Genetics and Cell Division Study Guide
Explore topics ranging from cell division phases, mitosis stages, genetic variation in sexual reproduction, chromosome structures, karyotypes, Mendel's laws, Punnett squares, and more in this comprehensive study guide. Understand key concepts such as DNA replication, chromosomal abnormalities, gametes, alleles, and genetic inheritance principles. Enhance your knowledge of genetics and meiosis through detailed explanations and visual aids.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
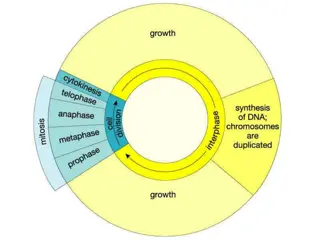
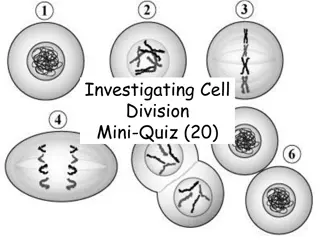
BLOCK 1/7 1/8 What are the 3 parts of Interphase? When does the DNA replicate? What are the four stages of Mitosis? What is the end result of Mitosis? What occurs after Mitosis?
Thursday 1/9 What are somatic cells? What are gametes? Humans have ___ total chromosomes? ___ pair? What are autosomes? What do we call a change in an organism s chromosome structure?
Friday 1/10 What are 4 ways that genetic variation is achieved regarding sexual reproduction/meiosis: What occurs during Anaphase 1 of Meiosis? What occurs during Anaphase 2 of Meiosis? What is an Allele?
In Humans, gametes contain _____ autosome(s) and ______ sex chromosome(s) Alternate versions of a gene or trait (such as eye color or hair texture) are called _________ Separation of Homologous Chromosomes (pairs) occurs during ____________ of Meiosis ____ Sister Chromatids separate during _________ of Meiosis _____
How are Chromosomes arranged in a Karyotype? 3 What information can we determine from a Karyotype? 2 What is nondisjunction? 1 When can nondisjunction occur during meiosis? 2
Monday 1/13/2020 List 4 things you know about genetics What is a Punnett Square? What is it used for?
BLOCK 1/14 1/15 A = Dominant a = recessive (Airhead) (brainiac) Show a Heterozygous genotype: Show a Homozygous recessive: Show a Homozygous dominant: Draw a Punnett Square crossing Aa X Aa: What is the Phenotypic Ratio: What is the Genotypic Ratio:
Friday 1/17 Explain what a Test Cross is and how/why you would use it: Explain Mendel s Law of Segregation: Explain Mendel s Law of Independent Assortment: What is the exception to Independent Assortment?
Answer for Previous Q Law of Segregation: the two alleles for a trait segregate (separate) when gametes are formed during meiosis Bb parent could contribute B or b to gamete Law of Independent Assortment: alleles of different genes separate independently of one another during gamete formation Note: genes must be located on different chromosomes or far apart from each other on the same chromosome (due to crossing over) Example: plant height isn t affected by plant s flower color
BLOCK 1/21-1/22 What are the possible gamete combinations for an individual with the following genotype: DdRr ________ ________ ________ ________ Remember to use the F-O-I-L What are the possible gamete combinations for an individual with the following genotype: TtPP method !!
Thursday 1/23 In Snapdragons, flower color is controlled by incomplete dominance. Show a Punnett Square cross that would produce the most variety of genotypes in the offspring: Describe the resulting phenotype(s) of offspring produced from a Co-Dominant crossing of a pure Blue frog and a pure Yellow frog:
Friday 1/24 Show the (6) possible genotypes for human blood types: Which blood type is considered to be the Universal Recipient ? Which blood type is considered to be the Universal Donor ?
Monday 1/27 Show the 5 possible genotypes for a sex-linked trait (use B and b to represent color blindness, remember that it is a sex-linked recessive trait) Show a Punnett Square cross of a female who is heterozygous for color blindness with a man who is color blind What % of their children are colorblind? If a woman is colorblind, what % of her sons will also be color blind?
BLOCK 1/28-1/29 A man with blood type AB is married to a woman with blood type A. What are the possible blood genotypes of their children (hint: 2 ways to be A) Man with normal vision marries woman with normal vision. Their first child is a color-blind boy. Their second child is a color-blind female. Should the husband be mad at the wife?? If so, why?
Thursday 1/30 When looking at a Pedigree Chart: How can you determine if a disorder is autosomal or x-linked? How can you determine if a disorder is Dominant or Recessive? If a trait is autosomal recessive, what is a term we can use for an individual heterozygous for that trait (H h)?
Friday 1/31 True of False? (don t write out) A gene can have more than 2 alleles. Individuals must show a trait for it to appear in their offspring In Incomplete Dominance, two different dominant alleles are expressed at the same time Mendel did his experiments just like everyone before him. If all of the 500 offspring resulting from a Test Cross are DOMINANT, the unknown genotype is heterozygous
Monday 2/3 Name 2 Nucleic Acids What are the monomers of Nucleic Acids? What three parts make up this monomer? What Nitrogen bases are associated with DNA? What do we call a segment of DNA that codes for a protein?
