Exploring Periodic Trends and Diatomic Elements
Dive into the world of periodic trends, atomic size variations, ionization energy, electronegativity, and diatomic elements like H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, and I2. Discover how atomic structure influences these properties and learn about the fascinating characteristics of cations, anions, and shielding effects.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
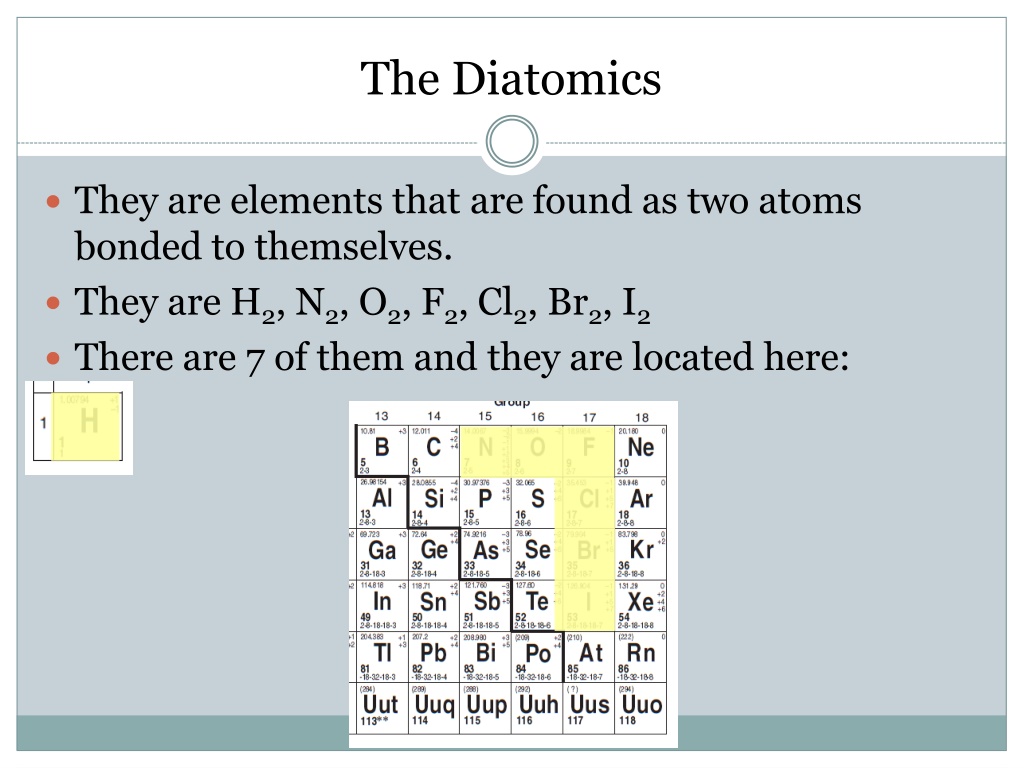
The Diatomics They are elements that are found as two atoms bonded to themselves. They are H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 There are 7 of them and they are located here:
Even More About the Periodic Table Periodic Trends
Trends in Atomic Size Atomic radius - one-half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms of the same element when the atoms are joined In general, atomic size increases from top to bottom within a group and decreases from left to right across a period.
Trend in Ionic Size Cations are always smaller than the atoms from which they form. Anions are always larger than the atoms from which they form.
Trends in Ionization Energy First ionization energy tends to decrease from top to bottom within a group and increase from left to right across a period.
Trends in Electronegativity In general, electronegativity values decrease from top to bottom within a group. For representative elements, the values tend to increase from left to right across a period.
Summary of Trends The trends that exist among these properties can be explained by variations in atomic structure. The increase in nuclear charge within groups and across periods explains many trends. Within groups an increase in shielding (distance from the nucleus) has a significant effect
Atomic size DECREASES Ionization energy INCREASES Electronegativity INCREASES Nuclear charge INCREASES Shielding is constant 18 1 Ionization energy DECREASES Electronegativity DECREASES 15 16 2 14 17 13 Nuclear charge INCREASES Atomic size INCREASES Ionic size INCREASES Shielding INCREASES Size of cations decreases Size of anions decreases