and more. Understand how physical properties can be observed without altering the substance's identity, while chemical properties indicate potential chemical changes. Discover how physical properties can aid in separating substances in mixtures. Dive into the characteristics that define the nature of matter.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
PROPERTIES OF MATTER Chapter 15 Section 2
CLASSIFY THESE PROPERTIES AS PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL. IF YOU AREN T SURE, GUESS! Color ______________________________ Flammability ______________________________ Odor ______________________________ Shape ______________________________ Taste ______________________________ Density ______________________________ Melting Point ______________________________ Tendency to Rust ______________________________ Reacts with light ______________________________ Boiling Point ______________________________ Volume ______________________________ Malleable ______________________________ Mass ______________________________ Magnetism ______________________________ Ductile ______________________________ Ability to dissolve ______________________________
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES A characteristic of a material that you can observe without changing the identity of the substance that makes up the material
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Physical Properties can be related to: Appearance What color is the item? What shape is the item? What is the item s phase of matter? Behavior Does it attract a magnet? i.e. iron Can it be pulled into wires (ductile)? i.e. copper Can it be hammered into sheets (malleable)? i.e. gold At what temperature does it boil (boiling point)?
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Physical properties can be used to separate substances in a mixture How would you separate a mixture of iron, sand, and salt using physical properties? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rc9o2tbOxxY
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES A characteristic of a material that indicates whether it can undergo a certain chemical change The result of the chemical change would be the production of a new substance Some examples: tendency of something to burn (flammability) i.e. lighter fluid, paint thinner tendency of something to react with light i.e. medicines that come in dark bottles like hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
TRY THIS AGAIN! CLASSIFY THESE PROPERTIES AS PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL. IF YOU AREN T SURE, GUESS! Color ______________________________ Flammability ______________________________ Odor ______________________________ Shape ______________________________ Taste ______________________________ Density ______________________________ Melting Point ______________________________ Tendency to Rust ______________________________ Mass ______________________________ Boiling Point ______________________________ Volume ______________________________ Malleable ______________________________ Reacts with light ______________________________ Magnetism ______________________________ Ductile ______________________________ Ability to dissolve ______________________________ Physical Physical Chemical Chemical Physical Chemical Physical Physical Chemical Physical Physical Physical Physical Chemical Physical Physical
CLASSIFYTHESECHANGES ASPHYSICALOR CHEMICAL. IFYOUAREN TSURE, GUESS! Evaporating water __________________________ Rust on an iron nail __________________________ Baking cookies __________________________ Dissolving salt in water __________________________ Hammering Aluminum into a sheet _________________ Cooking scrambled eggs _________________________ Burning a marshmallow __________________________ Melting an M&M in your mouth ____________________ Alka seltzer in water __________________________ Raising bread dough __________________________ Cutting an apple __________________________
PHYSICAL CHANGE A change in the size, shape, state of matter, etc. that does not change the identity of a substance A phase change is a physical change even though energy may be removed or added to the substance In the new state of mater, the substance is still made of the same components, the atoms just have more or less energy i.e. if liquid water evaporates, it becomes water vapor if water vapor condenses, it becomes liquid water
PHASE CHANGES SOLID LIQUID GAS Evaporation Boiling Condensing
DISTILLATION Distillation is a process that takes advantage of physical properties and physical changes to separate mixtures If two substances have different boiling points (temperature at which they boil), they can be separated. The mixture is heated slowly until it begins to boil. The vapors of the liquid with the lowest boiling point form first and are condensed and collected. If the other substance also needs to be collected, then the temperature is increased until the second liquid boils, condenses, and is collected
CHEMICAL CHANGE The change of one substance into a new substance (chemical reaction) A chemical change alters the original chemical make-up of the substance
INDICATIONSOFA CHEMICAL REACTION How can you tell if a chemical change has taken place? ENERGY Evolution of heat, light, and/or sound (sometimes heat can be absorbed too) GAS A gas is produced, bubbles (effervescence) PRECIPITATE When solid particles form from 2 liquids COLOR Unexpected Color change (i.e. clear liquid + clear liquid purple liquid)
TRYTHIS AGAIN! CLASSIFYTHESECHANGES AS PHYSICALORCHEMICAL. IFYOUAREN TSURE, GUESS! Evaporating water __________________________ Rust on an iron nail __________________________ Baking cookies __________________________ Dissolving salt in water __________________________ Hammering Aluminum into a sheet _________________ Cooking scrambled eggs _________________________ Burning a marshmallow __________________________ Melting an M&M in your mouth ____________________ Alka seltzer in water __________________________ Raising bread dough __________________________ Cutting an apple __________________________ Physical Chemical Chemical Physical Physical Chemical Chemical Physical Chemical Chemical Physical
LAWOF CONSERVATIONOF MASS Matter is neither created nor destroyed during a chemical change (reaction) The mass of the substances present before the chemical change equals the mass of the substances that remain after the change Example Is burning wood a physical or chemical change? Chemical change - Combustion After a log burns, only ashes remain. Where do you think the rest of the mass went? Some mass left as solid particles in the smoke, some mass left as gas (CO2)
EXAMPLEOF CHEMICAL CHANGES What color was the Statue of Liberty when it was dedicated in 1886? NOT green! The Statue of Liberty is made of copper The copper at the surface has undergone a chemical change as the result of exposure to air and water. She is now covered in patina which is green!