BLOCK 2/4 2/5 What is the full name for DNA? What was Rosalind Franklin s contribution? What two men were credited with creating the first model of DNA s structure? The backbone of the Double helix is made of: The rungs of the Double helix are made of:
Thursday 2/6 List 3 enzymes involved in DNA Replication and their functions: What does Semi-Conservative Replication mean If a sample of DNA has 36% Thymine, what % of the sample will be Cytosine? show your math!!
Monday 2/10 What are the building blocks (monomers) of Proteins? Where in the cell are Proteins made? What are 3 differences between RNA and DNA DNA 1. Structure: 2. Bases: 3. Sugars: What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide? RNA
BLOCK 2/11 2/12 There are _________ amino acids but _______ possible codons. A ____________ bond links amino acids together, so another name for a protein is a _____________ The 3 types of RNA are: -- -- -- A sequence of 3 bases on a mRNA strand is called a:
Thursday 2/13 What is the START codon? What are the 3 STOP codons? A tRNA molecule has an _______ _______ on one end and an __________ on the other. The 3 bases of a codon (on mRNA) are _____________ to the 3 bases on it s corresponding anticodon (on tRNA). DNA --------- _____________ ------- Protein
BLOCK 2/18 - 2/19 What does RNA Polymerase do during Transcription? The mRNA strand gets copied from which strand of the DNA? What modifications does the mRNA undergo before leaving the nucleus? What amino acids are coded by these codons: GAC UUG UAA CUC
Thursday 2/20 Three types of Gene Point mutations are: Of these three, which are frame-shifts? Explain the following mutation results: - Silent - Mis-sense - Nonsense
What is the estimated age of Earth? How long ago did Dinosaurs become extinct? Of all the life forms to ever exist on Earth, what percentage have gone extinct? How many years have humans (Homo sapiens) been on Earth?
The Geologic Times Scale is broken into 4 Eras. Name them, oldest to most recent? What Era could be termed The Age of Dinosaurs ? List the periods of the Paleozoic, and name one Evolutionary Milestone that occurred in each one. When did the Cenozoic Era begin and end?
List and correct 3 common misconceptions regarding Evolution:
With the extinction of the Dinosaurs, what class of animals became dominant? Describe Darwin s idea of Natural Selection : What were reptile s main adaptations for life on land? What class of animals did reptiles evolve from? What current animals are thought to be the closest relatives to small Dinosaurs?
How many Million Years Before Present (MYBP) do we have evidence of: Eukaryotic cells? First Bird (Archeopteryx)? First flowering plants? First insects? First fish? First dinosaurs? T-rex and Velociraptor?
Darwins travels were 1831-1836. Why did he wait until 1859 to publish On the Origin of Species ? What was Lamark incorrect about? In evolutionary terms, what does fitness mean? Every population has ______________ .
List the 5 categories of Evolutionary Evidence along with a description and/or examples:
What are 4 types of Physical Adaptations? What are 2 types of Behavioral Adaptations?
What are the 8 Levels of Classification (from broadest to most specific): What are the 3 Domains? Which are Prokaryotic? What are the 6 Kingdoms?
We can break down the Archaebacteria into what 3 Phyla: What are the three main shapes associated with Eubacteria? Example of good bacteria: Example of bad bacteria:
The smallest living organisms are ______________. Protists can be ____________ , ____________ , or __________ - like. Spirogyra, Volvox, Diatoms and Euglena all contain _______________ so are considered plant-like. Algae/Phytoplankton are major producers of _________ and are also a major part of the food chain.
List 4 Categories of Fungi and give an example of each: Describe the make-up of a lichen: Describe Mycorrhizae:
What are the three Environmental factors that determine whether stomata are Open or Closed? Which cells in a leaf contain the most chlorophyll? What are the three reactants needed for Photosynthesis?
Name 3 Phyla of Non Vascular Plants: Name 4 examples of Vascular, non-seeded plants: Which generation is dominant in vascular plants? Gametophyte or Sporophyte Which is dominant in non-vascular plants?
Name the three parts of the Pistil (female) Name the 2 parts of the Stamen (male) Name 2 characteristics of Dicots Name 2 characteristics of Monocots Another name for Flowering Plants is ___________
Describe the purposes of these Body Systems: Nervous Respiratory Digestive Circulatory Excretory
List 8 animals that are as different from each other as possible (appearance, function, size, etc):
List the 9 Main Phyla of the Animal Kingdom Which Phyla has the most species? Which Phyla s members have nematocysts? Which Phyla s members are unsegmented parasites?
What do you hope to learn from our Fetal Pig Dissection? What questions or comments do you have before we begin??
List some factors that determine whether a population grows, decreases, or stays constant: