Cell Division: Functions and Stages
Explore the functions and stages of cell division through a comprehensive overview covering topics such as the importance of cell division in growth, repair, and reproduction, the stages of the cell cycle, and the comparison of different cell cycles. Engage with visual aids and concept maps to deepen your understanding of this fundamental biological process.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CELL DIVISION Chapter 2, Lesson 3 Page 56 Page 56 Page 56
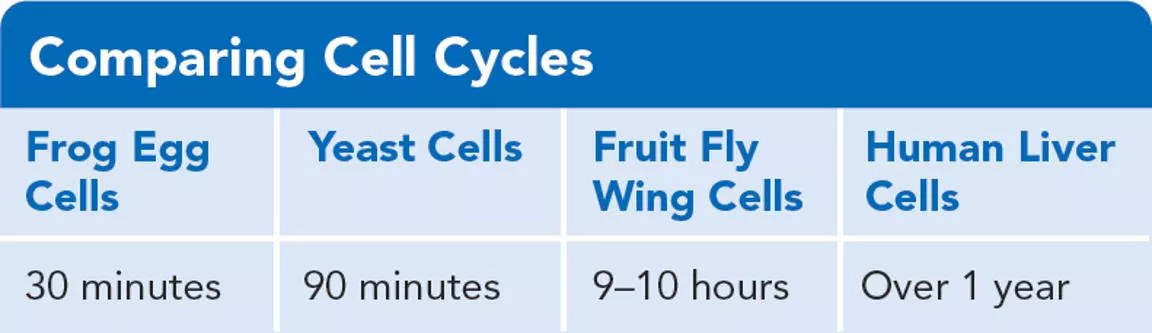
What Are the Functions of Cell Division? Read the My Planet Diary: Cycling On p. 56 Comparing Cell Cycles The table below compares the length of different cell cycles.
WHATARETHE FUNCTIONSOF CELL DIVISION? Use the data table to help answer the following questions: 1. Which type of cell completes a cell cycle fastest? Frog egg cells 2. With each cell cycle, two cells form from one cell. In three hours, how many cells could form from one frog egg cell? 64 cells
SEE FIGURE 1, PAGE 57. Label each photo as: (A) growth (B) repair, or (C) reproduction Answers: A = plant shoot GROWING B = Arm scrape healing C = Cougar with babies - reproduction
WHAT ARETHE FUNCTIONSOF CELL DIVISION? Cell division allows organisms to: GROW REPAIR damaged structures REPRODUCE
WHAT HAPPENS DURINGTHE CELL CYCLE? During the Cell Cycle, a cell grows, prepares for division, and divides into two new cells, which are called daughter cells.
3 STAGESOFTHECELLCYCLE The cell cycle consists of three stages: Interphase Mitosis Cytokinesis I M Cool
LOOKATPG 58 62 TOHELPWITHTHE CONCEPTMAP FILLOUTTHE OVERVIEWOFTHECELLCYCLE
The Cell Cycle What are the 3 stages? Interphase Cytokinesis What happens? Mitosis Cell grows DNA gets copied Prepares for division What are the 4 phases of Mitosis? Telophase Anaphase Prophase Metaphase
The Cell Cycle What are the 3 stages? Interphase Cytokinesis What happens? Mitosis Cell grows DNA gets copied Prepares for division
INTERPHASE: TO DO LISTPAGE 58 FILLINAFEWTHINGSYOUSEEONTHETO-DOLIST GROWING: COPYING DNA: PREPARING FOR DIVISION:
INTERPHASE 1STSTAGEOFCELLCYCLE MOREDETAILS GROWING: Cell grows to full size Produces organelles it needs Makes more enzymes COPYING DNA: Makes an exact copy of DNA: REPLICATION At the end of replication, the cell has 2 identical sets of chromosomes PREPARING FOR DIVISION: Produces structures that will help it to divide centrioles, spindle fibers, etc.
BACKGROUNDOFACHROMOSOME P. 59 (STAGE 2: MITOSIS) Chromosomes are made of 2 rod-like parts called chromatids; chromatids are identical to each other w/ the same DNA. Centromere holds the two chromatids together When a cell divides, one chromatid will go to each new cell
The Cell Cycle What are the 3 stages? Interphase Cytokinesis What happens? Mitosis Cell grows DNA gets copied Prepares for division What are the 4 phases of Mitosis? Telophase Anaphase Prophase Metaphase
STAGE 2: MITOSIS The cell s nucleus divides into two new nuclei One set of DNA is distributed into each daughter cell Divided into 4 phases:
MITOSIS HAS 4 PHASES Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase (Pandas Must Always Talk!)
PHASESOF MITOSIS PROPHASE: Chromosomes in the nucleus condense (smash together) Nuclear envelope breaks down
PHASESOF MITOSIS Interphase How does prophase look different from interphase? Prophase
PHASESOF MITOSIS How does prophase look different from interphase? Chromosomes condense (the Xs); the nucleus is changing (nuclear envelope goes away)
PHASESOF MITOSIS The Cell Cycle Cells undergo an orderly sequence of events as they grow and divide. What are the missing parts of the stages?
PHASESOF MITOSIS Metaphase: Each chromosome attaches to a spindle fiber at its centromere. What is missing from the cell? What happened to the chromosomes?
PHASESOF MITOSIS Metaphase: Each chromosome attaches to a spindle fiber at its centromere. What is missing from the cell? What happened to the chromosomes? The nucleus is missing; chromosomes moved to the center of the cell
PHASESOF MITOSIS METAPHASE: Chromosomes move to center of the cell Meta = middle
PHASESOF MITOSIS Anaphase: The centromere of each chromosome splits, pulling the chromatids apart. Each is now called a chromosome. They are drawn by their spindle fibers to opposite ends of the cell. The cell stretches out. Draw the missing structures.
PHASESOF MITOSIS Anaphase: Draw the missing structures.
PHASESOF MITOSIS ANAPHASE: Chromatids (now called chromosomes) move to opposite ends of the cell Cell stretches out
PHASESOF MITOSIS Telophase How does the diagram of a cell in telophase look different from the one in anaphase?
PHASESOF MITOSIS Telophase Nuclei are forming; spindle fibers have disappeared cell is pinched in around its middle. Telophase How does the diagram of a cell in telophase look different from the one in anaphase?
PHASESOF MITOSIS TELOPHASE: Nuclei are forming (nuclear envelope reappears) Cell is pinching in at the middle
CYTOKINESIS Stage 3 Cytokinesis Cell splits into two daughter cells. Each daughter cell has an identical set of chromosomes. Draw the daughter cell.
CYTOKINESIS Cytokinesis: Draw the daughter cell.
STAGE 3: CYTOKINESIS Cytokinesis: Cytoplasm divides Each daughter cell has the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell
STAGE 3: CYTOKINESIS The cell s nucleus divides into two new nuclei One set of DNA is distributed into each daughter cell Divided into 4 phases:
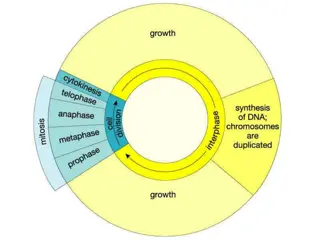
DOTHE MATHP. 63 Length of a Liver Cell Cycle Human liver cells generally reproduce less than once per year. At other times, they can complete one cell cycle in about 22 hours. The circle graph to the left displays this.
DOTHE MATHP. 63 What do the three curved arrows outside of the circle represent?
DOTHE MATHP. 63 What do the three curved arrows outside of the circle represent? Interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis
DOTHE MATHP. 63 The wedge representing growth is in which stage of the cell cycle?
DOTHE MATHP. 63 The wedge representing growth is in which stage of the cell cycle? Interphase
DOTHE MATHP. 63 About what percentage of the cell cycle is shown for DNA replication?
DOTHE MATHP. 63 About what percentage of the cell cycle is shown for DNA replication? About 45%
DOTHE MATHP. 63 What stage of the cell cycle takes the shortest amount of time? How do you know?
DOTHE MATHP. 63 What stage of the cell cycle takes the shortest amount of time? How do you know? Cytokinesis; it is the smallest section of the graph
 undefined
undefined