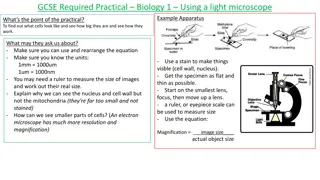
Demonstration of Salivary Enzyme Amylase Action in B.Sc. Practical
Salivary enzyme amylase, also known as ptyalin, plays a crucial role in breaking down starch and glycogen into maltose. This practical session in the Zoology department explores the action of salivary enzyme amylase at a temperature of 37°C and pH of 6.6. By conducting experiments with starch, iodine solution, and saliva samples, students demonstrate how amylase hydrolyzes starch into glucose and maltose, resulting in a color change from blue to colorless. The procedure involves mixing starch and saliva solutions, incubating them, and observing the enzymatic activity through iodine staining.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Demonstrate Action of Salivary Enzyme Amylase (ptyalin). Class- B.Sc. III Year Practical Date: 07.10.2020 Time: 03:00-05:00PM Presented by Manoj Joshi Department of Zoology UCoS,MLSU, Udaipur.
Enzyme amylase found in saliva which is secreted by salivary glands in mouth palate. Amylase partially hydrolyzed (breaks) starch or glycogen and maltose. Salivary amylase acts at a temperature of 37 C and at pH of 6.6 (acidic). When iodine solution is mixed with starch, blue colour is obtained. When starch is first hydrolyzed with amylase and then mixed with iodine solution, blue colour is not obtained because starch has been broken into glucose and maltose.
Requirements:- Beakers (100ml), pipettes, test tube, glass-stoppered bottles, plain cavity slides, Staining tube, cavity blocks, toluene, starch paste, 0,02N iodine solution, incubator set at 37 C . Procedure:- Prepare 0.02N iodine solution and 1% starch solution (1 gm starch + 100 ml DW). For collection of saliva, rinse own mouth with warm water quickly. Then take 20-25 ml of water in mouth, rotate water with tongue for 2-3 min and collect saliva solution in a beaker. This contains salivary enzyme amylase.
In another beaker mix 5 ml of 1% starch solution and 5 ml of saliva solution. Incubate the beaker in an oven set at 37 C for one hour. Take two cavity blocks or staining tube and mark them A and B respectively. In each cavity block or staining tube, add 2 drop of iodine solution, In cavity block A add drop of starch-saliva mixed solution with pipette. With another pipette add a drop of starch only in cavity block B. Result:- In cavity block B, solution become blue white in cavity block A it remains colourless as starch has been hydrolysed into glucose and demostrating activity of enzyme amylase.
Requirements:- Beakers (100ml), pipettes, test tube, glass-stoppered bottles, plain cavity slides, Staining tube, cavity blocks, toluene, starch paste, 0,02N iodine solution, incubator set at 37 C . Procedure:- Prepare 0.02N iodine solution and 1% starch solution (1 gm starch + 100 ml DW). For collection of saliva, rinse own mouth with warm water quickly. Then take 20-25 ml of water in mouth, rotate water with tongue for 2-3 min and collect saliva solution in a beaker. This contains salivary enzyme amylase.
Requirements:- Beakers (100ml), pipettes, test tube, glass-stoppered bottles, plain cavity slides, Staining tube, cavity blocks, toluene, starch paste, 0,02N iodine solution, incubator set at 37 C . Procedure:- Prepare 0.02N iodine solution and 1% starch solution (1 gm starch + 100 ml DW). For collection of saliva, rinse own mouth with warm water quickly. Then take 20-25 ml of water in mouth, rotate water with tongue for 2-3 min and collect saliva solution in a beaker. This contains salivary enzyme amylase.